how does climate influence weathering?
Hi, welcome to solsarin site, today we want to talk about“how does climate influence weathering?”,
thank you for choosing us.
how does climate influence weathering?
Weathering occurs one of three ways: through physical processes such as freezing and thawing, because of live organisms whose roots break rocks or through chemical processes that occur when carbon dioxide in the soil and air and mixes with water and specific minerals in rocks to form a weak acid that reduces rocks into silt, soil and sediment.
Chemical weathering typically increases as temperatures rise and rain falls, which means rocks in hot and wet climates experience faster rates of chemical weathering than do rocks in cold, dry climates.
Biological weathering occurs when living organisms break up rocks. Tree roots, for example, can fracture rocks in the same way they buckle pavement. Warm, humid climates are most favorable to life. Contrast the rich diversity of life in a rainforest, for example, with the scarcity of life in the dry Sahara or the frigid Antarctic. Consequently, rates of biological weathering are most rapid in warm humid climates like those in tropical regions.


how does climate influence weathering?
Weathering is an important biogeochemical process that is both influenced by and influences climate over the course of Earth history. Weathering processes control the flux of solutes and many nutrients to the oceans and the marine and terrestrial biospheres, and the transfer of carbon from the ocean-atmosphere system to sedimentary rocks.
it rates are dependent on climate, among several factors, and vary widely across the Earth’s surface. In turn, weathering processes can alter the atmospheric concentrations of the important greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide. Weathering processes thus have the potential to act as a climate feedback, an idea that has been important in our understanding of the long-term evolution and stabilization of the Earth’s climate for over 150 years.
“Weathering” refers to the chemical alteration of rock and sedimentary deposits under sub-aerial conditions at the Earth’s surface. While some analogous processes occur in the oceanic crust during low temperature…
Weathering
The weathering of rocks occurs through both physical and chemical processes. Physical weathering is the breakdown of rock into smaller pieces without altering the chemical composition of the rock. For example, physical weathering can happen as the temperature changes, causing rocks to expand as they warm and contract as they cool, resulting in cracks that lead to the breakdown of the rock. Additional causes of physical weathering include the freezing and expansion of water in rock cracks, and tree roots that dig into rocks that can split them apart.
Chemical weathering occurs when the breakdown of rock results from chemical change in the rock, or the when the rock is dissolved away. The rate of these chemical reactions is affected by climatic conditions such as precipitation and temperature, with water and warmer temperatures increasing the rate. Plant growth, aside from physically breaking up rocks, can also change the environmental chemistry (for example, increase acidity) contributing to chemical weathering.
Over thousands to many millions of years, the weathering of silicate rocks on land (rocks made of minerals that contain the element silica) is an important part of the carbon cycle. Over long-time scales, significant amounts of carbon dioxide (a greenhouse gas) are removed from the atmosphere when rainwater (H2O) mixes with CO2 to form carbonic acid (H2CO3).


Weathering
This weak acid reacts with rocks, breaking them down, resulting in the transport of carbon via rivers to the ocean, where it ultimately becomes buried in ocean sediments to become limestone rock. In contrast, the weathering of limestone by carbonic acid releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, but there is no net removal of CO2 from the atmosphere as happens with the weathering of silicate rocks.
The burning of fossil fuels returns carbon to the atmosphere (as CO2) at a rate that is hundreds to thousands of times faster than it took to bury. This rate is so high that even though the warming produced by the increased CO2 increases the rate of weathering of silicate rocks, which draws down atmospheric CO2, is not nearly enough to offset the increase in carbon dioxide added to the atmosphere by human activities.
