Accomplishments of the Persian Empire
Hello and welcome to our discussion in solsarin. Today we want to talk about “Accomplishments of the Persian Empire” in our site. Thanks for choosing us!

History of Iran
The history of Iran, which was commonly known until the mid-20th century as Persia in the Western world, is intertwined with the history of a larger region, also to an extent known as Greater Iran, comprising the area from Anatolia in the west to the borders of Ancient India and the Syr Darya in the east, and from the Caucasus and the Eurasian Steppe in the north to the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman in the south.
Iran is home to one of the world’s oldest continuous major civilizations, with historical and urban settlements dating back to 7000 BC. The south-western and western part of the Iranian Plateau participated in the traditional Ancient Near East with Elam (3200 – 539 BC), from the Early Bronze Age, and later with various other peoples, such as the Kassites, Mannaeans, and Gutians.
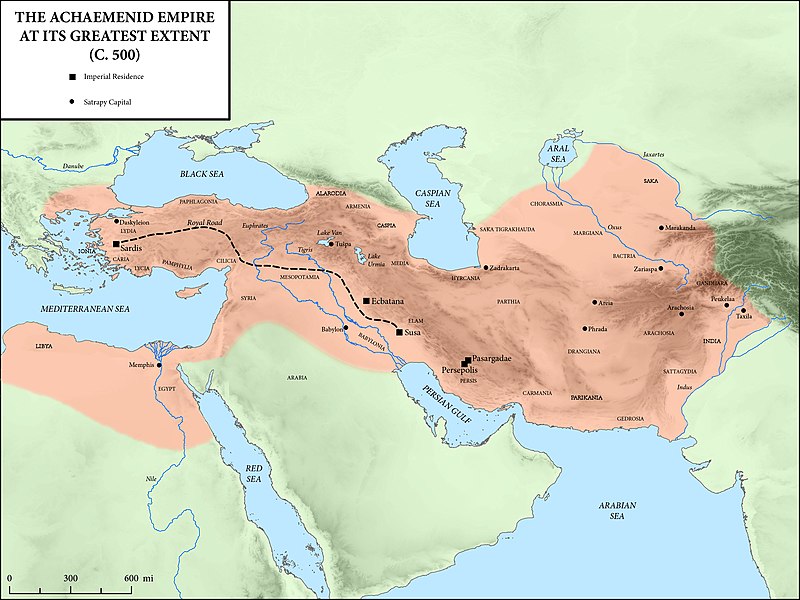
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel calls the Persians the “first Historical People”. The Medes unified Iran as a nation and empire in 625 BC. The Achaemenid Empire (550–330 BC), founded by Cyrus the Great, was the first true global superpower state and it ruled from the Balkans to North Africa and also Central Asia, spanning three continents, from their seat of power in Persis (Persepolis).
It was the largest empire yet seen and the first world empire. The Achaemenid Empire was the only civilization in all of history to connect over 40% of the global population, accounting for approximately 49.4 million of the world’s 112.4 million people in around 480 BCE.
They were succeeded by the Seleucid, Parthian, and Sasanian Empires, who successively governed Iran for almost 1,000 years and made Iran once again as a leading power in the world. Persia’s arch-rival was the Roman Empire and its successor, the Byzantine Empire.
The Iranian Empire proper begins in the Iron Age, following the influx of Iranian peoples. Iranian people gave rise to the Medes, the Achaemenid, Parthian, and Sasanian Empires of classical antiquity.
Once a major empire, Iran has endured invasions too, by the Macedonians, Arabs, Turks, and the Mongols. Iran has continually reasserted its national identity throughout the centuries and has developed as a distinct political and cultural entity.
The Muslim conquest of Persia (633–654) ended the Sasanian Empire and is a turning point in Iranian history. Islamization of Iran took place during the eighth to tenth centuries, leading to the eventual decline of Zoroastrianism in Iran as well as many of its dependencies. However, the achievements of the previous Persian civilizations were not lost but were to a great extent absorbed by the new Islamic polity and civilization.
