byte sizes smallest to largest
Hello. Welcome to solsarin. This post is about “byte sizes smallest to largest“.
Byte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer[1][2] and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit of memory in many computer architectures. To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit definition, network protocol documents such as The Internet Protocol (RFC 791) refer to an 8-bit byte as an octet.[3] Those bits in an octet are usually counted with numbering from 0 to 7 or 7 to 0 depending on the bit endianness. The first bit is number 0, making the eighth bit number 7.
The size of the byte has historically been hardware-dependent and no definitive standards existed that mandated the size. Sizes from 1 to 48 bits have been used.[4][5][6][7] The six-bit character code was an often-used implementation in early encoding systems, and computers using six-bit and nine-bit bytes were common in the 1960s. These systems often had memory words of 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 48, or 60 bits, corresponding to 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, or 10 six-bit bytes. In this era, bit groupings in the instruction stream were often referred to as syllables[a] or slab, before the term byte became common.
IEC
The modern de facto standard of eight bits, as documented in ISO/IEC 2382-1:1993, is a convenient power of two permitting the binary-encoded values 0 through 255 for one byte—2 to the power of 8 is 256.[8] The international standard IEC 80000-13 codified this common meaning. Many types of applications use information representable in eight or fewer bits and processor designers commonly optimize for this usage. The popularity of major commercial computing architectures has aided in the ubiquitous acceptance of the 8-bit byte.