elephant trunk snake lifespan
Hello dear friends, thank you for choosing us. In this post on the solsarin site, we will talk about ” elephant trunk snake lifespan”.
Stay with us.
Thank you for your choice.


Geographic Range
The Javan wart snake is found on the coastal regions of India and Ceylon, and also across the Indo-Australian islands as far as the Solomons. It originated in India.
- Biogeographic Regions
- oriental
- native
- australian
- native
Habitat
The Javan wart snake lives in the brackish zone of rivers, streams, and estuaries, and it sometimes swims short distances into the sea. It is also found near washed out banks.
- Aquatic Biomes
- lakes and ponds
- rivers and streams
- coastal
Physical Description
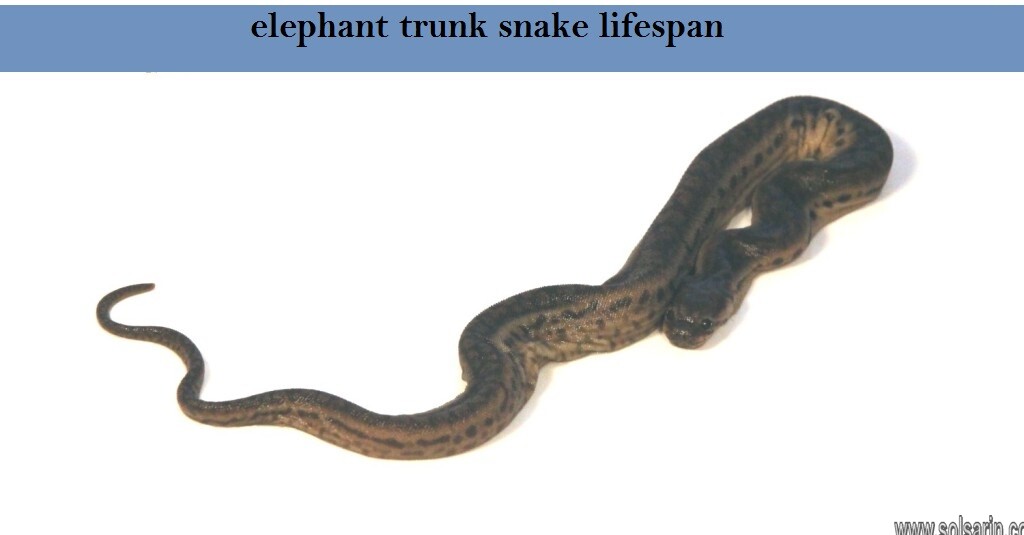
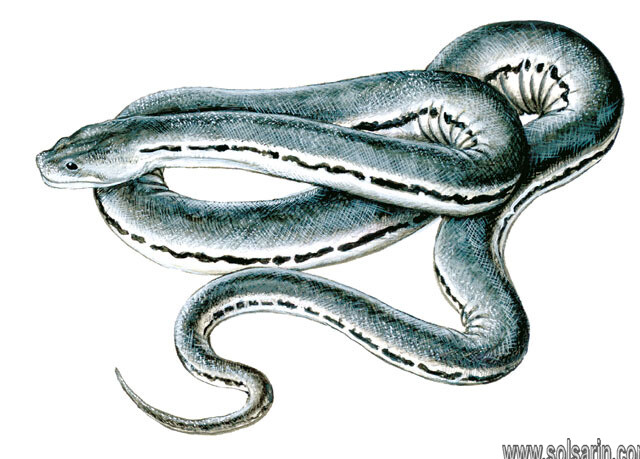
The Javan wart snake has a muscular body and the male grows up to a length of five feet. The female is usually bigger and more powerfully built, with a length of up to eight feet. The top side of the snake’s body is brown in color, and its sides and belly are pale yellow. The skin of the Javan wart snake is loose and baggy, with small rough scales. The scales are formed adjacent to each other and they do not overlap. On each scale, there is a sharp triangular ridge. The ventral scales of this snake are of the same size and shape as the other scales, unlike other types of snakes that often have enlarged ventral scales.
The shape of the snake’s snouted head is flat and broad, with nostrils located at the top side of its head, giving this snake a boa-like appearance, although the width of the snake’s trunk is identical to its head. The snake also has a short and mobile tail.
-
-
Range mass
- 3 to 10 kg
- 6.61 to 22.03 lb
-
Reproduction
The Javan wart snake bears live young, about 20 to 30 offspring at one time. It has amniotic eggs, which are retained in the oviducts of the snake and are fertilized internally. The young snakes are semi-terrestrial, until their baggy skin is fully developed. This is because the baggy skin restricts them from moving efficiently on land. Besides a difference in size, the young can also be distinguished by the irregular, longitudinal blotches on their skin. These blotches fade over time, and eventually disappear when the adult stage is reached.
Behavior
The Javan wart snake usually hides in the daytime and becomes active at night. Sometimes it will forage both during the day and at night. The snake captures its prey by folding its body around it, using its prehensile tail and the sharp scales to ensure a firm grip. The Javan wart snake rarely comes onto land. Their baggy skin is developed for agility under water and restricts them from traveling efficiently on land. Most of the time, the snake stays under the water surface, and it can do so for up to 40 minutes continously. When it need to breathe, the snake floats to the water surface and position its nostrils above water for 15 to 20 seconds.
Food Habits
The Javan wart snake is a carnivore. It feeds primarily on fish and other aquatic animals, but will sometimes feed on frogs. An interesting fact about this snake is that it does not bulge after feeding like other snakes do. Its body remains slack all the time because its skin is so loose and baggy.
Economic Importance for Humans: Positive
Their skin can be processed for manufacturing leather goods.
Economic Importance for Humans: Negative
They are easily aggravated. Although they are not venomous, their recurved teeth break off easily and are left inside one’s flesh if a person is being bitten, thus creating unpleasant wounds.

