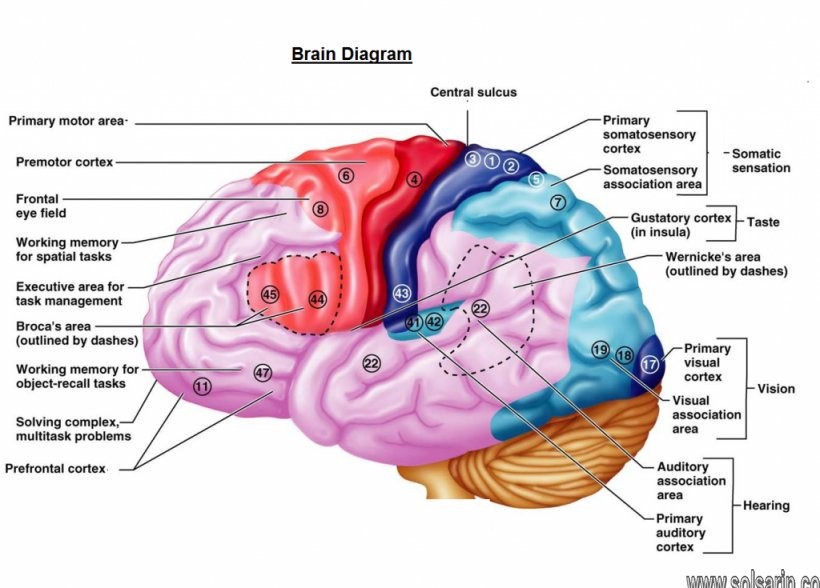
primary somatosensory cortex
Hello dear friends, thank you for choosing us. In this post on the solsarin site, we will talk about ”primary somatosensory cortex”.
Stay with us.
Thank you for your choice.
The primary somatosensory cortex is responsible for processing somatic sensations. These sensations arise from receptors positioned throughout the body that are responsible for detecting touch, proprioception (i.e. the position of the body in space), nociception (i.e. pain), and temperature.
What is the function of the primary somatosensory cortex?
The primary somatosensory cortex (S1) plays a critical role in processing afferent somatosensory input and contributes to the integration of sensory and motor signals necessary for skilled movement.
What controls the primary somatosensory cortex?
The primary somatosensory cortex receives projections from nuclei of the thalamus of the brain. These nuclei receive fibers from the contralateral half of the body, meaning the opposite side of the body from which the area is located in the brain.

What is the main job of the cerebellum?
Coordination of voluntary movements. Most movements are composed of a number of different muscle groups acting together in a temporally coordinated fashion. One major function of the cerebellum is to coordinate the timing and force of these different muscle groups to produce fluid limb or body movements.
What are the primary afferents of the somatosensory system?
The primary (1°) somatosensory afferent neuron. The 1° afferent’s cell body is located in the ganglion of a cranial or posterior (spinal) nerve root. The 1° afferent’s peripheral process travels to skin, muscle or joint – where it branches into terminal fibers. … The locations of somatosensory receptors in the body.
Is the somatosensory cortex part of the neocortex?
Somatosensory cortex, like other neocortex, is layered. Like other sensory cortex (i.e., visual and auditory) the thalamic inputs project into layer IV, which in turn project into other layers.
What is the amygdala function?
The amygdala is commonly thought to form the core of a neural system for processing fearful and threatening stimuli (4), including detection of threat and activation of appropriate fear-related behaviors in response to threatening or dangerous stimuli.
What are the three major functions of the somatosensory system?
Somatic information is provided by receptors distributed throughout the body. One of the earliest investigators of the bodily senses, Charles Sherrington, noted that the somatosensory system serves three major functions: proprioception, exteroception, and interoception.
What somatosensory means?
Medical Definition of somatosensory
: of, relating to, or being sensory activity having its origin elsewhere than in the special sense organs (as eyes and ears) and conveying information about the state of the body proper and its immediate environment somatosensory pathways.
What controls the primary somatosensory cortex?
What is the difference between primary motor cortex and primary somatosensory cortex?
The somatosensory cortex coordinates the sensory data that comes up from all over the body. … The motor cortex, as the name implies, coordinates our bodily movements (in strong relation with the cerebellum.

