countries controlled by napoleon
Hello. Welcome to solsarin. This post is about “countries controlled by napoleon “.
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of French domination over most of continental Europe. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and its resultant conflict. The wars are often categorised into five conflicts, each termed after the coalition that fought Napoleon: the Third Coalition (1805), the Fourth (1806–07), the Fifth (1809), the Sixth (1813–14), and the Seventh (1815).
Napoleon, upon ascending to First Consul of France in 1799, had inherited a republic in chaos; he subsequently created a state with stable finances, a strong bureaucracy, and a well-trained army. In 1805, Austria and Russia formed the Third Coalition and waged war against France. In response, Napoleon defeated the allied Russo-Austrian army at Austerlitz in December 1805, which is considered his greatest victory. At sea, the British severely defeated the joint Franco-Spanish navy in the Battle of Trafalgar on 21 October 1805.
October 1806
This victory secured British control of the seas and prevented the invasion of Britain itself. Concerned about increasing French power, Prussia led the creation of the Fourth Coalition with Russia, Saxony, and Sweden, and the resumption of war in October 1806. Napoleon quickly defeated the Prussians at Jena and the Russians at Friedland, bringing an uneasy peace to the continent. The peace failed, though, as war broke out in 1809, with the badly prepared Fifth Coalition, led by Austria. At first, the Austrians won a stunning victory at Aspern-Essling, but were quickly defeated at the bloody Wagram, which was the bloodiest battle in history until the battle of Leipzig.

Hoping to isolate and weaken Britain economically through his Continental System, Napoleon launched an invasion of Portugal, the only remaining British ally in continental Europe. After occupying Lisbon in November 1807, and with the bulk of French troops present in Spain, Napoleon seized the opportunity to turn against his former ally, depose the reigning Spanish royal family and declare his brother King of Spain in 1808 as José I. The Spanish and Portuguese revolted with British support and expelled the French from Iberia in 1814 after six years of fighting.
Russia in 1812
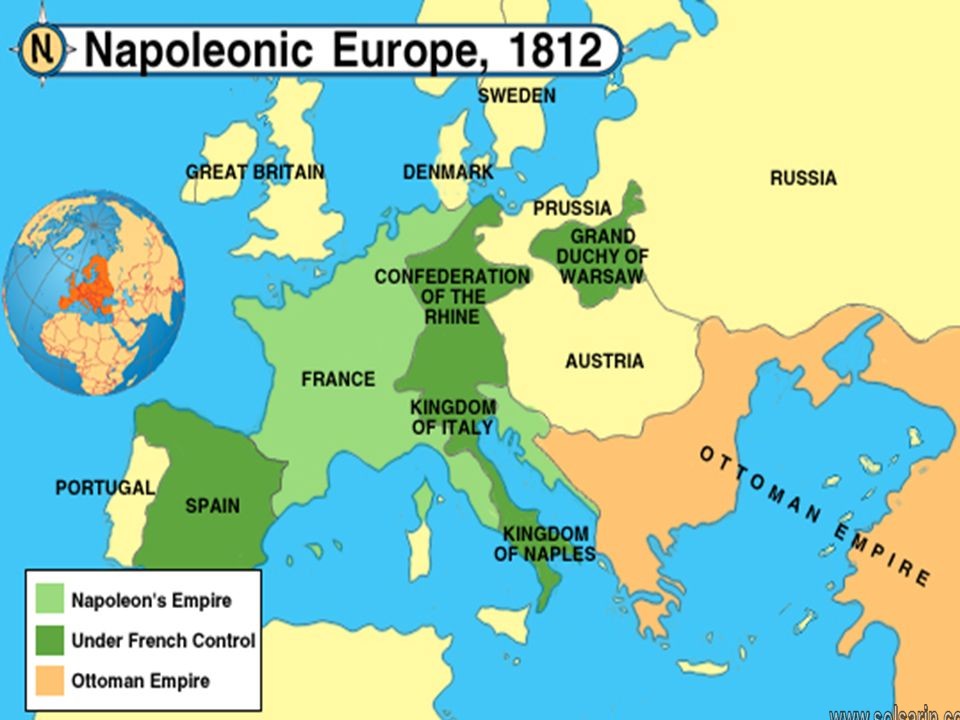
Concurrently, Russia, unwilling to bear the economic consequences of reduced trade, routinely violated the Continental System, prompting Napoleon to launch a massive invasion of Russia in 1812. The resulting campaign ended in disaster and the near destruction of Napoleon’s Grande Armée.
Encouraged by the defeat, Austria, Prussia, Sweden, and Russia formed the Sixth Coalition and began a new campaign against France, decisively defeating Napoleon at Leipzig in October 1813 after several inconclusive engagements. The Allies then invaded France from the east, while the Peninsular War spilled over into southwestern France. Coalition troops captured Paris at the end of March 1814 and forced Napoleon to abdicate in April.