[9] Modern architectures typically use 32- or 64-bit words, built of four or eight bytes, respectively.

The unit symbol for the byte was designated as the upper-case letter B by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).[10] Internationally, the unit octet, symbol o, explicitly defines a sequence of eight bits, eliminating the potential ambiguity of the term “byte”.[11][12]
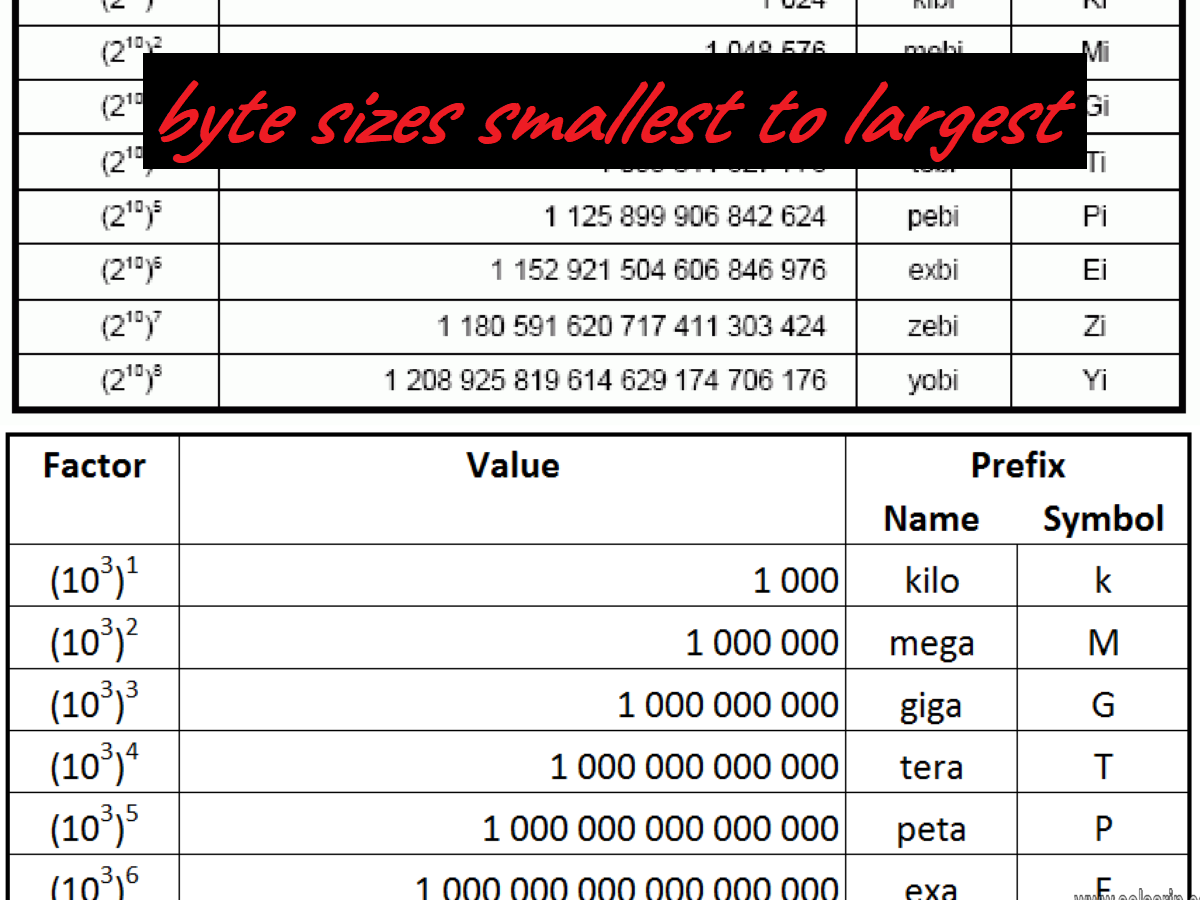
Computer Storage Units Smallest to Largest
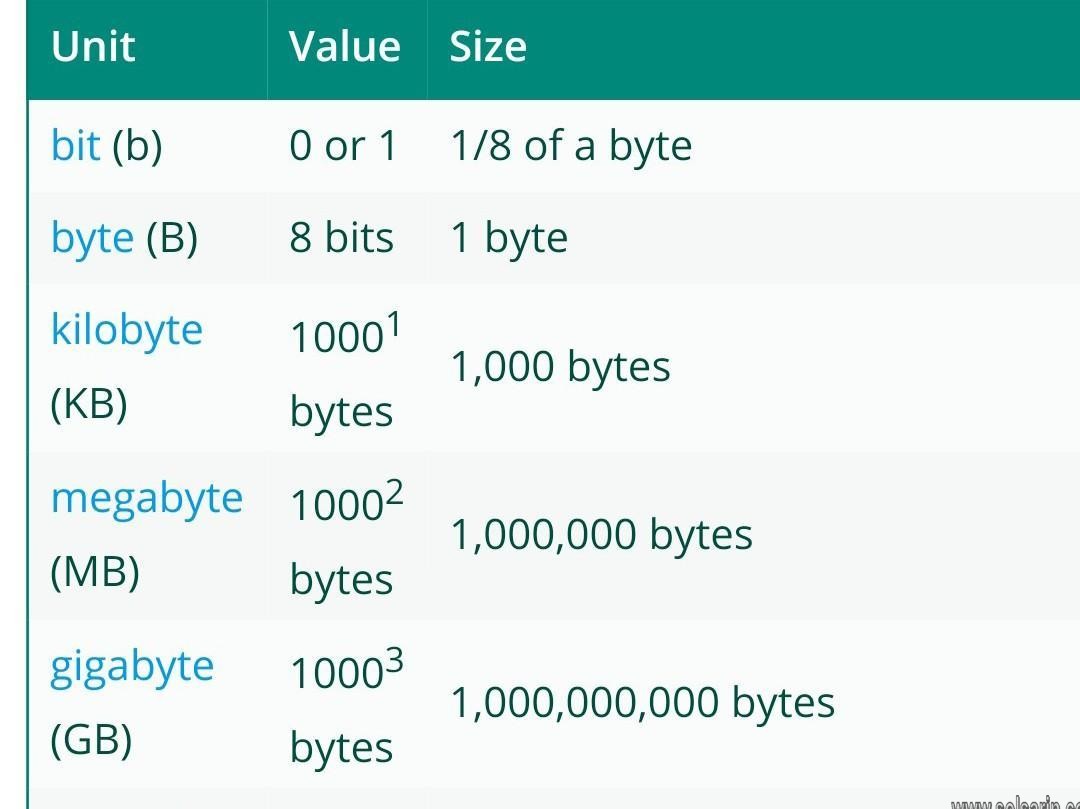
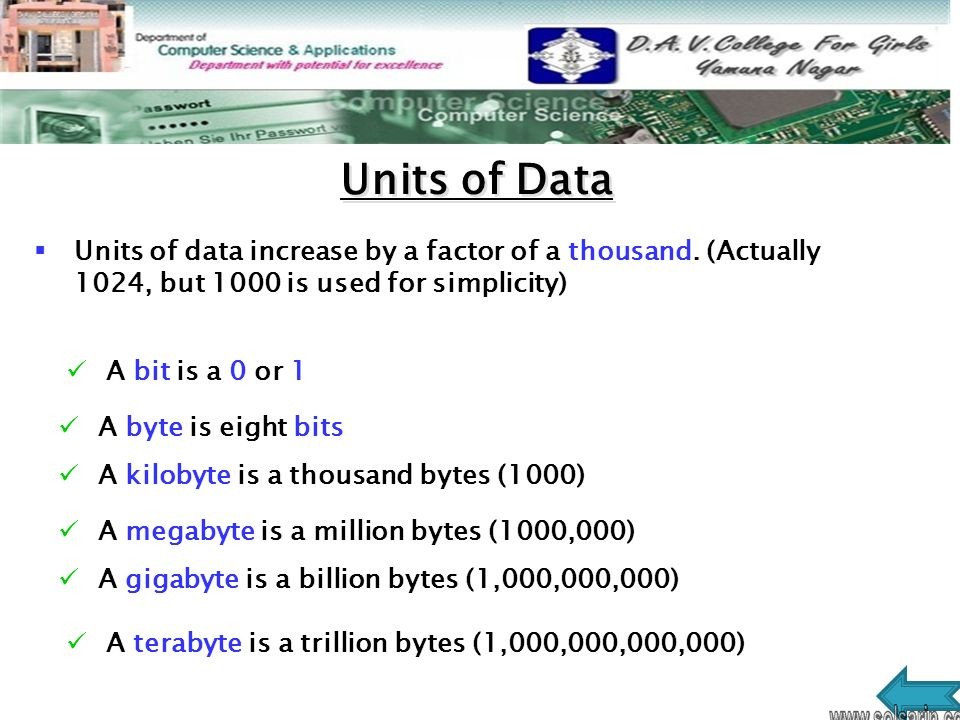
Bit is an eighth of a byte*
The bit is the smallest fundamental size of data storage. It is a binary digit meaning that it can take the value of either 1 or 0. All computer data can be broken down to a string of these 1 and 0 (like in the Matrix, only it doesn’t fall down the screen like rain). When represented as a string it is called binary code.
Byte: 1 Byte
A single byte stores eight bits*, eight 1’s or 0’s. This octet of bits is the smallest unit for a base 1,000 order of magnitude naming system as follows…
Kilobyte: 1 thousand or, 1,000 bytes
Files not relying on on the kilo prefix are the boring ones, word docs, excel sheets, most pictures.
Megabyte: 1 million, or 1,000,000 bytes
Still pretty lame. Short videos, music. Even a pre-historic floppy disc can store a bunch of these.
Gigabyte: 1 billion, or 1,000,000,000 bytes
Finally respectable. The GB is quickly becoming the standard by which storage capacity is judged as most computer hardware will advertize capacity in terms of GB’s
