are viruses prokaryotic or eukaryotic
hello dear friend thank you for choosing us.
in this post on the solsarin. site. we will talk a bout are viruses prokaryotic or eukaryotic .
stay with us .
thank you for your choice

Viruses are considered neither prokaryotes nor eukaryotes because they lack the characteristics of living things, except the ability to replicate (which they accomplish only in living cells).
Are bacteria eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Prokaryotic cells (i.e., Bacteria and Archaea) are fundamentally different from the eukaryotic cells that constitute other forms of life. Prokaryotic cells are defined by a much simpler design than is found in eukaryotic cells.
How are viruses different from prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Viruses are considered neither prokaryotes nor eukaryotes because they lack the characteristics of living things, except the ability to replicate (which they accomplish only in living cells).
What are the differences between prokaryotes and viruses?
Viruses are not defined as living. Both viruses and bacteria can cause infections, but in different ways.
What are the differences between cells and viruses?
Living things have cells.
Viruses do not have cells. They have a protein coat that protects their genetic material (either DNA or RNA). But they do not have a cell membrane or other organelles (for example, ribosomes or mitochondria) that cells have.
What do prokaryotic eukaryotic and viruses have in common?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have structures in common. All cells have a plasma membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and DNA. The plasma membrane, or cell membrane, is the phospholipid layer that surrounds the cell and protects it from the outside environment.

What are eukaryotic viruses?
Eukaryotic viruses include a vast array of viruses that permanently infect the host and can exist for decades in asymptomatic individuals. These viruses can persist locally or systemically. They can directly impact tissue-specific immunity, including in the GI tract.
Have you heard anything about “how much is the coca-cola brand worth?“? Click on it.
What is the most obvious difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
The most obvious difference between them is that prokaryotes have no nuclei, but there are four major differences between a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell: No prokaryotic cell has a nucleus; every eukaryotic cell has a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells have no mitochondria; nearly every eukaryotic cell has mitochondria.
How are the size of eukaryotic cells prokaryotic cells and viruses related?
A virus is about ten times smaller than a typical bacteria cell, and at least 100 times smaller than a typical eukaryotic cell. A virus is about ten times smaller than a typical bacteria cell, and at least 100 times smaller than a typical eukaryotic cell.
How do viruses differ from prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells How are viruses similar to prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Most scientists do not consider viruses to be living.
What is prokaryotic virus?
Prokaryotic viruses which include phages and archaeal viruses play an important role in balancing the global ecosystem by regulating the composition of bacteria and archaea in water and soil. Identifying the viral host is essential for characterizing the virus, as the virus relies on the host for survival.
What are viruses similar to prokaryotic cells?
Viruses contain DNA but not much else. They lack the other parts shared by all cells, including a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes. Therefore, viruses are not cells, but are they alive? All living things not only have cells; they are also capable of reproduction.
What are the 4 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts, the cell wall, and the structure of chromosomal DNA.
What is difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell class 9?
What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cell? The defining characteristic feature that distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, the true nucleus is absent, moreover, membrane-bound organelles are present only in eukaryotic cells.
What do viruses do to eukaryotic cells?
For example, bacteriophages attack bacteria (prokaryotes), and viruses attack eukaryotic cells. Once inside the host the bacteriophage or virus will either destroy the host cell during reproduction or enter into a parasitic type of partnership with it.
How does a virus get into a eukaryotic cell?
Virus entry into animal cells is initiated by attachment to receptors and is followed by important conformational changes of viral proteins, penetration through (non-enveloped viruses) or fusion with (enveloped viruses) cellular membranes. The process ends with transfer of viral genomes inside host cells.
A virus with a nonenveloped capsid enters the cell by attaching to the attachment factor located on a host cell
A virus with a nonenveloped capsid enters the cell by attaching to the attachment factor located on a host cell. It then enters the cell by endocytosis or by making a hole in the membrane of the host cell and inserting its viral genome.
What is similar between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Similarities between Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells
In both types of cells, DNA exists that relates to genes. The cell wall is present in both. In both, there are four types of major molecules that are common to both. The process of DNA copying is similar in both.
Why is it important to know the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
It is important to know the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; allows us to control disease-causing bacteria without harming our own cells.
Are viruses smaller than prokaryotic cells?
A virus is a sub-microscopic particle that can infect living cells. Viruses are much smaller than prokaryotes, ranging in size from about 20–300 nanometers (nm), though some can be larger. Prokaryotes are typically 0.5–5.0 micrometers (µm) in length.
Are viruses or prokaryotic cells bigger?
Viruses are about 1,000 times smaller than bacteria and are visible under an electron microscope.
How big are viruses compared to prokaryotic cells?
Bacteria are giants when compared to viruses.
The smallest bacteria are about 0.4 micron (one millionth of a meter) in diameter while viruses range in size from 0.02 to 0.25 micron.
Is a bacteria prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Bacteria lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other internal structures and are therefore ranked among the unicellular life-forms called prokaryotes.
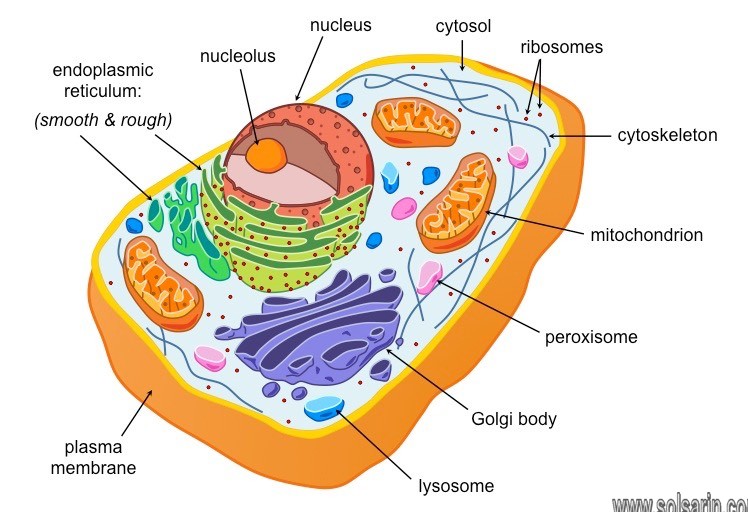

