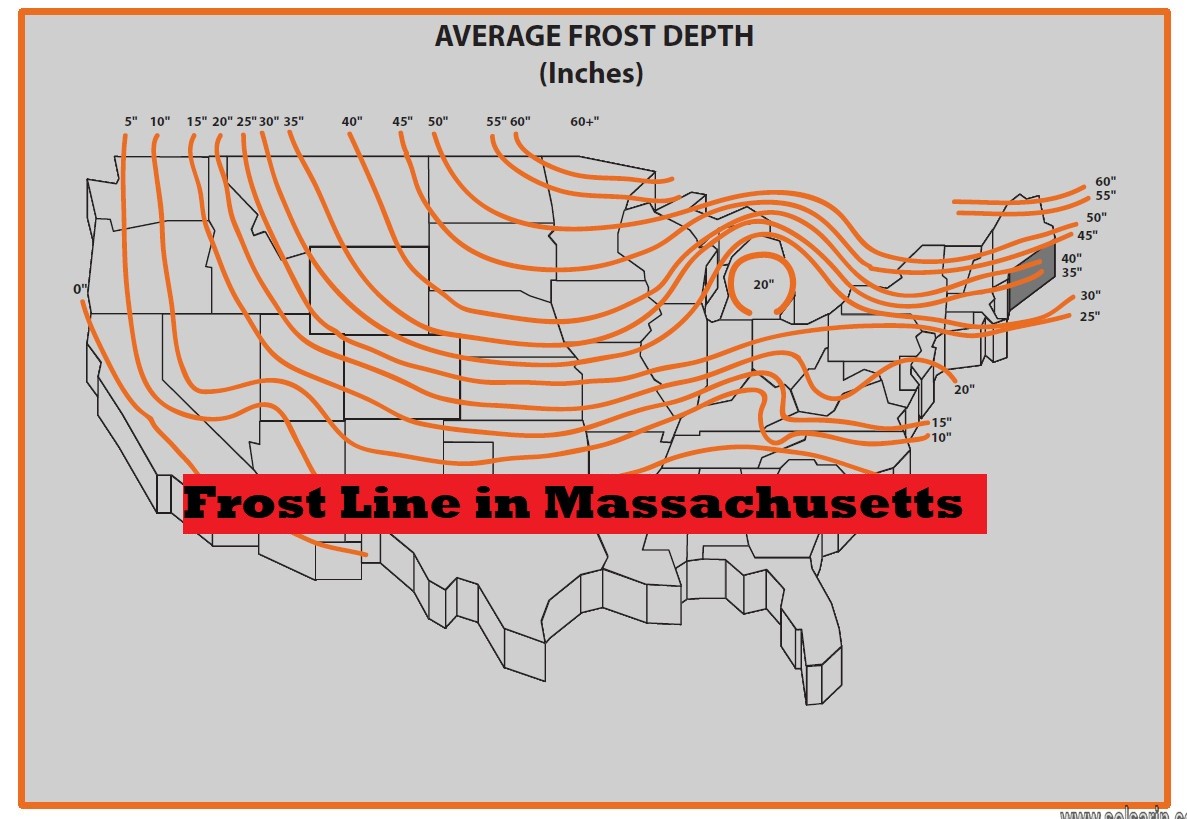
Frost Line in Massachusetts
Hello everyone. Welcome to our site solsarin. This topic is about “Frost Line in Massachusetts”. Please stay with us. Thank you for your patience.
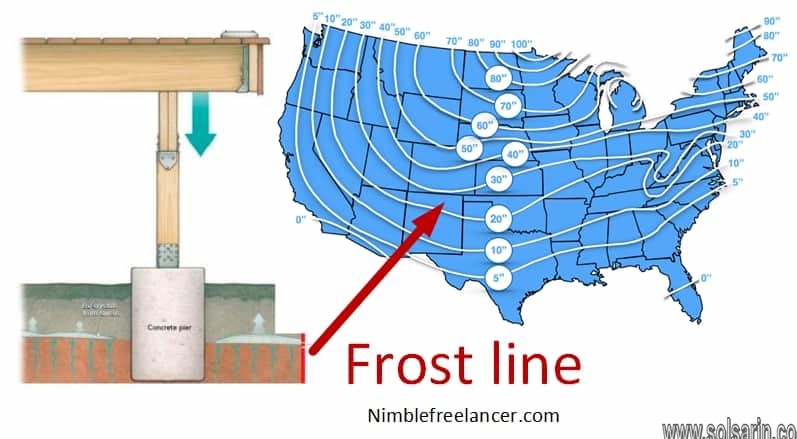

Frost line
The frost line—also known as frost depth or freezing depth—is most commonly the depth to which the groundwater in soil is expected to freeze. The frost depth depends on the climatic conditions of an area; the heat transfer properties of the soil and adjacent materials; and on nearby heat sources. For example, snow cover and asphalt insulate the ground and homes can heat the ground (see also heat island).
