is venezuela part of the caribbean
Hello, welcome to solsarin. This post is about “is venezuela part of the caribbean“.
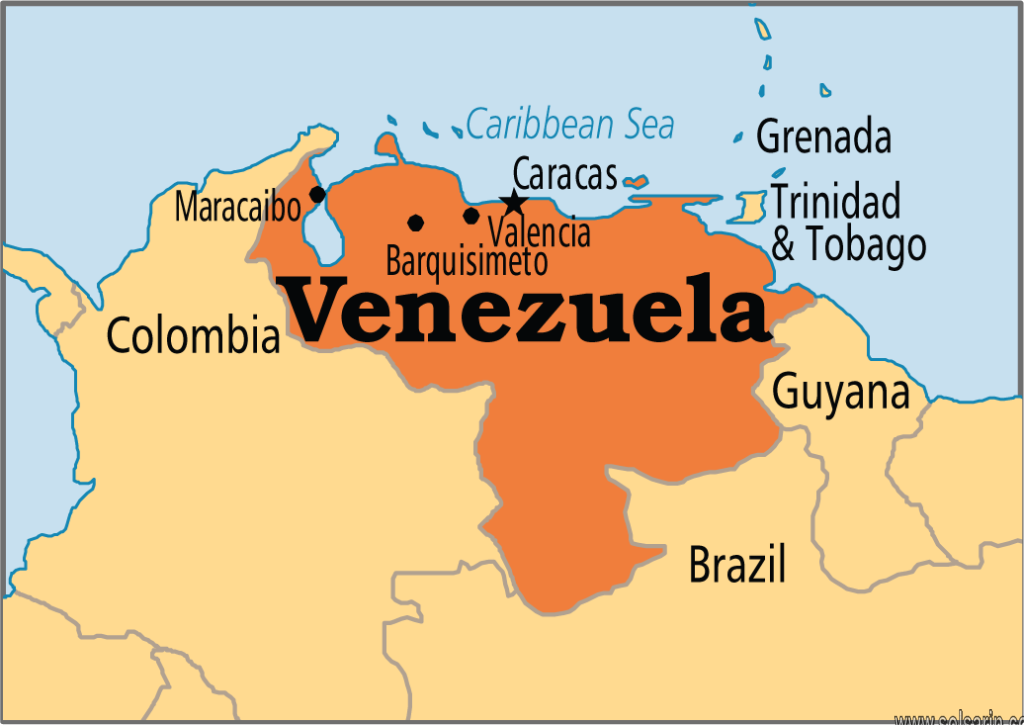
Geography of Venezuela

Caribbean
The Caribbean (/ˌkærɪˈbiːən, kəˈrɪbiən/, locally /ˈkærɪbiæn/; Spanish: Caribe; French: Caraïbes; Haitian Creole: Karayib; also Antillean Creole: Kawayib; Dutch: Caraïben; Papiamento: Karibe) is a region of the Americas that comprises the Caribbean Sea, its surrounding coasts, and its islands (some of which lie within the Caribbean Sea and some of which lie on the edge of the Caribbean Sea where it borders the North Atlantic Ocean).
The region lies southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and of the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America. The region, situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, has more than 700 islands, islets, reefs and cays (see the list of Caribbean islands). Three island arcs delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea.