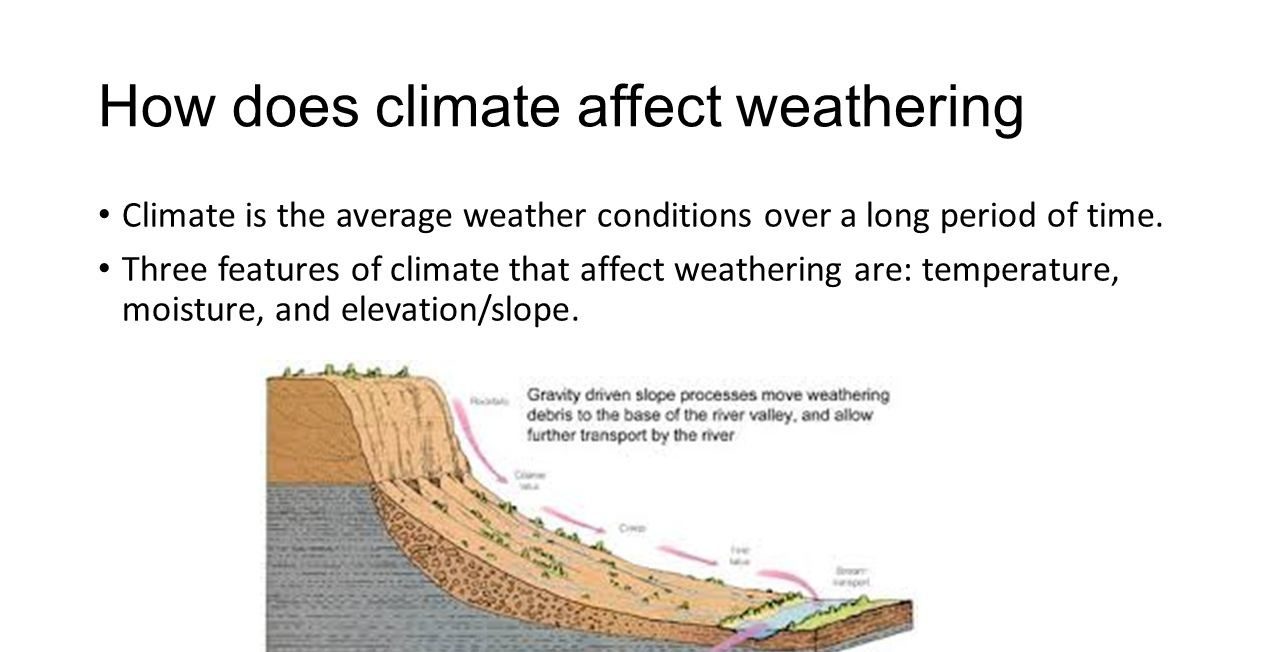
The weathering of rocks affects how much and what kind of rock is eroded by water, ice, wind, and gravity, which can affect soil formation, and where various sedimentary rocks form over thousands to millions of years. Additionally, regional soil quality, nutrient levels (especially nitrogen and phosphorus levels), are dependent on the type of rock that is weathered, which in turn affects local biodiversity. Ultimately, over millions of years, geologic changes in the uplift of land, driven by plate tectonics, alter the geographic location and amount of rock exposed for weathering.
Climate
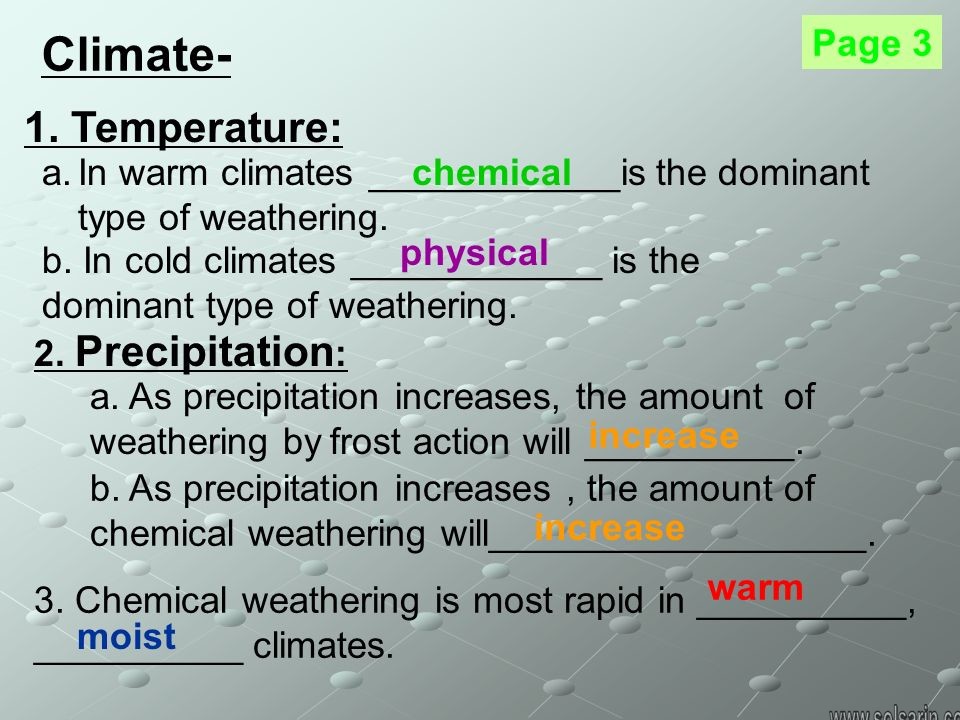
A region’s climate strongly influences weathering. Climate is determined by the temperature of a region plus the amount of precipitation it receives. Climate is weather averaged over a long period of time. Chemical weathering increases as:
- Temperature increases: Chemical reactions proceed more rapidly at higher temperatures. For each 10oC increase in average temperature, the rate of chemical reactions doubles.