The line varies by latitude, it is deeper closer to the poles. Per Federal Highway Administration Publication Number FHWA-HRT-08-057; the maximum frost depth observed in the contiguous United States ranges from 0 to 8 feet (2.4 m). Below that depth, the temperature varies; but is always above 32 °F (0 °C).
Alternatively, in Arctic and Antarctic locations the freezing depth is so deep that it becomes year-round permafrost; and the term “thaw depth” is used instead. Finally, in tropical regions, frost line may refer to the vertical geographic elevation below which frost does not occur.
Frost front refers to the varying position of the frost line during seasonal periods of freezing and thawing.
Massachusetts
Massachusetts, officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous state in the New England region of the United States. It borders on the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Maine to the east; Connecticut and Rhode Island to the south; New Hampshire and Vermont to the north and New York to the west. The capital of Massachusetts is Boston, which is also the most populous city in New England. It is home to the Greater Boston metropolitan area, a region influential upon American history, academia, and industry.
Originally dependent on agriculture, fishing and trade, Massachusetts was transformed into a manufacturing center during the Industrial Revolution. During the 20th century, Massachusetts’s economy shifted from manufacturing to services. Modern Massachusetts is a global leader in biotechnology, engineering, higher education, finance, and maritime trade.
Massachusetts was a site of early English colonization: the Plymouth Colony was founded in 1620 by the Pilgrims of the Mayflower; and in 1630 the Massachusetts Bay Colony; taking its name from the indigenous Massachusett people; established settlements in Boston and Salem. And In 1692, the town of Salem and surrounding areas experienced one of America’s most infamous cases of mass hysteria; the Salem witch trials.
In 1777, General Henry Knox founded the Springfield Armory; which, during the Industrial Revolution, catalyzed numerous important technological advances, including interchangeable parts.And In 1786, Shays’ Rebellion, a populist revolt led by disaffected American Revolutionary War veterans; influenced the United States Constitutional Convention.
In the 18th century, the Protestant First Great Awakening, which swept Britain and the Thirteen Colonies; originated from the pulpit of Northampton preacher Jonathan Edwards.And In the late 18th century, Boston became known as the “Cradle of Liberty” for the agitation there that later led to the American Revolution.
What is frost line depth in Massachusetts?
Everything I read says to go past the frost line you must go 4 feet deep.
What is the depth of a frost line?
The depth of the line changes with latitude; closer to the poles, it is deeper. The highest frost depth measured in the contiguous United States varies from zero to nearly eight feet; according to Federal Highway Administration Publication Number FHWA-HRT-08-057 (2.4m). The temperature below that depth fluctuates, although it is always above 0 °C (32 °F).

Frost Lines by State 2022
The frost line, also referred to as the frost depth, is the depth at which the groundwater in soil is expecting to freeze. Frost lines depend on an area’s climatic conditions; including the heat transfer properties of materials in the ground (such as soil); and nearby heat sources.
Frost lines vary by latitude and are deeper closer to the poles. According to the Federal Highway Administration, the maximum frost depth ranges between zero to eight feet in the contiguous United States.
Generally, the coldest U.S. states have the deepest frost lines. Alaska’s is the deepest at 100 inches, followed by Minnesota with 80 and North Dakota with 75. On the other hand, the hottest U.S. states have more shallow frost lines. Florida and Hawaii are zero inches, Louisiana and South Carolina’s are four inches, followed by California and Georgia with five.
