end result of transcription
Hello. Welcome to solsarin. This post is about

.
What happens at the end of translation?
Lastly, termination occurs when the ribosome reaches a stop codon (UAA, UAG, and UGA). Since there are no tRNA molecules that can recognize these codons, the ribosome recognizes that translation is complete. The new protein is then released, and the translation complex comes apart.
What is transcribed in transcription?
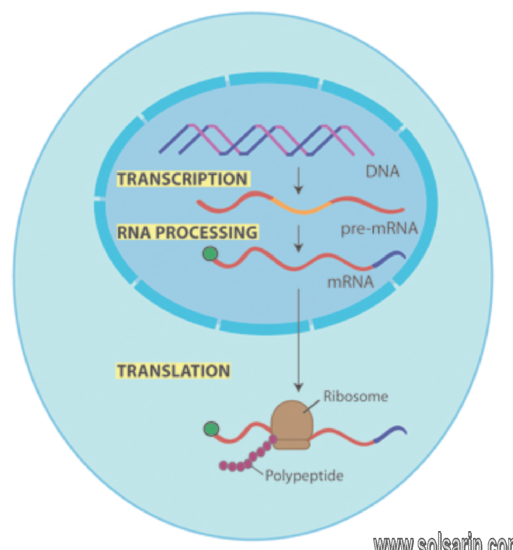
Transcription
= Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene sequence. This copy, called a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, leaves the cell nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where it directs the synthesis of the protein, which it encodes.
Which molecule is the end result of transcription?
In transcription, a portion of the double-stranded DNA template gives rise to a single-stranded RNA molecule. In some cases, the RNA molecule itself is a “finished product” that serves some important function within the cell.
What is created at the end of the transcription stage of protein synthesis?
After termination, transcription is finished. An RNA transcript that is ready to be used in translation is called a messenger RNA (mRNA). In bacteria, RNA transcripts are ready to be translated right after transcription.
translation?
The presence of a stop codon—UAA, UAG or UGA—in the A site of the ribosome is generally a signal to terminate protein synthesis. This process constitutes the last essential stage of translation, as it ensures the formation of full-sized proteins. Translation termination involves two classes of release factors (RFs).
What usually terminates the process of translation quizlet?
termination of translation happens when the ribosome hits a stop codon on the mRNA.
Polyribosomes?
What are the advantages of polyribosomes? This occurs when multiple ribosomes translate a single mRNA simultaneously- forms polyribosome/ polysome.
Where does mRNA go after transcription?
The RNA made during transcription (in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, or the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells) will go to the ribosomes. The ribosomes read the RNA during translation to make proteins.
How is transcription done?
Transcription is the first step in gene expression. It involves copying a gene’s DNA sequence to make an RNA molecule.
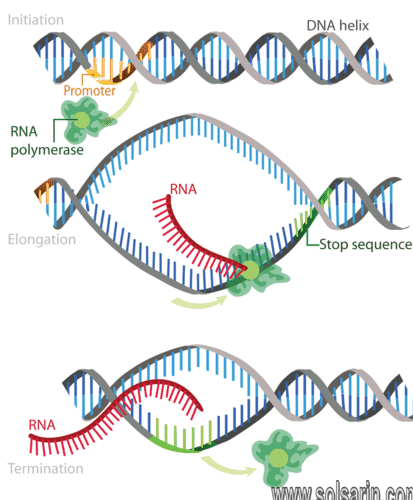
is the termination sequence?
termination sequence. The sequence of DNA which signals the transcription to stop. , which follows the promoter and coding region, is the last region of the. gene. The fundamental unit of heredity that carries genetic information from one generation to the next.

