How far is the Sun from Earth?
Hello and welcome to solsarin. The “How far is the Sun from Earth?” is the new topic for today’s discussion. Read the text below, share it to your friends and comment your idea.


Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large amounts of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth’s surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth’s polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth’s surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth’s surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, interacting to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes earth’s liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes Earth’s magnetosphere, deflecting destructive solar winds.
Earth’s atmosphere consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. More solar energy is received by tropical regions than polar regions and is redistributed by atmospheric and ocean circulation. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. A region’s climate is governed by latitude, but also by elevation and proximity to moderating oceans. Severe weather, such as tropical cyclones, thunderstorms, and heatwaves, occurs in most areas and greatly impacts life.
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy mainly as visible light, ultraviolet light, and infrared radiation. It is by far the most important source of energy for life on Earth. Its diameter is about 1.39 million kilometers (864,000 miles), or 109 times that of Earth. Its mass is about 330,000 times that of Earth, and it accounts for about 99.86% of the total mass of the Solar System. Roughly three quarters of the Sun’s mass consists of hydrogen (~73%); the rest is mostly helium (~25%), with much smaller quantities of heavier elements, including oxygen, carbon, neon and iron.
According to its spectral class, the Sun is a G-type main-sequence star (G2V). As such, it is informally, and not completely accurately, referred to as a yellow dwarf (its light is closer to white than yellow). It formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of matter within a region of a large molecular cloud. Most of this matter gathered in the center, whereas the rest flattened into an orbiting disk that became the Solar System. The central mass became so hot and dense that it eventually initiated nuclear fusion in its core. It is thought that almost all stars form by this process.
The Sun’s core fuses about 600 million tons of hydrogen into helium every second, converting 4 million tons of matter into energy every second as a result. This energy, which can take between 10,000 and 170,000 years to escape the core, is the source of the Sun’s light and heat. When hydrogen fusion in its core has diminished to the point at which the Sun is no longer in hydrostatic equilibrium; its core will undergo a marked increase in density and temperature while its outer layers expand, eventually transforming the Sun into a red giant.
It is calculated that the Sun will become sufficiently large to engulf the current orbits of Mercury and Venus, and render Earth uninhabitable – but not for about five billion years. After this, it will shed its outer layers and become a dense type of cooling star known as a white dwarf, and no longer produce energy by fusion, but still glow and give off heat from its previous fusion.
The enormous effect of the Sun on Earth has been recognized since prehistoric times. The Sun was thought of by some cultures as a deity. The synodic rotation of Earth and its orbit around the Sun are the basis of some solar calendars. The predominant calendar in use today is the Gregorian calendar which is based upon the standard 16th Century interpretation that the Sun’s observed movement is primarily due to it actually moving.