Frost lines can be important for building construction and are taken into consideration when laying a foundation. When water transitions from liquid to solid, it expands 9% in volume. Frost heaving, which is the upward swelling of soil during freezing conditions; can move the foundations of buildings, severely damaging them. For this reason, building codes will consider frost lines and build the foundations below the line. Additionally, water and sewer pipes need to be placed below the frost lines as well.
Here are the 10 states with the deepest frost lines:
- Alaska (100 inches)
- Minnesota (80 inches)
- North Dakota (75 inches)
- Maine (74 inches)
- Wisconsin (65 inches)
- South Dakota (64 inches)
- Montana (61 inches)
- New Hampshire (60 inches)
- Vermont (60 inches)
- Iowa (58 inches)
Frost Line Depth: 5 Important Things All Homeowners Should Know
Before attempting to build a workshop or put up a fence, take some time to learn about frost line depth and how it can impact your projects.
1. Frost line is the depth at which groundwater freezes.
It’s necessary to understand what the frost line is and how to determine frost line depth in order to grasp the risks associated with constructing buildings or other structures. The ground contains moisture that is used by plants and animals to live and thrive; however, when cold weather hits, the groundwater begins to freeze and expand; pushing and crushing objects that are in the frozen dirt.
Frost lines are typically determined by the moisture and soil content, as well as the average temperatures in the region. Testing the exact depth relies on instruments known as frost tubes that consist of a small hollow tube that is inserted into a drilled hole in the frozen ground. Testers put a bag of water with measurement indicators into the tube and determine the depth based on the line at which the water freezes. Always refer to local building codes to find out the approved depth to install footings.
2. Frost line depths vary greatly across the United States.
The weather across the United States doesn’t remain consistent, so it only makes sense that the colder areas of the country would have a different frost line depth than the warmer areas of the country. With this variability in mind, it’s necessary to check local building codes, as well as frost line depth maps to get an accurate idea of how deep you will need to dig in order to install deck footings, fence posts, and foundations.
For accurate, up-to-date information about the current frost level in your area, the National Weather Service provides a country-wide frost line depths map that can be referencing by entering your address or zip code. Just keep in mind that this map only indicates the current frost depth, so if it’s checking in the middle of summer then most locations will not have any frost. Alternately, there are many frost line depth maps that display that average frost line maximum for the region.


3. Frost heave can damage foundations, footings, and other important structural elements.
When posts, foundations, footings, and other supports are installing above the frost line; the structures become vulnerable to significant damage that can cause by frost heaves. A frost heave occurs; when the water in the soil freezes and expands, forming a pocket of ice called a frost lens. This lens pushes dirt, rocks, and any other objects upwards, as it gradually expands. The result is a chaotic movement of hardened earth that has enough force to bend posts, break rock; and shift entire building foundations.
Even after the frost lens melts, allowing the dirt to settle back into position, the structure will likely remain unbalanced and damaged. However, installing the structural supports at a point at least 2 feet below the maximum frost depth provides an anchor to help prevent the structure from being forcing up and out of position.
4. Most building codes include frost depth requirements.
There are many resources to check in order to determine the average frost line for a specific city, state, or region; though it’s important to note that the main reference for building projects should be the local building codes.
These regulations, including frost line depth; are meticulously kept up to date to provide the best information to a wide range of professionals in the area; so that commercial, industrial, and residential construction meets the safety restrictions put in place by the local government and the state.
Given that most building projects that would be affecting by the frost line require a building permit; checking the frost line depth shouldn’t be a problem. Just ask for the information while applying for a permit; or check the local building codes on the government website.
5. Some projects may require factoring in lateral frost line depth.
The planning stage of a project is the best time to determine the local frost line depth; and how it impacts the structure. Some projects can be completed without giving much thought to the frost line; like constructing a semi-permanent gazebo that sits on a patio or deck. However, for projects that have structural supports in the ground; the frost line depth is a key factor that needs to be accounted for during planning.
Tasks that can be impacted by the frost line depth include building a new deck, putting in a fence, installing a retaining wall, or pouring the foundation for a workshop. While frost heaves may only shift the ground by a few inches each year, this can result in cracked foundations, split fence posts, and unsafe decks if the supports are not installed below the frost line to help prevent significant movement during the winter months.