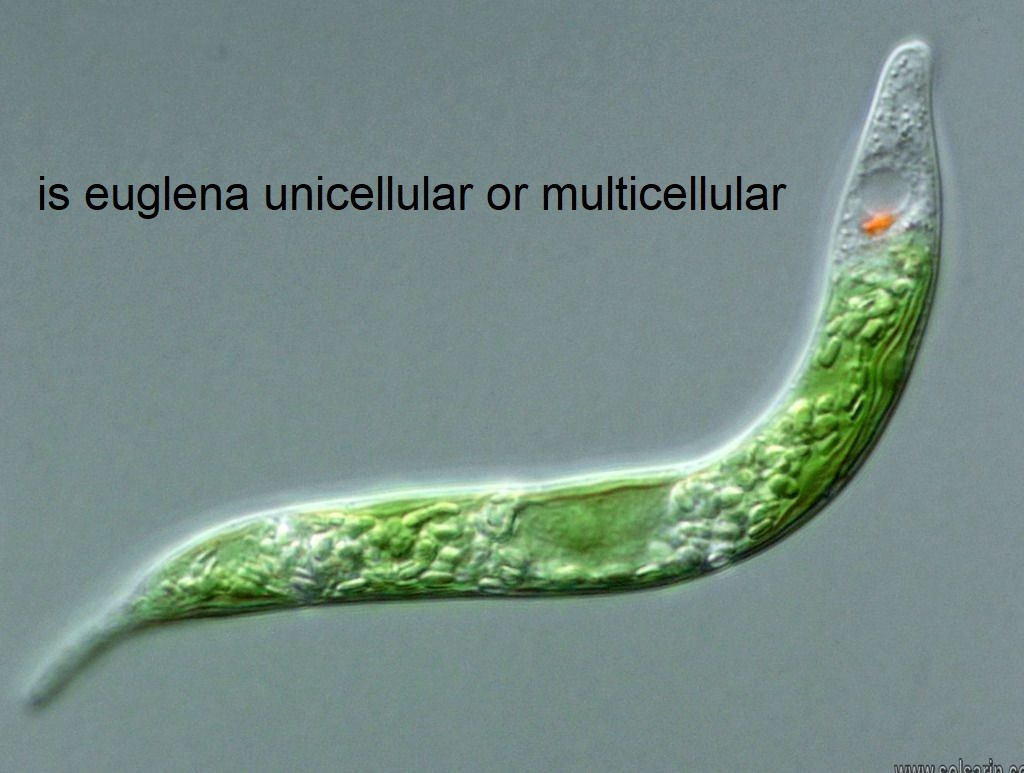
is euglena unicellular or multicellular
Hello good night. Welcome to solsarin. The post is about “is euglena unicellular or multicellular“. Thank you for choosing us. Let’s look at this together.
Euglena
Euglena is a genus of single cell flagellate eukaryotes. It is the best known and most widely studied member of the class Euglenoidea, a diverse group containing some 54 genera and at least 800 species. Species of Euglena are found in fresh water and salt water. They are often abundant in quiet inland waters where they may bloom in numbers sufficient to color the surface of ponds and ditches green (E. viridis) or red (E. sanguinea).
Autotrophy
Most species of Euglena have photosynthesizing chloroplasts within the body of the cell, which enable them to feed by autotrophy, like plants. However, they can also take nourishment heterotrophically, like animals. Since Euglena have features of both animals and plants, early taxonomists, working within the Linnaean two-kingdom system of biological classification, found them difficult to classify.
It was the question of where to put such “unclassifiable” creatures that prompted Ernst Haeckel to add a third living kingdom (a fourth kingdom in toto) to the Animale, Vegetabile (and Lapideum meaning Mineral) of Linnaeus: the Kingdom Protista.