What is termination in biology?
Termination is the ending of transcription, and occurs when RNA polymerase crosses a stop (termination) sequence in the gene. The mRNA strand is complete, and it detaches from DNA.
What is the importance of the start and stop codons?
The start codon marks the site at which translation into protein sequence begins, and the stop codon marks the site at which translation ends.
Do you want to know about “an empty-kcalorie food is one that contains“? Click on it.
termination?
Translation termination occurs when the ribosome encounters a stop codon (UAG, UAA, or UGA) in the A site. … Upon stop-codon recognition, RF1 and RF2 promote the hydrolysis of the ester bond in peptidyl–tRNA in the P site, leading to the release of the completed protein and the termination of protein synthesis.
How does a stop codon affect transcription?
A stop codon tells the ribosome and transfer DNA that the process can stop and the new polypeptide chain can be released. If ribosomes and transfer DNA are still a mystery, either read on or visit the protein synthesis page. Without stop codons, an organism is unable to produce specific proteins.
example?
Stop codon: A set of three adjacent bases in the DNA or their complementary bases in messenger RNA that specifies the end of a polypeptide chain. The three stop codons (in messenger RNA) are UAA, UAG, and UGA. They are also called termination codons or nonsense codons. U = uracil; A = adenine; G = guanine.
What is the function of the anticodon?
String of amino acids make up protein’s primary structure. anticodon – a sequence of three nucleotides on a tRNA molecule that bond to a complementary sequence on an mRNA molecule. The anticodon sequence determines the amino acid that the tRNA carries.
Which of the following typically stops the process of translation?
Translation stops when the ribosome encounters a termination codon, normally UAG, UAA, or UGA (where U, A, and G represent the RNA bases uracil, adenine, and guanine, respectively).
How do polyribosomes work?
.. Multiple ribosomes move along the coding region of mRNA, creating a polysome. The ability of multiple ribosomes to function on an mRNA molecule explains the limited abundance of mRNA in the cell.
Where are polyribosomes found?
Polyribosomes are found either free in the cytosol or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. In general,”free” polyribosomes synthesize proteins that remain in the cell, such as hemoglobin in red blood cells or contractile proteins in muscle cells.
What happens to the mRNA after the process is complete?
The “life cycle” of an mRNA in a eukaryotic cell.
What leaves the nucleus after transcription is complete?
RNA
It actually consists of two processes: transcription and translation. Transcription takes place in the nucleus. It uses DNA as a template to make an RNA molecule. RNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs.
What happens to the mRNA after the protein is produced?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) mediates the transfer of genetic information from the cell nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where it serves as a template for protein synthesis.
What is a transcription job?
Definition of a Transcriptionist
A transcriptionist is a specialist in documentation. The job entails listening to voice recordings and converting them into written documents. It requires patience and serious training. The job might involve transcribing recordings of legal, medical and other topics.
Can you make money as a transcriptionist?
The average median annual income for a general transcriptionist is currently $45,000. Legal transcriptionists can earn around $60,000. Of course, if you start your own business and hire subcontractors while working as a project manager yourself, your income can grow well beyond these figures.
What is the difference between transcriptionist and transcriber?
As nouns the difference between transcriptionist and transcriber. is that transcriptionist is a person who transcribes while transcriber is a person who transcribes; a transcriptionist.

What is transcription example?
Maybe someone left a message on your voicemail, and you had to write it down on paper. Or maybe you took notes in class, then rewrote them neatly to help you review.
What happens in transcription and translation?
Transcription and translation take the information in DNA and use it to produce proteins. Transcription uses a strand of DNA as a template to build a molecule called RNA. … During translation, the RNA molecule created in the transcription process delivers information from the DNA to the protein-building machines.
How is termination different in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes have three types of RNA polymerases, I, II, and III, and prokaryotes only have one type.
Is termination codon on mRNA?(end result of transcription)
Chain-termination codon: A set of three adjacent bases in the DNA or their complementary bases in messenger RNA that specifies the end of a polypeptide chain. The three chain-termination codons (in messenger RNA) are UAA, UAG, and UGA.
What is the Stop amino acid?(end result of transcription)
Tryptophan is unique because it is the only amino acid specified by a single codon. The remaining 19 amino acids are specified by between two and six codons each. The codons UAA, UAG, and UGA are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation.
What happens if there is no termination in transcription?(end result of transcription)
Without a stop codon, the signal to release the ribosome from the transcript is missing and the ribosome becomes stalled at the end of the transcript.
Have you heard anything about “how much is the coca-cola brand worth?“? Click on it.
What is RNA and what is its function?(end result of transcription)
What is difference between DNA and RNA?(end result of transcription)
Reverse transcriptase(end result of transcription)
Which viruses are RNA viruses?(end result of transcription)
Is Influenza an RNA virus?(end result of transcription)
Is Ebola an RNA virus?(end result of transcription)

Dengue Virus Genome and Structure(end result of transcription)
The dengue virus genome is a single strand of RNA. The viral genome encodes ten genes