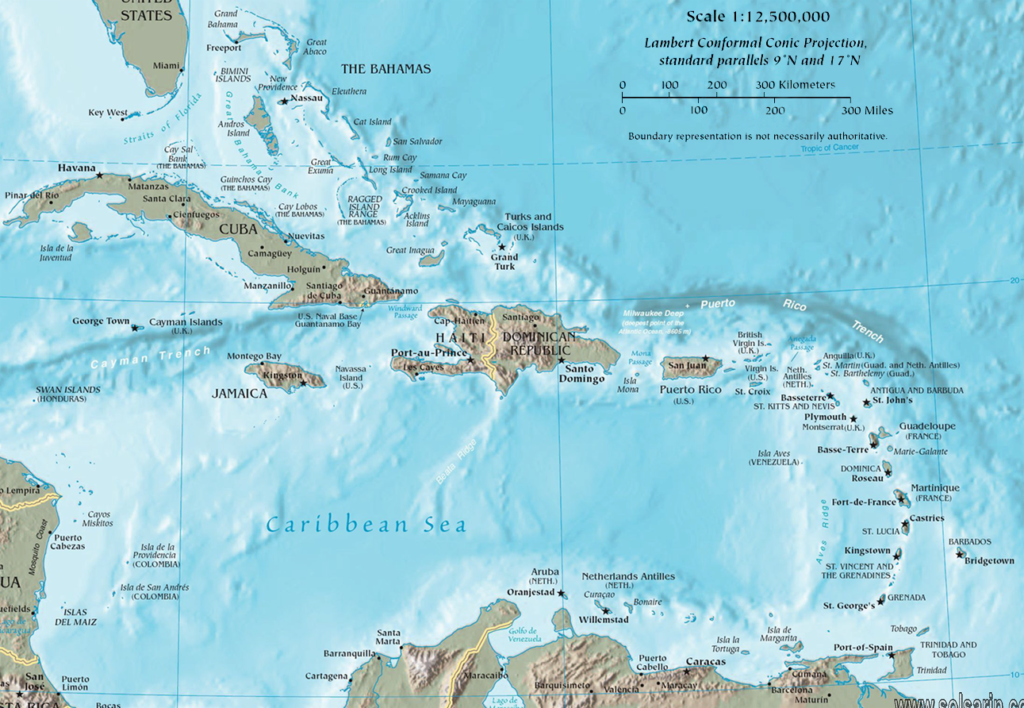
The Greater Antilles to the north, and the Lesser Antilles and Leeward Antilles to the south and east. Together with the nearby Lucayan Archipelago, these island arcs make up the West Indies. The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands are sometimes considered to be a part of the Caribbean, even though they are neither within the Caribbean Sea nor on its border.
Bahamas
However, The Bahamas is a full member state of the Caribbean Community and the Turks and Caicos Islands are an associate member. Belize, Guyana, and Suriname are also considered part of the Caribbean despite being mainland countries and they are full member states of the Caribbean Community and the Association of Caribbean States. Several regions of mainland South and Central America are also often seen as part of the Caribbean because of their political and cultural ties with the region.
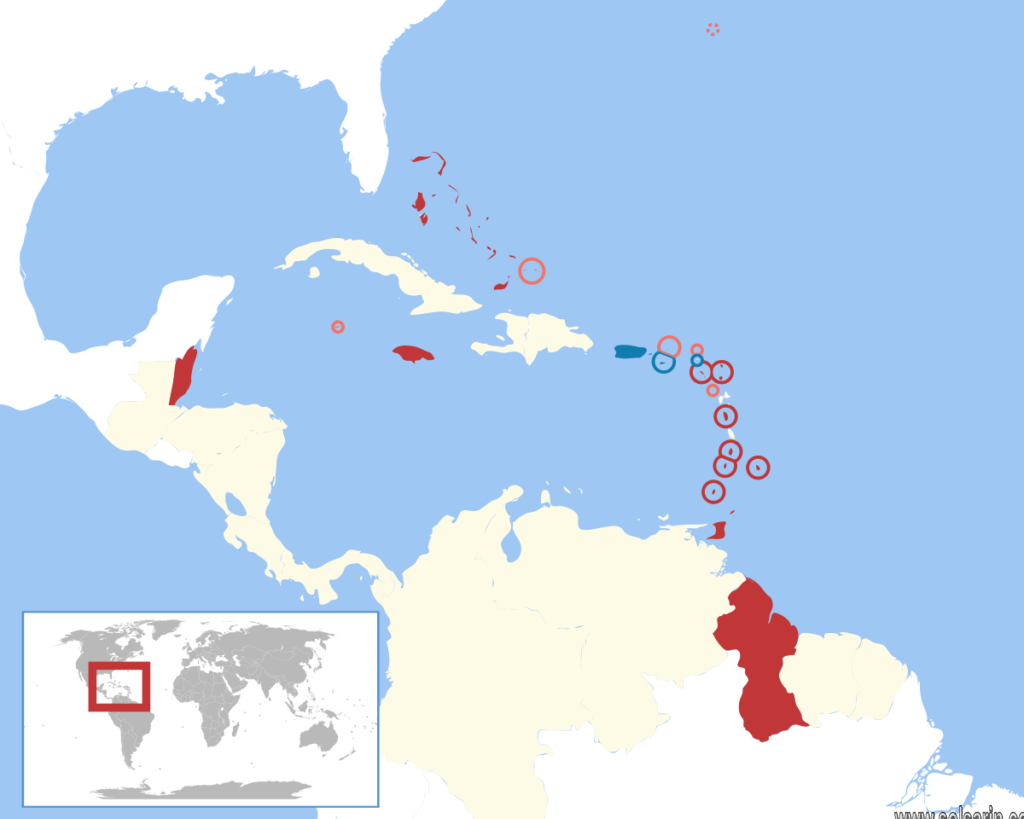
These include Belize, the Caribbean region of Colombia, the Venezuelan Caribbean, Quintana Roo in Mexico (consisting of Cozumel and the Caribbean coast of the Yucatán Peninsula), and The Guianas (Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, Guayana Region in Venezuela, and Amapá in Brazil).
The Caribbean, also often referred to as the Antillen or the West Indies, is a region that denotes the existence of numerous islands and countries over and around the Caribbean Sea. More specifically, it encompasses the terrain that is situated above the Caribbean Plate. A conglomeration of 7,000 islands, islets, reefs and cayes, the Caribbean islands are scattered around the sea, with Mexico on the north to Venezuela of South America.

Caribbean archipelago