- Precipitation increases: More water allows more chemical reactions. Since water participates in both mechanical and chemical weathering, more water strongly increases weathering.
So how do different climates influence weathering?
-
-
- A warm, wet climate will produce the highest rate of weathering.
- The warmer a climate is, the more types of vegetation it will have and the greater the rate of biological weathering . This happens because plants and bacteria grow and multiply faster in warmer temperatures.
- Some resources are concentrated by weathering processes.
- In tropical climates, intense chemical weathering carries away all soluble minerals, leaving behind just the least soluble components. The aluminum oxide, bauxite, forms this way and is our main source of aluminum ore.
- A cold, dry climate will produce the lowest rate of weathering.
-

Rock and Mineral Type
Some types of minerals weather easily. Some minerals in a rock might completely dissolve in water. A beautiful example of this effect is the “Stone Forest” in China, shown in the video below:
Rocks also weather differently. Igneous rocks are usually solid and are more resistant to weathering. Intrusive igneous rocks weather slowly because it is hard for water to penetrate them. Sedimentary rocks usually weather more easily. For example, limestone dissolves in weak acids like rainwater.
Different types of sedimentary rocks can weather differently. This will lead to differential erosion. In the photo of the Grand Canyon, some layers create cliffs. These are hard rocks that do not weather easily. Rock layers that resist weathering and erosion form the top of the canyon and the top of features. Softer layers form slopes. These are rocks that weather more easily .
What are three ways that climate affects the rate of weathering?
Some features of climate that affect weathering are temperature, mois- ture, elevation, and slope. Temperature is a major factor in both chemical and mechanical weathering. Cycles of freezing and thawing increase the chance that ice wedging will take place.
What types of climate does weathering happen faster?
Weathering occurs fastest in hot, wet climates.
It occurs very slowly in hot and dry climates. Without temperature changes, ice wedging cannot occur. In very cold, dry areas, there is little weathering.
What are two climate factors that affect the rate of weathering?
Rainfall and temperature can affect the rate in which rocks weather. High temperatures and greater rainfall increase the rate of chemical weathering.
What climate factor that contributes to the acidity of atmospheric moisture accelerates weathering rates?
Moisture speeds up chemical weathering. Weathering occurs fastest in hot, wet climates.moreover, It occurs very slowly in hot and dry climates. Without temperature changes, ice wedging cannot occur.
Which climate conditions normally produce the greatest amount of chemical weathering?
1) Chemical Weathering: Most intense in warm, humid climate. Very little in cold, dry climates.moreover, Many minerals are not stable at earth surface conditions. They react with surface waters, atmospheric gases, and dissolved compounds (acids) and form a new set of minerals.


Warm and humid weather
Warm and humid weather plays a major role in accelerating the weathering process of rocks, breaking them down faster, a new study has found.
Weathering is the natural process of breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces and minerals. The slow phenomenon is an ongoing process over millions of years, leading to formation of soil and sand. The process also releases carbon.
The study by researchers at the University of North Carolina, US, published in the Geophysical Research Letters journal in December, was undertaken by “listening” to acoustic emissions from naturally cracking rock over many years.
The research team attached numerous sensors to multiple rocks to listen for signs of cracking internally.moreover, These sensors recorded seismic activity or vibrations, and collected weather data including temperatures and humidity.
Understanding the impact of a warming world on weathering of rocks is important as rocks play a crucial role in trapping carbon for millions of years. moreover, This is a part of the carbon cycle on earth, where carbon takes about 100 to 200 million years to move between rocks, soil, water and atmosphere.