Iran, with its long history of early cultures and empires, had suffered particularly hard during the late Middle Ages and the early modern period. Many invasions of nomadic tribes, whose leaders became rulers in this country, affected it negatively.
Iran was reunified as an independent state in 1501 by the Safavid dynasty, which set Shia Islam as the empire’s official religion, marking one of the most important turning points in the history of Islam.
Functioning again as a leading world power, this time amongst the neighbouring Ottoman Empire, its arch-rival for centuries, Iran had been a monarchy ruled by an emperor almost without interruption from 1501 until the 1979 Iranian Revolution, when Iran officially became an Islamic republic on April 1, 1979.
Over the course of the first half of the 19th century, Iran lost many of its territories in the Caucasus, which had been a part of Iran for centuries, comprising modern-day Eastern Georgia, Dagestan, Republic of Azerbaijan, and Armenia, to its rapidly expanding and emerging rival neighbor, the Russian Empire, following the Russo-Persian Wars between 1804–13 and 1826–8.


A king on the rise
That story begins in the middle of the sixth century with the rise of one of the most remarkable rulers of the ancient world: Cyrus II, or “the Great”. When Cyrus came to power in 559 BC, Persia was a small kingdom located in south-west Iran, one of several Iranian tribes in the vassalage of the kingdom of the Medes. By the time he died in 530 BC, it was well on its way to superpower status.
The breakthrough moment came in 550 BC when Cyrus, supported by a coalition of south Iranian tribes, marched north to attack the Medes and sacked their capital, Ecbatana. He then moved against the powerful kingdom of Lydia in Asia Minor, capturing its wealthy capital, Sardis – a victory that cleared the path for him to seize other important cities along the Ionian coast.
Another milestone in Persia’s rise arrived in 540 BC when Cyrus launched an attack on the Neo-Babylonian empire, centred in Mesopotamia, and entered the fabulously wealthy city of Babylon. The Persian ruler apparently met no military or political resistance, and maintained the status quo by allowing Babylonian officials to continue in their governmental and religious offices.
Much of our knowledge of the fall of Babylon comes from the Cyrus Cylinder, composed on Cyrus’s orders, although written from a Babylonian perspective. As a piece of imperial propaganda, the Cylinder attempts to legitimise Cyrus’s conquest of Babylon by representing the king as the chosen champion of the god Marduk.
Following the conquest of Babylonia, Cyrus forged a truly international empire. At Pasargadae in Iran, the king built a tomb and a palace planted with a formal garden irrigated by a myriad of water-channels. The result was nothing short of a desert paradise – one that, with its architectural representations of the cultures now under Persian rule, acted as an empire in miniature.
The royal rhetoric emphasised that all conquered nations of this empire were united in service to the Great King, whose laws they were required to obey and whose majesty they were obliged to uphold.
The king was championed by the great god Ahuramazda, who granted the monarch the gift of kingship in order to stabilise world order, since unrest and rebellion were linked to cosmic disorder. Rebellion against Persian authority was seen as a revolt against divine authority because the Great King served Ahuramazda’s will on Earth.
Persian Culture
The ancient Persians of the Achaemenid Empire created art in many forms, including metalwork, rock carvings, weaving and architecture. As the Persian Empire expanded to encompass other artistic centers of early civilization, a new style was formed with influences from these sources.
Early Persian art included large, carved rock reliefs cut into cliffs; such as those found at Naqsh-e Rustam; an ancient cemetery filled with the tombs of Achaemenid kings. The elaborate rock murals depict equestrian scenes and battle victories.
Ancient Persians were also known for their metalwork. In the 1870s, smugglers discovered gold and silver artifacts among ruins near the Oxus River in present-day Tajikistan.
The artifacts included a small golden chariot, coins and bracelets decorated in a griffon motif. (The griffon is a mythical creature with the wings and head of an eagle and the body of a lion, and a symbol of the Persian capital of Persepolis.)