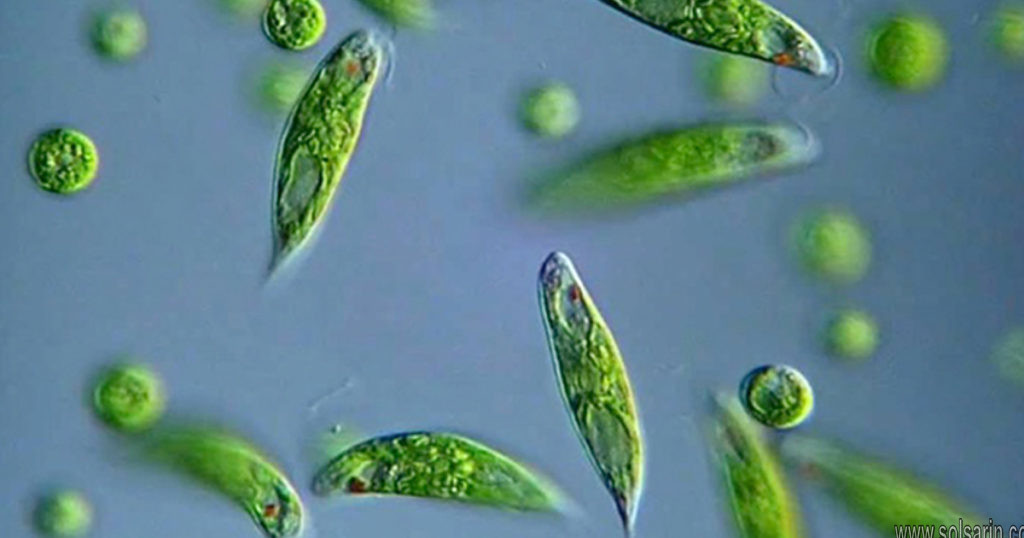

Taxonomy and Phylogeny
Euglena are in a small group (less than 1000 species), that in the past was claimed by both zoologists (because they are mobile and some are heterotrophic) and by botanists (because some members photosynthesize). Accordingly, the group has sometimes called ‘Euglenozoa’ by zoologists (‘zoa’ refers to animals) and has been called ‘Euglenophyta’ by botanists (‘phyta’ refers to plants).
Recent phylogenetic studies have them diverging very early from other eukaryotes and consequently putting them in a very small group that contains very unfamiliar unicellular organisms. Some close relatives of Euglena include the causal organism for sleeping sickness and for Chagas disease.
Structure
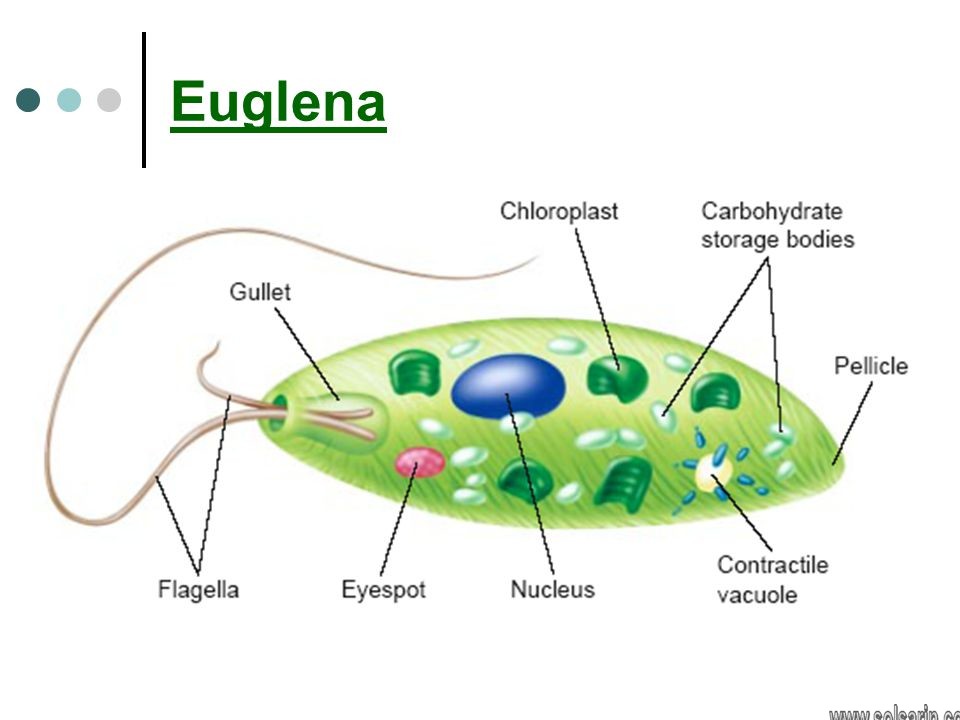
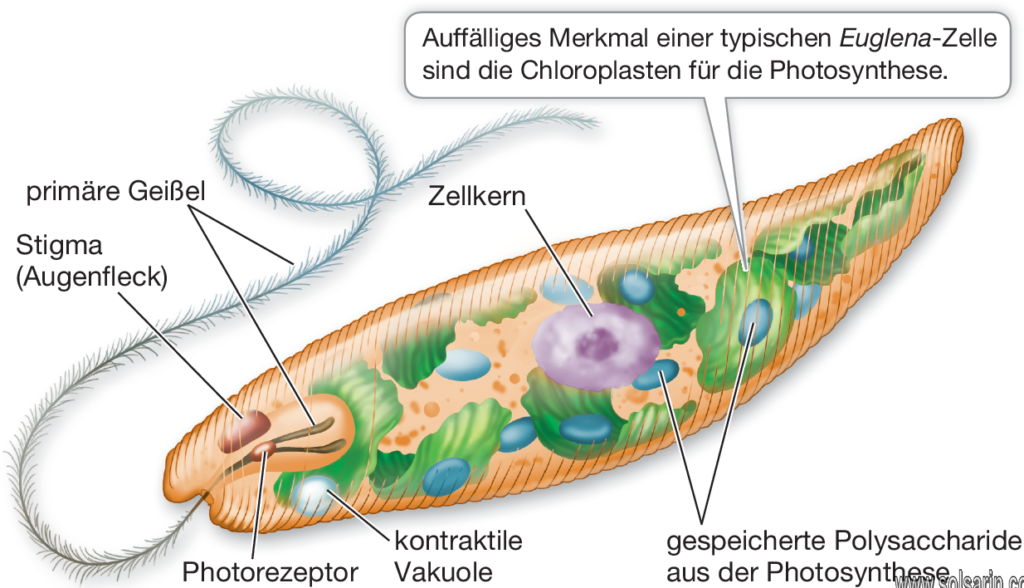
Euglena is a unicellular organism with a complex internal structure that includes a contractile vacuole that can expel water and a red ‘eyespot’. Photosynthetic forms contain a chloroplast. They possess two flagellae, one long, one short, which can allow the organisms to move. Euglena are also able to move by means of changing its shape (see video links). Outside the cell membrane is a flexible, protein-based structure called a pellicle.
Although not generally considered a cell wall, it has similar functions in providing some rigidity and strength that the membrane cannot provide. However the pellicle is much more flexible than most cell walls and allows for the change in form that is often seen in Euglena motion.
Carotenoid
Euglena are characterized by an elongated cell (15–500 micrometres [1 micrometre = 10−6 metre], or 0.0006–0.02 inch) with one nucleus, numerous chlorophyll-containing chloroplasts (cell organelles that are the site of photosynthesis), a contractile vacuole (organelle that regulates the cytoplasm), an eyespot, and one or two flagella. Certain species (e.g., E. rubra) appear red in sunlight because they contain a large amount of carotenoid pigments.
