how do space suits work
Hello. Welcome to solsarin. This post is about “how do space suits work”.


Spacesuits supply astronauts with oxygen to breathe while they are in the vacuum of space. The suits contain water to drink during spacewalks. They protect astronauts from being injured from impacts of small bits of space dust.
How are space suits pressurized?
The suit has inflatable bladders that fill it with oxygen from the orbiter. These bladders inflate automatically at reduced cabin pressure. They also can be manually inflated during entry to prevent the crew member from blacking out.
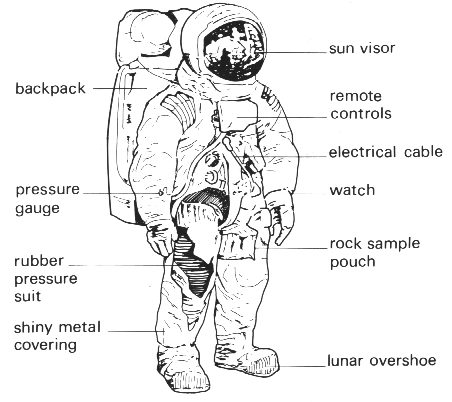
The flexible parts of the suit are made from as many as 16 layers of material
The flexible parts of the suit are made from as many as 16 layers of material. The layers perform different functions, from keeping oxygen within the spacesuit to protecting from space dust. Closest to the astronaut’s skin, the cooling garment makes up the first three layers.
astronauts poop in their space suits?
Eliminating Waste
Each spacewalking astronaut wears a large, absorbent diaper called a Maximum Absorption Garment (MAG) to collect urine and feces while in the space suit. The astronaut disposes the MAG when the spacewalk is over and he/she gets dressed in regular work clothes.
Do astronauts pee in their suits?
It is worn by both male and female astronauts. Astronauts can urinate into the MAG, and usually wait to defecate when they return to the spacecraft. However, the MAG is rarely used for this purpose, since the astronauts use the facilities of the station before EVA and also time the consumption of the in-suit water.
Why do astronauts wear white?
Space is a dangerous environment and presents extremes of both hot and cold for the human explorer. To allow spacesuit cooling (and heating) systems to work most efficiently, they are made of material that reflects much of the incident radiation (mostly sunlight) that falls on them; hence, they are white.
What happens if you take your space suit off in space?
Astronauts need space suits to stay alive. You could only last 15 seconds without a spacesuit — you’d die of asphyxiation or you’ll freeze. If there’s any air left in your lungs, they will rupture.
Can a space suit survive reentry?
Even if it is possible, it won’t happen; since the astronaut was in a space pod, his or her suit probably wasn’t designed for re-entry. A space suit strong enough to withstand re-entry would be so bulky and reinforced, it might as well be a small spaceship.
Are space suits comfortable?
No one ever donned a space suit because it was comfy. Quite the opposite–space suits can be terribly uncomfortable because of the layers and layers of material and technological systems that protect astronauts from the cold vacuum of space and the pressure of ascent and descent through the atmosphere.
What does space smell like?
A succession of astronauts have described the smell as ‘… a rather pleasant metallic sensation … [like] … sweet-smelling welding fumes’, ‘burning metal’, ‘a distinct odour of ozone, an acrid smell’, ‘walnuts and brake pads’, ‘gunpowder’ and even ‘burnt almond cookie’.
How much does a full NASA space suit cost?
US$12,000,000
The suit has a mass of 47 pounds (21 kg) without a life support backpack, and costs only a fraction of the standard US$12,000,000 cost for a flight-rated NASA space suit.
Why can’t you pour water in a glass in space?
Water poured into space (outside of a spacecraft) would rapidly vaporize or boil away. In space, where there is no air, there is no air pressure. As air pressure drops, the temperature needed to boil water becomes lower. That’s why water boils much faster on a mountaintop than it does at sea level.
Do astronauts feel cold in space?
“Do astronauts ever feel cold in a spacewalk like when we work outside in winter?” No, they don’t feel cold like you do when you work in cold weather, because they’re working in a vacuum. When you are outside in the cold air, you get cold because you are in contact with cold air.
How did astronauts stay warm on the moon?
Space blankets were used as insulation in the suits that astronauts wore when walking on the moon. They also serve as a radiation barrier for instruments, protecting them from extreme temperatures. On earth, space blankets are available to hikers who need to preserve body heat.
Can you fart in space?
Therefore, the fart will not be smelled by the astronaut, although they may marinate in it for a time. When astronauts are not in the space suit and floating about, the fart smell is exaggerated by the lack of airflow from the recycled air used and its inability to mask any smell.
Do astronauts age slower in space?
Scientists have recently observed for the first time that, on an epigenetic level, astronauts age more slowly during long-term simulated space travel than they would have if their feet had been planted on Planet Earth.