He was exiled to the island of Elba, and the Bourbons were restored to power. But Napoleon escaped in February 1815, and reassumed control of France for around one hundred days. After forming the Seventh Coalition, the allies defeated him at Waterloo in June 1815 and exiled him to Saint Helena, where he died six years later.
Napoleon’s Conquests That Altered the Course of Europe’s History
hese the final words uttered by Emporer Napoleon Bonaparte. Even whilst laying on his deathbed, this ambitious, egocentric leader expressed his untamed vendetta towards his foes, the British forces. The reason for this being that the French army under his leadership forced to bite the dust in the infamous Battle of Waterloo on the 8th of June 1815.
Following the war’s outcome, he was captured and exiled to the remote island of St. Helena for life. It was there that he spent his last days, tucked up in complete solitude. Around this time, he began suffering from an unknown illness that was slowly leading to the deterioration of his health. Within a few months, this illness would go on to take his life. The British autopsy claimed this illness to be stomach cancer.
However, since history is most often recorded by the winners, the legitimacy of the autopsy report could never be verified.
The Rise of Napoleon Bonaparte
At the peak of the French revolution, political and economic instability was at its highest. This period saw an uncontrolled rise in theft, armed robbery, ransom kidnapping, honour killings, and others.
For a short while, there was a vacuum of power as several factions tried to take control of the nation. Amidst all this chaos, a young leader emerged from obscurity with an audacious vision to unite and rule the entire continent of Europe. This young leader was none other than Napoleon Bonaparte.
Thanks to his unwavering zeal coupled with his ruthless conquests, he ascended the throne of France unchallenged. Then, one after another, he attacked and triumphed over the neighbouring kingdoms. The present-day nations of Italy, Austria, Poland, German States, Holland, Switzerland, Spain, Denmark, and Norway were all conquered by Napoleon and his men. He waged a total of over seventy wars, losing only eight of them towards the end.


The Napoleonic era
Napoleon ruled for 15 years, closing out the quarter-century so dominated by the French Revolution. His own ambitions were to establish a solid dynasty within France and to create a French-dominated empire in Europe. To this end he moved steadily to consolidate his personal power, proclaiming himself emperor and sketching a new aristocracy. He was almost constantly at war, with Britain his most dogged opponent but Prussia and Austria also joining successive coalitions. Until 1812, his campaigns were usually successful.
Although he frequently made errors in strategy—especially in the concentration of troops and the deployment of artillery—he was a master tactician, repeatedly snatching victory from initial defeat in the major battles. Napoleonic France directly annexed territories in the Low Countries and western Germany, applying revolutionary legislation in full.
after 1810
Satellite kingdoms set up in other parts of Germany and Italy, in Spain, and in Poland. Only after 1810 did Napoleon clearly overreach himself. His empire stirred enmity widely, and in conquered Spain an important guerrilla movement harassed his forces. Russia, briefly allied, turned hostile, and an 1812 invasion attempt failed miserably in the cold Russian winter.
A new alliance formed among the other great powers in 1813. France fell to the invading forces of this coalition in 1814, and Napoleon exiled. He returned dramatically, only to be defeated at Waterloo in 1815; his reign had finally ended.
The conservative reaction
Conservatism did dominate the European political agenda through the mid-1820s. Major governments, even in Britain, used police agents to ferret out agitators. The prestige of the Roman Catholic church soared in France and elsewhere. Europe’s conservative leader was Prince von Metternich, chief minister of the Habsburg monarchy. Metternich realized the fragility of Habsburg rule, not only wedded to church and monarchy but also, as a polyglot combination of German, Hungarian, and Slavic peoples, vulnerable to any nationalist sentiment.
He sedulously avoided significant change in his own lands and encouraged the international status quo as well. He sponsored congresses at several points through the early 1820s to discuss intervention against political unrest. He was particularly eager to promote conservatism in the German states and in Italy, where Austrian administration of northern provinces gave his regime a new stake.
1820
Nevertheless, in 1820 revolutionary agitation broke out in fringe areas. Risings in several Italian states put down. A rebellion in Spain was also suppressed, though only after several years, foreshadowing more than a century of recurrent political instability; the revolution also confirmed Spain’s loss of most of its American colonies, which had first risen during the Napoleonic occupation. A Greek revolution against Ottoman control fared better, for Greek nationalists appealed to European sympathy for a Christian nation struggling against Muslim dominance. With French, British, and Russian backing, Greece finally won its independence in 1829.
What Countries Did Napoleon Conquer?
Driven by a desire to spread the French revolutionary principles throughout Europe, Napoleon first conquered Egypt to cripple British trade. He returned to France and, using both diplomacy and warfare, conquered neighboring states. Because much of Europe at the time fragmented principalities and semi-autonomous states similar to modern Monaco or Luxembourg, it was simple to take over each country a bit at a time.