Unlike plant cells, Euglena lack a rigid cellulose wall and have a flexible pellicle (envelope) that allows them to change shape. Though they are photosynthetic, most species can also feed heterotrophically (on other organisms) and absorb food directly through the cell surface via phagocytosis (in which the cell membrane entraps food particles in a vacuole for digestion).
Paramylon
Food is often stored as a specialized complex carbohydrate known as paramylon, which enables the organisms to survive in low-light conditions. Euglena reproduce asexually by means of longitudinal cell division, in which they divide down their length, and several species produce dormant cysts that can withstand drying.
Some species, especially E. viridis and E. sanguinea, can develop large toxic populations of green or red “blooms” in ponds or lakes with high nitrogen content.

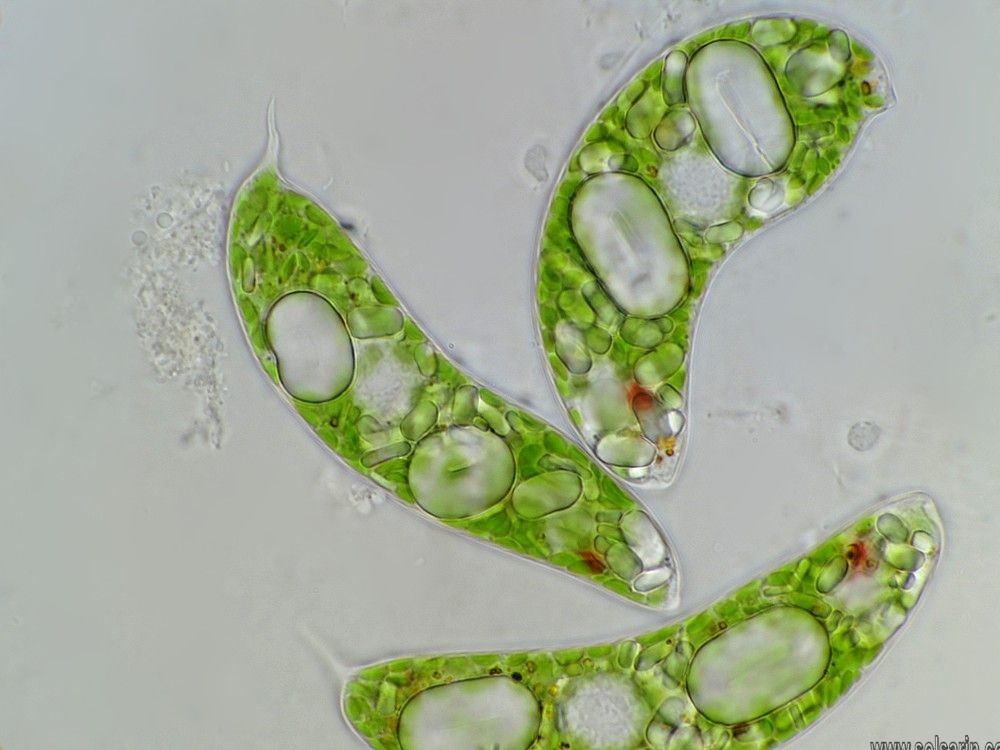
Reproduction
Euglena reproduce asexually through binary fission, a form of cell division. Reproduction begins with the mitosis of the cell nucleus, followed by the division of the cell itself. Euglena divide longitudinally, beginning at the front end of the cell, with the duplication of flagellar processes, gullet and stigma.
Matter and energy
Sometimes Euglena are a typical photoautotrophs, using the energy of sunlight to synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and then using the carbohydrates as an energy source in cellular respiration and as building materials to synthesize a variety of biomolecules.
Euglenoids store carbohydrates in a different glucose polymer than typical starch — the glucose units are combined in a 1,3 linkage, rather than the 1,4 linkage found in normal starch. Euglenoids may also behave like heterotrophs and acquire material by ingestion (phagocytosis) or by absorption of solutes from its aquatic environment. Some forms of Euglena lack chloroplasts and are solely heterotrophic.