Do astronauts shower in space?
The astronauts wipe their body clean by using a wet towel, and wash their hair by using waterless shampoo. Since water does not flow in a zero-gravity environment, the astronauts cannot wash their hands under a faucet as you do on Earth. So, there are no sinks or showers inside the space shuttle.
Do female astronauts wear bras?
According to this Salon article [1], yes they do. They don’t need the support, but the bra keeps their wobbly bits in place while floating around in microgravity. They also like having an extra layer between said bits and the cameras all over the space station.
Do astronauts eat their poop?
All astronaut pee is collected and turned back into clean, drinkable water. Astronauts say that “Today’s coffee is tomorrow’s coffee!” Sometimes, astronaut poop is brought back to Earth for scientists to study, but most of the time, bathroom waste — including poop — is burned.
How much do astronauts get paid?
The middle pay grades for astronauts are G-12 and G-13; each grade is divided into 10 steps, which depend on seniority and/or performance. The middle pay for a G-12 employee is $73,090 to $75,240, and the middle pay for a G-13 employee is $86,911 to $89,467. That means the average astronaut’s pay is $81,177.
Why did astronauts wear orange?
The white colour is to help reflect heat from the suit. The Advanced Crew Escape Suit (ACES), contains breathing apparatus but is only pressurised during emergencies. The suit is worn during transit between vehicles, take-offs and landings and is orange to improve its visibility.
How do astronauts breathe in space suits?
So, most space suits provide a pure oxygen atmosphere for breathing. Space suits get the oxygen either from a spacecraft via an umbilical cord or from a backpack life support system that the astronaut wears. Both the shuttle and the International Space Station have normal air mixtures that mimic our atmosphere.
Why are astronaut suits orange?
This peculiar shade of orange known as “International Orange” was chosen for safety as it is highly visible against any kind of landscape, especially in the sea. ACES are designed to help astronauts escape from any accidents while taking-off or landing of a space shuttle.
How cold is it in space?
Hot things move quickly, cold things very slowly. If atoms come to a complete stop, they are at absolute zero. Space is just above that, at an average temperature of 2.7 Kelvin (about minus 455 degrees Fahrenheit).
has anyone lost in space?
A total of 18 people have lost their lives either while in space or in preparation for a space mission, in four separate incidents. Given the risks involved in space flight, this number is surprisingly low.

How hot is re-entry to Earth?
It converts to heat (from friction) caused by the atmosphere’s molecules striking its leading edges. This heat makes the Shuttle’s surfaces reach temperatures of up to 1477° C (2691° F).
Why do spaceships not burn up while leaving the atmosphere?
“Objects coming back from space are traveling at many times Mach speed — faster than the speed of sound — so to keep from burning up or breaking up they must be protected from the intense heat caused by that friction.”
Why is Earth reentry so hot?
During re-entry, the shuttle is going so fast, it compresses the air ahead of it. The compression of the air layers near the leading edges of the shuttle is quick, causing the temperature of the air to rise to as high as 3000 degrees Fahrenheit!
it hard to move in a space suit?
After spacewalks, astronauts sometimes talk about how difficult it is to maneuver in a suit in space. The moving parts of spacesuits need to be sturdy and protected from breaking down, so sometimes the engineering of the suit makes it even more difficult for spaceflyers to move around comfortably.
How many hours of sleep do astronauts usually get each night?
eight hours
Each crew cabin is just big enough for one person. Generally, astronauts are scheduled for eight hours of sleep at the end of each mission day. Like on Earth, though, they may wake up in the middle of their sleep period to use the toilet, or stay up late and look out the window.
Why can’t you see the sun in space?
In space or on the Moon there is no atmosphere to scatter light. The light from the sun travels a straight line without scattering and all the colors stay together. Looking toward the sun we thus see a brilliant white light while looking away we would see only the darkness of empty space.
Can someone hear you scream in space?
That infamous tag line from 1979’s Alien, “In space no one can hear you scream.” No one can hear you because the audible sound waves from that scream can’t pass through space.


Where does space end?
It extends about 20 miles (32 kilometers) above the Earth. Floating around the atmosphere is a mixture of molecules – tiny bits of air so small you take in billions of them every time you breathe.
How much is a moon rock worth?
NASA assessed the value of the rocks at around $50,800 per gram in 1973 dollars, based on the total cost of retrieving the samples. That works to just a hair over $300,000 a gram in today’s currency.
How much is an astronaut suit worth?
What’s the cost of a good suit these days? At NASA, apparently, it’s about $500 million. That’s according to a new audit of the space agency’s 14-year quest to design and build a new generation of spacesuits.