Anguilla, Barbados, British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, Cayman Islands, Cuba, Guadeloupe, Haiti, Dominican Republic, Jamaica and Puerto Rico are some of the prominent islands of the Caribbean archipelago. Apart from these islands, there are many countries that are although situated on the mainland of Central America and South America but are considered as part of the Caribbean region.
Mexico, Panama, Venezuela, Costa Rica, French Guiana and Colombia are some such countries. Belize and Guyana are also members of CARICOM. The Caribbean is a paradise of blue water and white beaches that has an astounding treasure trove of physical beauty, fertile soil and mineral wealth. The region boasts of a strong contrast in climate, topography and landscape. The regional geography of real Caribbean is complex and interesting.
It is a result of interaction between sets of physical and environmental patterns that evolved through time. The Caribbean illustrates the construction of its terrain by plate tectonics theory, the evolution of plants, animals and island environments. A generous tropical climate, the accidents of geology and the action of ocean on land have bequeathed today’s Caribbean terrain.
Tropical forests
The varied landscape of this region ranges from volcanic mountains, lakes and limestone cliffs to lush green hills, mangrove swamps and forests. In fact, 40 per cent of the Caribbean terrain is covered with tropical forests. There are outstanding rain forest retreats on the islands of Trinidad, Dominica and Puerto Rico. On the other islands, spectacular national parks and nature reserves have been established to ensure the secured preservation of the fauna and flora, unique to the Caribbean.
The Caribbean is also home to the highest waterfall in the world, the Angel Falls that comes gushing down from more than 3,200ft. The Kaieteur Falls is another such natural wonder of the region. There are several mountainous peaks too including the remote Mount Roraima. The Caribbean also remains vulnerable to natural disasters like ocean storms and tornadoes but not in severe levels.