How Far is the Sun From Earth?
Everything in the Universe is moving, from a couple of kilometers/miles per second to more than 200 km / 124 mi per second, with space itself theorized to expand faster than even the speed of light, which is 299,792 km / 186,282 mi per second.
Most of the objects in our universe appear to be drifting away from us, while others, such as the Andromeda Galaxy, are closing in on us, but let us take a closer look at the celestial objects in our vicinity, like the Sun.
How far is the Sun from Earth? Well, when it comes to space, we apply different measurements, and in terms of distance, we speak trough astronomical units.
An astronomical unit (AU) is the equivalent of 150 million km / 93 million mi, and the Sun is 1 AU away from Earth. In light-years, the Sun is 0.00001581 light-years away, while in light minutes, the Sun is 8.20 light minutes away, or 500 light-seconds away from Earth.
If we were to speak in meters, then the Sun would be 150.4 billion meters away from Earth. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365.3 days, while farther planets such as Mars, completes an orbit around the Sun in 687 days. For comparison, Mars is 1.5 AU away from the Sun, which would translate to 227.94 million km / 141.70 million mi.
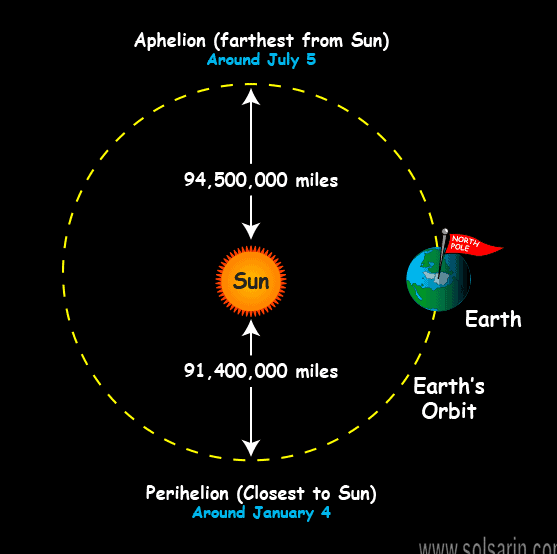
Since the Earth moves around the Sun, the distance differs, with Earth’s closest point from the Sun – perihelion – reaching 147.5 million km / 91.3 million mi.
When it comes to Earth’s farthest point from the Sun – aphelion – it is around 152 million km / 94.5 million mi, a little over 1 AU away from the Sun.
How Long Would It Take to Get to the Sun From Earth?
It’s tough to predict a spacecraft’s journey towards the Sun. If we were to launch an imaginary spacecraft from Earth that would travel around 153,454 mi / 246,960 km per hour constantly, it would reach the Sun in 606 hours, or 25 days.
However, what clouds our estimation is the fact that it is impossible to launch a spacecraft that would constantly maintain its top speed from the start. When the spacecraft is launched, it will take several minutes or hours to reach its top speed.
One of the fastest planned spacecraft on Earth is the Parker Solar Probe. This probe might reach a maximum speed of 430,000 mi / 692,017 km per hour. This means that the spaceship may get to the Sun in around 216 hours or nine days.
However, there is an additional problem. Nothing in space stays still, so we can’t launch anything directly at the Sun, because the moment the object would arrive at the Sun’s position, it would no longer be there.
Therefore, we first have to predict where the Sun would be, based upon its moving speed, and then calculate our object’s moving rate, and most of all, we even have to consider our Earth’s movement.
Elliptical Orbit Of The Earth
The au is not the exact distance, but the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, meaning the distance may sometimes vary. The Earth, like most of the planets, revolves around the Sun, with a complete revolution taking 365.25 days. However, the Earth does not move round the Sun in a perfect circle. The orbit of the Earth is elliptical or oval in shape, or like a stretched circle, with the Sun roughly at the center of the orbit.
At different times of the year, the Earth either moves closer or farther away from the Sun. At perihelion, the Earth’s closest distance to the Sun, the distance between the Sun and the Earth is 91.4 million miles. The Earth is closest to the Sun in early January. At aphelion, when the Earth is furthest to the Sun, the distance between them is about 94.5 million miles. The Earth is furthest from the Sun in early July.


Historical Estimations Of The Distance
Greek astronomer Aristarchus became the first person to obtain the distance between the Sun and the Earth in 250 BC. In 1653, Christiaan Huygens estimated the distance to the Sun by using the phase of Venus to get the Venus-Sun-Earth triangle. For instance, when Venus is half lit by the Sun, the Earth, Sun, and Venus form a right-angled triangle.
He was then able to calculate the distance between Venus and Earth, and with the distance obtained and the angle created by the triangle, Huygens managed to measure the distance between the Earth and the Sun. However, Huygen relied partly on guesswork and was not scientifically backed. In 1672, Giovanni Cassini used a parallax method to obtain the distance between Mars and Earth. He then used the distance to Mars to obtain the distance to the Sun. Cassini’s method has been considered more scientific than Huygen’s method.
Modern Equation
With the advanced technology and sophisticated spacecraft and radar, there are now direct methods of measuring the distance between the Sun and the Earth. By applying the old methods, the value of au changes according to the location of an observer in the solar system. Moreover, the measurement depended on the mass of the Sun, and since the Sun’s mass changes as it emits energy, the value of au also changes. In August 2012, the International Astronomical Union voted to change the definition of au to the plain old number, 92,955,807 miles, which is based on the light’s speed and a fixed distance without taking into account the Sun’s mass.
How far is the moon from Earth?
What’s a light year away? A light year is the distance traveled by a beam of light in a single Earth year, equivalent to about 6 trillion miles. At the scale of the universe, measuring distances in miles or kilometers is onerous giving the extremely large numbers being discussing.
How far away is the Moon from Earth in light years? The Moon is about 1.25 Light Seconds away from the earth as the sun reflected from the Moon takes about 1.25 seconds to reach the Earth. OR in light years 3.96 x 10â € 8 Light Years.




