imaginary line through the earth
Hi everyone, This article on Solsarin is going to give you some information about the “imaginary line through the earth”.

Imaginary line
In general, an imaginary line is usually any sort of geometric line that has only an abstract definition and does not physically exist. In fact, they are used to properly identify places on a map.
Some outside geography does exist, such as the Mendoza Line, which in baseball divides below-average hitters and extremely poor hitters. A centerline is a nautical term for a line down the center of a vessel lengthwise.
Geography
As a geographical concept, an imaginary line may serve as an arbitrary division, such as
- Antarctic Circle,
- Arctic Circle,
- Border,
- International Date Line,
- Latitude, including the Equator,
- Longitude, the prime meridian, the Tropic of Capricorn, and the Tropic of Cancer. Any axis about which an object spins is an imaginary line.
- Mason–Dixon Line, which informally marks pieces of the borders of four U.S. states: Delaware, Maryland, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia, once part of Virginia. Symbolically, the line separates the American North from the American South,
- Missouri Compromise Line,
- Time zones.
Glossary
Axis of the Earth
Day Length
Equinox
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)
or Universal Time (UT)
Hemisphere
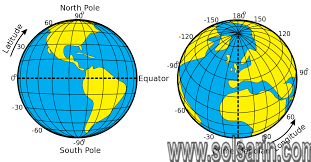
Latitude
Longitude
Imaginary vertical mapping lines on Earth are known as “meridians” of longitude. The number of degrees of longitude shows how far east or west of the Prime Meridian a specific location is.
Meridian
Photoperiod
Prime Meridian:
Revolution of the Earth
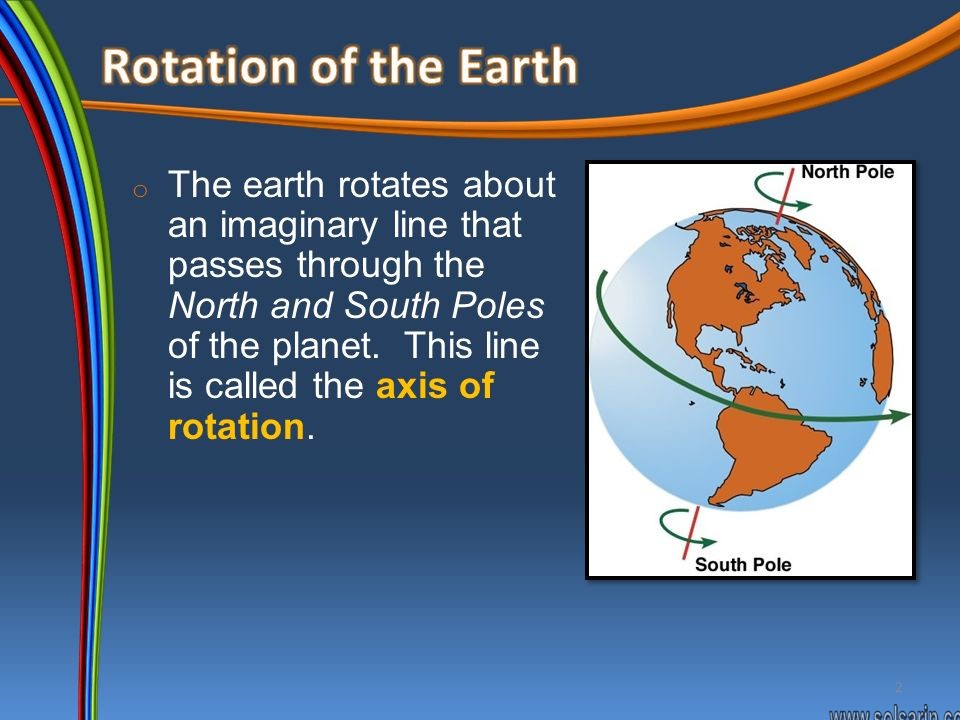
Rotation of the Earth
Solstice
Twenty-Four Hour Clock
an imaginary line through the earth crossword
an imaginary line around which the earth rotates
The Earth is the 3rd planet from the Sun. It supports life because it has water and oxygen. It has a protective atmosphere that blocks out most of the Sun’s damaging rays and protects it from small objects floating in space. It is made mostly of rock. The Moon revolves around Earth (it is a satellite of Earth). It is 240,000 miles away and is ¼ the size of Earth. There is NO atmosphere. It has no air, wind, or liquid water. It reflects the light of the Sun. The Sun is made of hot, glowing gases. It is about 93 million miles away.
EARTH’S ROTATION
Rotation = A single complete turn The Earth rotates on an imaginary line called an axis, which runs through Earth from the North Pole to the South Pole. The rotation of the Earth causes day and night. One complete rotation of the Earth takes 24 hours or 1 day As it rotates, one side of Earth faces the sun. This side has daytime. The side of Earth facing away from the sun has nighttime.
EARTH’S REVOLUTION AROUND THE SUN
Gravity pulls Earth toward the Sun, holding it in orbit. Orbit is the path that an object takes around another object.
Earth revolves or travels around the Sun. It takes Earth about 365 days or 1 year to complete one revolution around the
Sun. Earth rotates on a tilted axis. Earth’s axis is always tilted in the same direction. The Earth has seasons because
it revolves around the Sun on a tilted axis. The Earth is divided into halves called hemispheres The Northern Hemisphere extends from the equator to the North Pole. The Southern Hemisphere extends from the equator to the South Pole.
The part of the Earth that tilts toward the Sun will get more direct sunlight and will experience summer.
The part of the Earth that tilts away from the Sun will get less direct sunlight and will experience winter.
Earth’s Revolution
Earth’s Motions
Imagine a line passing through the center of Earth that goes through both the North Pole and the South Pole. Earth spins around its axis, just as a top spins around its spindle. At the same time that the Earth spins on its axis, it also orbits or revolves around the Sun. A pendulum set in motion will not change its motion, and so the direction of its swinging should not change. However, Foucault observed that his pendulum did seem to change direction.
Since he knew that the pendulum could not change its motion, he concluded that the Earth, underneath the pendulum was moving. An observer in space will see that Earth requires 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds to make one complete rotation on its axis. But because Earth moves around the Sun at the same time that it is rotating, the planet must turn just a little bit more to reach the same place relative to the Sun. Hence the length of a day on Earth is actually 24 hours. At the equator, the Earth rotates at a speed of about 1,700 km per hour, but at the poles, the movement speed is nearly nothing.
Thank you for being with us.