Maracaibo
A physiographically diverse country, Venezuela incorporates the northern Andean mountain chains and interior highlands, the main portions of the Orinoco River basin with its expansive Llanos (plains), Lake Maracaibo, which is the largest lake in South America, and the spectacular Angel Falls, the world’s highest waterfall. The republic’s development pattern has been unique among Latin American countries in terms of the speed, sequence, and timing of economic and demographic growth.
In the 20th century Venezuela was transformed from a relatively poor agrarian society to a rapidly urbanizing one. A condition made possible by exploiting huge petroleum reserves. These changes, however, were accompanied by imbalances among the country’s regions and socioeconomic groups. And Venezuela’s cities swelled because of a massive and largely uncontrolled migration from rural areas. As well as mass immigration, much of it illegal, from Colombia and other neighbours.
in late 1999
Venezuela, like many other Latin American countries, has a high percentage of urban poverty, a massive foreign debt, and widespread governmental patronage and corruption. Such as the floods that devastated sections of Caracas, La Guaira, and other coastal areas in late 1999.
On the other hand, from 1958 to the early 21st century the republic was more democratic and politically stable than most other Latin American nations. And its economy benefited from a thriving petroleum industry that capitalized on the world’s largest known oil reserves. Venezuela’s position in the world became more precarious during the second decade of the 21st century. As a result of the controversial rule of revolutionary leader Hugo Chávez, a significant decline in the fortunes of its petroleum industry. And the increasing authoritarianism of Chávez’s successor, Nicholás Maduro.


Land
The Venezuelan landscape includes towering mountains, tropical jungles, broad river plains, and arid coastal plains, all of which provide a diversity of natural habitats and a range of challenges to social integration and economic development.
Caribbean Islands off the coast of Venezuela
Located on the islands of Aruba, Bonaire, and Curaçao (sometimes called the A-B-C’s) in the southern Caribbean. This dry desert scrub ecoregion receives little rainfall. Tourism is a major threat to this habitat as development for. Also, feral goats and sheep destroy much of the natural vegetation through grazing.
Biodiversity Features
There are very few endemic plant species on the islands. Only 1 on Bonaire, 5 on Curaçao, and 2 on Aruba. Nevertheless, the floral community has a distinct character. The xerophytic community of the ABC’s may not have the diversity of a tropical rainforest. But it does boast a unique fauna, with its own radiation’s. The most important components of this community are the cacti. They dominate the landscape and provide critical food resources for nectarivores and frugivores.
Bats in particular rely upon the cacti for food resources. And the cacti in turn rely upon the bats for pollination services and for some seed dispersal. There are 7 species of bats on Curaçao. The most abundant being Glossophaga longirostris elongata, with a population of almost 2000 individuals.

1996
The other six species include L. curasoe, a subspecies of Leaf-chinned bats (Mormoops megalophylla intermedia), a species of Funnel-eared bats (Natalis tumidirostris), of Little Brown bats (Myotis nesopolus), of Leaf-lipped bats (Pteronotus davyi), Bulldog bats (Noctilio leporinus) are all rare. And Petit (1996) has argues that they should all be classified as endangered on Curaçao. The loss of cactus-scrub is an important factor in the decline of these bat species.
Lizards are also an abundant and diverse component of the cactus scrub community. There are endemic lizards on all three islands, as well as species with more widespread distributions. Aruba also has two snakes. The cascabel (Crotalus thurissus unicolor), an endangered subspecies of rattlesnake, which does not use its rattle; and the Aruba cat-eyed snake (Leptodira bakeri).
200 species of birds
There are approximately 200 resident bird species on the three islands, many of which are rare. Species of particular concern include the endangered Bonaire Lora (Amazonia barbadensis). And Aruban burrowing owl (Athene cunicularia arubensis), the Aruban parakeet (Aratinga pertinax arubensis), Bonaire Green parrot, and flamingos. The islands are also a favored stop-over and wintering ground for North American migrants.
Thank you for staying with this post “is venezuela part of the caribbean” until the end.