British diplomats and members of the military serving in Pakistan brought roughly 180 of these gold and silver pieces—known as the Oxus Treasure—to London where they are now housed at the British Museum.
The history of carpet weaving in Persia dates back to the nomadic tribes. The ancient Greeks prized the artistry of these hand-woven rugs—famous for their elaborate design and bright colors. Today, most Persian rugs are made of wool, silk and cotton.
Fall of the Persian Empire
The Persian Empire entered a period of decline after a failed invasion of Greece by Xerxes I in 480 BC. The costly defense of Persia’s lands depleted the empire’s funds, leading to heavier taxation among Persia’s subjects.
The Achaemenid dynasty finally fell to the invading armies of Alexander the Great of Macedon in 330 B.C. Subsequent rulers sought to restore the Persian Empire to its Achaemenian boundaries; though the empire never quite regained the enormous size it had achieved under Cyrus the Great.
Persian Empire Accomplishments, Achievements, Contributions
Persian Empire Accomplishments, Achievements, Contributions: When they talk about the Persian Empire people usually just talk about how large their empire was and how wealthy they were with palaces larger than most could imagine and streets laden with gold.
But actually, everyone knows that the Persians were one of the most influential empires of all times. They had made progress on all tiers and the Persian Empire accomplishments, achievements, contributions are hard to overlook.


1.Persian Empire Accomplishments in Architecture
Of all the Persian Empire achievements the most magnificent and extravagant are the Hanging Gardens of Babylon. They were taken to be one of the Wonders of the Old World and are still a mystery to us.
Other than this there is also a number of magnificent monuments and designs of unthinkable palaces that pays tribute to the architectural genius of the Persians. The domes that are today taking to be the pride of any building had its roots in Persian Architecture.
2.Persian Empire Contribution in Mathematics
One of the greatest Persian Empire contributions to the modern world is Algebra. This is a form of mathematics without; which almost none of the modern day inventions or discovery would have been possible. The one who made all this possible was a mathematician named Khwarizmi.
Another man named Khayyam was a poet and a mathematician who contributed to the concept of duality in numbers. These are concepts that form the basis of modern day mathematics and are now proving to be a Persian Empire accomplishment.
3.Persian Empire Achievements in Music
The Persian music has always enthralled the lovers of music because of its spirituality; and the unique assortment of instruments that they used. Overall accepted as a spiritual vessel; Persian Empire accomplishments in the field of music included the use of instruments such as the Tambour or the tambourine; the Sitar and many unique percussion instruments.
Many Asian musical styles of classical fields owe their origins to the Persian style of music including Sufi and Indian Classical music.
4. Persian Empire achievements in Art
Persian Empire achievements in painting styles have been praised as one of the most influential to date. The geometrically symmetrical and asymmetrical paintings seen in Asia today have its origin in Persian Art.
5. Persian Empire Contribution in Legal and Government
The first ever bill of rights, the religious equality and freedom and the first form of paper money were the Persian Empire contribution to the modern world. They had a fixed legal system and a constitution of a nation.
This along with a Silk Route that stretched from them to China through India made it the prime trading grounds for silk and spice. Prosperity was ample through the Persian Empire achievements.
6. The Contribution of Persian Empire in Military
The Persian Empire accomplishments on the field of battle need no tribute. They were feared as the largest and the most advanced. Iranian had the first ever standard navy and their foot soldiers used gunpowder.
They believed in an edge over their enemy through advancements. The Persian Empire accomplishments; achievements; contributions and greatness are beyond question as they were truly the first global empire that made a mark on the world map.
Random Posts
- recently fired wwe wrestlers
- batman was created in what year?
- red wine served cold
- where did aretha franklin go to college
- stamp size photo dimensions
- qualities of a wife material
- what percentage of water on earth is available for human use
- when were polar bears first discovered?
- what event threatened the fabric of the union
- pork roast per pound cooking time