Interactions
Euglena can be important components of certain aquatic environments and play a role as both a primary producer, eaten by other organisms, and also as a decomposer (heterotroph) that consumes other organisms and breaks them down, or consumes dead organic material and breaks it down.
Certain Euglena species (e.g. Euglena sanguinea) can turn a pond red and can also produce toxins that kill fish.
Human consumption
Kemin Industries sells a euglena nutraceutical supplement ingredient featuring dried Euglena gracilis with high levels of beta glucan.
Feedstock for biofuel production
Under the aegis of Itochu, a start-up company called Euglena Co., Ltd. has completed a refinery plant in Yokohama in 2018, with a production capacity of 125 kiloliters of bio jet fuel and biodiesel per year.
Is A Euglena Unicellular Or Multicellular
Does Euglena have cilia or flagella?
Euglena: genus of several single-celled organisms, some of which have both animal and plant characteristics. (They eat food like animals and can photosynthesize like plants.).
Will the amoeba have cilia or flagella if I keep it?
Amoebas and sarcodines are examples of protists moving through pseudopodia. Some similar protists move their lashes. Lashes are hair-like extensions that move in waves. They are ■■■■■■■ and move with the help of the flagella.
Which protist has flagella in the same way?
Protists such as owls have one or more flagella that rotate or whip to create movement.
Why does the owl have flagella here?
All owls have chloroplasts and can produce their own food through photosynthesis. Euglena moves through a flagellum (plural, flagellum), a long, whip-like structure that serves as a small motor. The flagellum is front (front) and rotates to pull the cell into the water.

Does paramecium have a scourge?
Section 19.4 Cilia and flagella: structure and movement.
Does amoeba have chloroplasts?
Answer and explanation: No, neither amoeba nor paramecia have chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts are specialized cells that allow an organism to produce its own food with Har euglena cilia?
Euglena: genus of several single-celled organisms, some of which have both animal and plant characteristics. (They eat food like animals and can photosynthesize like plants.).
Does algae have eyelashes?
Common in Protists Most protists are unicellular, with the exception of a few multicellular algae protists. Many protists have flagella-like or cilia-like attacks that push them through the water, some use pseudopods or false feet to move.
Why do some protists have cilia and other flagella?
Types of Protist Eyelashes Some protists use microscopic hairs called cilia to move around. These tiny hairs can fold back to help the body move through water or other fluids. Flagella Other protists have long tails called flagella. This tail can move back and forth and push the body.
Do amoebas have a brain?
One of the prerequisites for mental states is a brain. Amoebas have no brain, no central nervous system, or no nervous system. The structures we see in the diagram are the cell membrane, the pseudopods, the vacuoles and the cell nucleus.
What type of organism is euglena and why?
The Euglena. Euglena are unicellular organisms classified into the Kingdom Protista, and the Phylum Euglenophyta. All euglena have chloroplasts and can make their own food by photosynthesis.
How is euglena classified?
Classification of EuglenaEuglena is a unicellular microorganism belonging to the kingdom Protista.
Is a euglena a bacteria?
Euglena is a genus of microorganisms belonging to the Protozoa kingdom; it is an unusual example of a unicellular animal with chlorophyll.
Is euglena a parasitic organism?
The Euglenozoa are a monophyletic group of flagellated protists including free-living, symbiotic, and parasitic species.
Is euglena a multicellular organism or unicellular organism?
Euglena is single-celled, and the cell is enclosed in a semi-rigid protein sheath, not a true cell wall but not a simple cell membrane. Euglena is entirely unicellular, has no collagen and no cellulose, stores energy in paramylon bodies (not starch as plants do).
Is a euglena a plant or animal?

Is euglena a fungi?
Euglena are single celled organisms that belong to the genus protist. As such, they are not plants, animal or fungi. In particular, they share some characteristics of both plants and animals.
Is euglena a living organism?