Terabyte: 1 trillion, or 1,000,000,000,000 bytes
Currently, hard drive capacity does not exceed this order of magnitude. One terabyte of data can store just under two and a half years of music played continuously. The entire library of congress can be stored on 82 terabytes of data.
Petabye: 1 quadrillion, or 1,000,000,000,000,000 bytes
Now things are getting hardcore. This is the largest order of magnitude which is any single organization claims to have the capacity of and/or handle. All of the user photo’s on Facebook is estimated at close to 1 petabyte of data. Google processes an estimated 20 petabytes of data a day.
Exabyte: 1 quintillion, or 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 bytes
The exabyte is borderline hypothetical at this point. It is theorized that, per month, the entire internet (yeah, lolcats and all) see’s about 5-8 exabytes of traffic. It was proposed that in 2006 all computer data would fit on 160 exabytes of data.
Zettabyte: one sextillion or 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
WARNING, WARNING you are now in the DANGER ZONE of data storage capacity.It is estimated that by the year 2010 all digital data in existence will sum up to just under one Zettabyte.

Yottabyte: 1 septillion, or 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 bytes
Trying to quantify this may make your head explode so you’ll need to sign a release before I go any further.
*a byte can actually be composed of any number of bits, however, eight is standard
As crazy as those names sound, it’s the real deal.
How big is a petabyte, exabyte or yottabyte? What’s the biggest byte for that matter?