Although the French Empire ultimately failed, Napoleon changed the face of Europe, forcing the consolidation of Italy and Germany and crippling the power of the aristocracy.

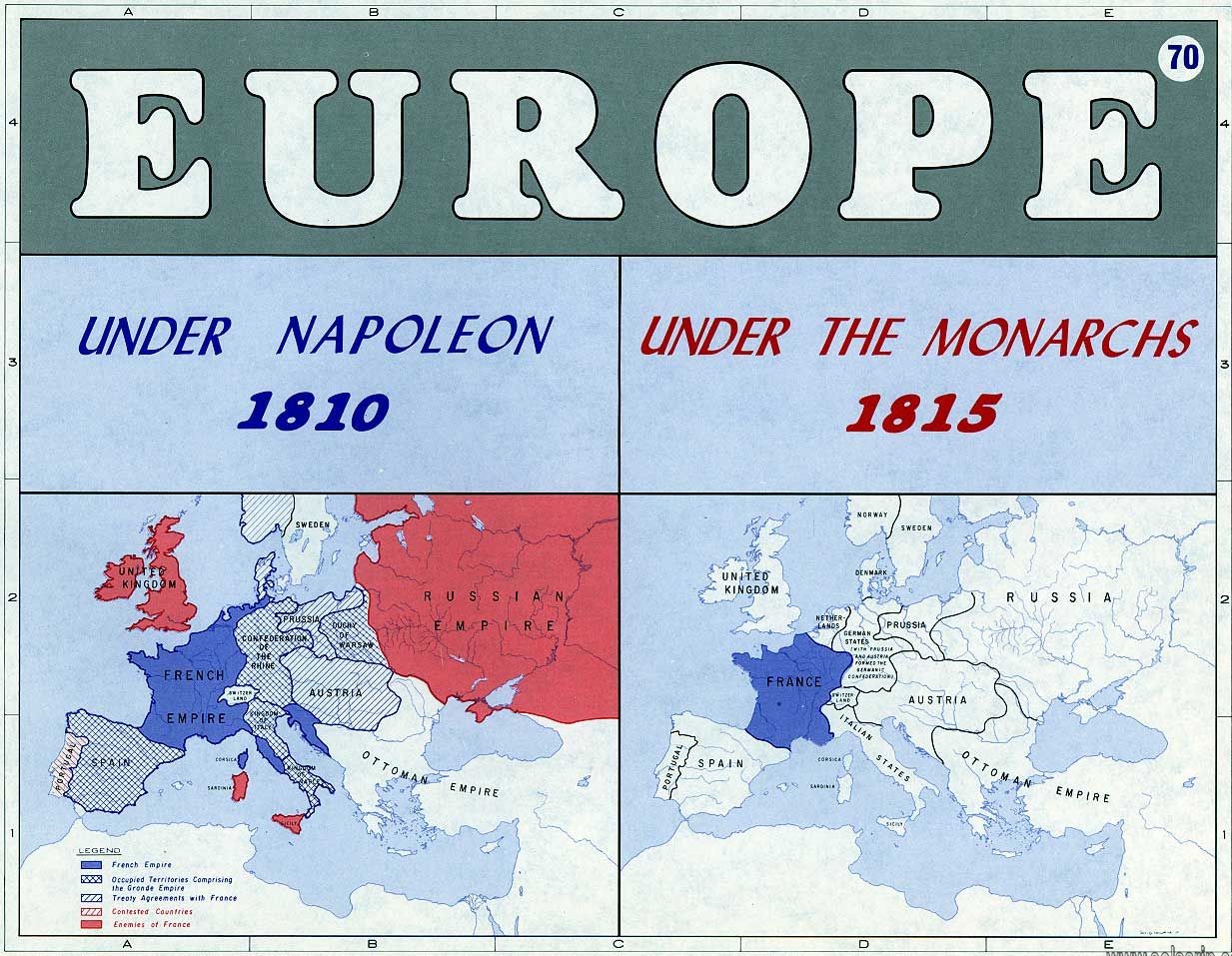
What was the extent from east to west in miles or kilometers of land that Napoleon governed or controlled?
Basically, the English and Russians were the major counterparts that maintained Europe from the increasing influence of Napoleon, but many regions felt for his influence: Italy, Slovakia, Switzerland, Netherlands, among many others, they encompassed 200 km from east to west.
What the name of the three countries Napoleon controlled?
name three countries Napoleon controlled Spain, Confederation of the Rhine and Grand Duchy of Warsaw what was the extent from east to west in miles or kilometers of the land that Napoleon governed or controlled it is about 200 km from east coast bulge of the sabine river in newton country to wester most points near El pasa.
Thank you for staying with this post “countries controlled by napoleon ” until the end.