Conservation Status
The Javan wart snake is becoming increasingly rare. This is indicated by the fact that they are now seldom offered for sale. One reason for their scarcity is that they have been captured in large numbers because their skin is used for making leather goods. The other reason is that an effective and successful method of breeding is still not availiable yet.
Elephant Trunk Snake Care Sheet
The Elephant Trunk Snake is a challenging snake to care for and as such, their care is best left to advanced reptile caretakers. As aquatic snakes, they require an aquarium. Also, they are not to be held.
They dislike it, and regular handling stresses them. Taking them out of water is bad for them and can cause serious injuries. However, they are excellent display pets and are wonderful to keep and care for.
Facts and Information
The elephant trunk snake is endemic to East Asia. The first wild population can be found in north and central Sumatra and on Malaysia’s west coast which also includes the islands of Penang and Langkawi as well as Sarawak (a state in Malaysia).
Other wild populations can be found in Thailand (south Thailand all the way to Bangkok), and in Indonesia (Kalimantan, Java). They occur up to depths of 150 m.
The binomial name of the elephant trunk snake is Acrochordus javanicus. The snake belongs to the genus Acrochordus, which is native to Australasia and contains 3 aquatic snakes namely the Arafura file snake, little wart snake, and the elephant trunk snake. The genus belongs to the family Acrochordidae. As a monogeneric family, only the 3 species already mentioned belong to the family.
As an entirely aquatic snake, the elephant trunk snakes spend all their time underwater, only coming up to breathe. Even with that, the snake sticks only the nostrils out of water.
Elephant Trunk Snake Habitat
Although they can found in freshwater, they usually inhabit brackish water. They prefer to live in rivers, streams, and estuaries. Additionally, they may be found in rice paddies and peat swamps.
Enclosure
As aquatic snakes, they need an aquatic set up. As usual, the size of the enclosure depends on the size of the snake. For individuals that are 20 inches or less, a 10 to 15-gallon aquatic tank will do.
The water needs to be filtered. An ideal filtration system is the Penn Plax Undergravel Filter – Premium Aquarium. These work well and keep the tank clean. Additionally, you need to install a sump (submersible pump) that is adequate for the volume of water in the aquarium.
Install sponge pre-filters such as the BCP Pre-Filter Foam on the return pumps of the sump. A canister filter is also a good investment as it filters the water properly and ensures the snake is comfortable. This is essential to their health. I recommend the Polar Aurora
Substrate
While there are several substrate choices available but it is best to go with no substrate at all. Gravel and sand can be used but these can be tough to clean. Other choices that are aesthetically pleasing include coral rubble such as Nature’s Ocean 12-Inch Coral Base Rocks (which helps buffer pH levels), GloFish Aquarium Gravel and Seachem Flourite Black Clay Gravel. Also, consider ornament turf such as Anleo Artificial Aquarium Ornament Turf.


Temperature
The water needs a submersible water heater such as the Hygger Saltwater Tank Titanium Tube Submersible Pinpoint Aquarium Heater or the ISTA In-Line External Aquarium Heater to keep the temperature between 84 to 86 F.
Creating a temperature gradient in such a small tank is not possible, so it’s best to keep the water at a comfortable temperature. Use a thermometer such as the Zacro LCD Digital Aquarium Thermometer to check the temperature at all times. Getting an external heat controller is advisable.