The scale at which data storage is growing can be dizzying. Here’s a brief bottom-up overview starting from the tiny byte to the mammoth yottabyte.
Thirty years ago, back in 1983, the biggest hard drives stored about 10MB of data. That’s barely enough to store two or three .mp3 tracks. Now, a typical notebook has one terabyte of storage or nearly 100,000 times more but even this is figure is laughable when you consider how much data we’re generating. According to IBM, every day we’re creating 2.5 quintillion bytes of data and 90% of today’s digital data created in the last two years.
Even those who are computer savvy still look at data at the gigabyte or terabyte scale but it’s clear we’re moving well past this point. It can get confusing and dizzy so let’s take a brief overview of how we quantify data and put some context on some of the more obscure units of digital information like the petabyte or yottabyte.
About digital storage or memory
We humans perceive information in analog. For instance, what we see or hear processed in the brain from a continuous stream. In contrast, a computer is digital and estimates such information using 1s and 0s.
Communicating only in 1s and 0s may sound limiting at first but people have been using sequences of on and off to transmit messages for a long time. In Victorian times, for instance, people used the telegraph to send ‘dots’ (short signal) or ‘dashes’ (a longer signal) by changing the length of time a switch was on. The person listening on the other end would then decipher the binary data written in Morse code into plain English.
number 97
Transmitting a message over telegraph could take a while, much longer than a message relayed over the telephone for instance, but in today’s digital age this is not a problem because digital data can decoded in an instant by computers. In binary, 01100001 could be the number 97, or it could represent the letter ‘a’.
Digital storage has several advantages over analog much in the same way digital communication of information holds advantages over analog communication. Perhaps the clearest example of why digital storage is superior to analog is resistance to data corruption. Let’s look at audio or video tapes for a moment. To store data, a thin plastic tape impregnated with particles of iron-oxide which become magnetized or demagnetized in the presence of a magnetic field from an electromagnet coil. Data then retrieved from the tape by moving it past another coil of wire which magnetizes certain spots around the tape to induce a voltage.
What comes after Geopbyte?
Geopbyte (GpB/GeB) (2100) Googolbyte (GgB) (2100) Saganbyte (SB) (2110) Pijabyte (PjB) (2120)
Likewise, What is the largest byte size?
1 septillion bytes
Also, What are the bytes in order from smallest to largest?
Unit Shortened Capacity
Kilobyte KB 1024 bytes
Megabyte MB 1024 kilobytes
Gigabyte GB 1024 megabytes
Terabyte TB 1024 gigabytes
What is the highest byte?
1 septillion bytes
What are the bytes in order?
– Nibble – 4 bits (half a byte)
– Byte – 8 bits.
– Kilobyte (KB) – 1000 bytes.
– Megabyte (MB) – 1000 kilobytes.
– Gigabyte (GB) – 1000 megabytes.
– Terabyte (TB) – 1000 gigabytes.
What are the byte measurements?
Unit Shortened Capacity
Byte B 8 bits
Kilobyte KB 1024 bytes
Megabyte MB 1024 kilobytes
Gigabyte GB 1024 megabytes
What is the largest bytes to smallest?
Unit Shortened Capacity
Kilobyte KB 1024 bytes
Megabyte MB 1024 kilobytes
Gigabyte GB 1024 megabytes
Terabyte TB 1024 gigabytes


what comes after the yottabyte?
Two proposed names for the next levels are hellabyte or brontobyte (1,000 yottabytes). Forbes noted that the names have less-than-scientific origins — the hellabyte, derived from having “a hell of a lot of bytes” and the brontobyte named after Brontosaurus, the largest dinosaur. As of 2017, there was nothing measurable on the hella/brontobyte scale. But Cisco estimated that brontobytes could used as soon as 2020 — so we’re still not there yet.
And what happens when the amounts of data exceed scientific names that correlate with their size? Forbes addressed this in 2013 while projecting the next tier of data: a geopbyte (1,000 brontobytes).
Is 1000 GB enough for a month?
Averages will be lower than this, but for U.S. usage, I consider 300–500 GB a month to be normal, and 500–1000 GB to be high. Anything higher than 1000 GB a month takes some real doing to achieve, but it probably just means watching enough 4K streaming content.
Thank you for staying with this post “byte sizes smallest to largest” until the end.