What is in a prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles. Prokaryotes are divided into two distinct groups: the bacteria and the archaea, which scientists believe have unique evolutionary lineages. Most prokaryotes are small, single-celled organisms that have a relatively simple structure.
What is meant by prokaryotic?
prokaryote, also spelled procaryote, any organism that lacks a distinct nucleus and other organelles due to the absence of internal membranes. Bacteria are among the best-known prokaryotic organisms.
What type of cell is a virus?
Because they can’t reproduce by themselves (without a host), viruses are not considered living. Nor do viruses have cells: they’re very small, much smaller than the cells of living things, and are basically just packages of nucleic acid and protein.
What viruses infect eukaryotic cells?
9.2 Viral infection
The NF-κB pathway is a major target for a number of common eukaryotic viruses including Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1), Human T-cell Leukaemia Virus (HTLV-1), Hepatitis-B and-C, Epstein Bar Virus and Influenza Virus (Hiscott et al., 2001).
Do you want to know about “an empty-kcalorie food is one that contains“? Click on it.
Is sperm a eukaryote?
A sperm cell is a eukaryote cell. That is so because it isn’t a type of bacteria. Also because it has membrane bound organelles and a nucleus that carries DNA. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus for storing DNA.
Are viruses asexual?
Viruses can’t reproduce on their own. They need a host cell in order to be able to do it. The virus infects a host cell and releases its genetic material into it.
Do prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound structures, the most noteworthy of which is the nucleus. Prokaryotic cells tend to be small, simple cells, measuring around 0.1-5 μm in diameter. While prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound structures, they do have distinct cellular regions.
What does a virus inject into a cell?
In the lytic cycle, the virus attaches to the host cell and injects its DNA. Using the host’s cellular metabolism, the viral DNA begins to replicate and form proteins. Then fully formed viruses assemble. These viruses break, or lyse, the cell and spread to other cells to continue the cycle.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells under a microscope?
The difference between the two groups is the presence or absence of a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells do not contain a membrane-bound nucleus. They are generally smaller and less complicated than eukaryotic cells.

What are at least two major differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and one major similarity between the two?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic are similar in which they have a plasma membrane and cytoplasm; meaning all cells have plasma membrane surrounding them. A difference between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic is that eukaryotic have organelles, for example, a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus.
a eukaryotic bigger than a virus?
(DOK2) One such pattern is the size trend: most viruses are smaller than most bacteria, which are smaller than most eukaryotic cells. As a class, information is compiled to identify and explain phenomena in terms of concepts.
Is eukaryotic bigger than prokaryotic?
Eukaryotic cells are generally bigger — up to 10 times bigger, on average, than prokaryotes. Their cells also hold much more DNA than prokaryotic cells do.
Why is a virus not alive?
Viruses are not made out of cells, they can’t keep themselves in a stable state, they don’t grow, and they can’t make their own energy. Even though they definitely replicate and adapt to their environment, viruses are more like androids than real living organisms.
- nerve specialist called
- lilac flower meaning
- advantages of java beans
- what color are tendons
- madagascar points of interest