How did Wilder Penfield map the cortex?
Wilder Penfield, a pioneering brain surgeon, mapped the motor cortex using mild electric current. … While operating on epileptic patients, Penfield applied electric currents to the surface of patients’ brains in order to find problem areas.
What are primary sensory neurons?
Primary afferents are sensory neurons (axons or nerve fibers) in the peripheral nervous system that transduce information about mechanical, thermal, and chemical states of the body and transmit it to sites in the central nervous system.
What are the two primary functions of the cerebellum?
It is made of two halves known as the cerebellar hemispheres. The main function of the cerebellum is maintaining balance, posture, and tone of the body. Other functions of the cerebellum include: Fine-tuning and coordination of movements, such as while riding a bike or playing a musical instrument (e.g., guitar).
What is the center of your brain called?
The brainstem (middle of brain) connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. The brainstem includes the midbrain, the pons and the medulla.
Do you want to know about “an empty-kcalorie food is one that contains“? Click on it.
Which body parts have the largest representation in the primary somatosensory area?
Which body parts have the largest representation in the primary somatosensory area? Lips, face and tongue. What type of sensory information is carried in the spinocerebellar tracts and what is its function? These tracts are the major routes for proprioceptive impulses.
What are two somatosensory receptors?
These sensory neurons have receptors that are classified according to the stimulus they respond to – there are mechanoreceptors for touch and proprioception, nociceptors for pain, and thermoreceptors for temperature.
Is a medulla oblongata?
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum.
Which lobe is primarily responsible for Somatosensation and reaching the limbic lobe The frontal lobe The parietal lobe The occipital lobe?
The Four Brain Lobes
The temporal lobe is located at the base of the brain by the ears.

What does the forebrain develop into?
The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions. At the five-vesicle stage, the forebrain separates into the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, and epithalamus) and the telencephalon which develops into the cerebrum.
Have you heard anything about “how much is the coca-cola brand worth?“? Click on it.
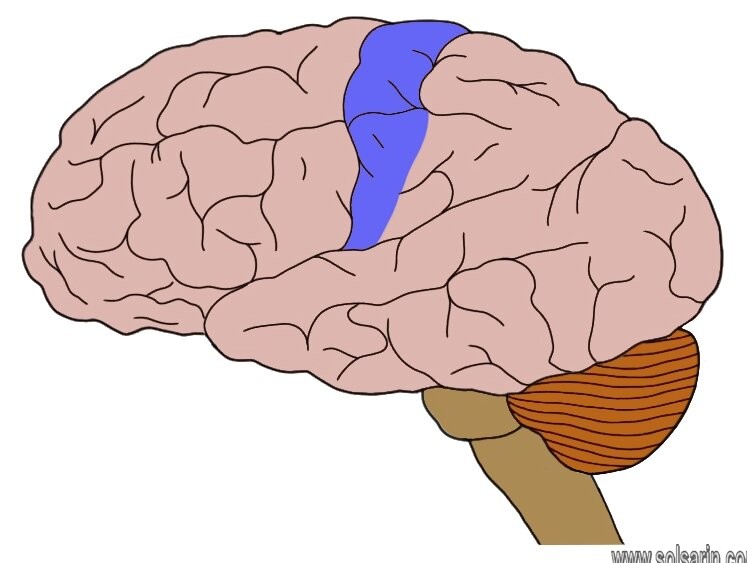
Is the primary somatosensory cortex caudal to the central sulcus?
Where is the primary somatosensory cortex?
Where is the secondary somatosensory cortex?
parietal operculum
The secondary somatosensory cortex is located in the superior bank of the Sylvian fissure, where it makes up a major part of the parietal operculum.

Is the somatosensory cortex in both hemispheres?
In general, the two hemispheres receive information from the opposite side of the body. For example, the right primary somatosensory cortex receives information from the left limbs, and the right visual cortex receives information from the left eye.
Do we have 2 amygdala?
The term amygdala comes from Latin and translates to “almond,” because one of the most prominent nuclei of the amygdala has an almond-like shape. Although we often refer to it in the singular, there are two amygdalae—one in each cerebral hemisphere.
Why is the amygdala called the lizard brain?
It is the part of the brain that is phylogenetically very primitive. Many people call it the “Lizard Brain,” because the limbic system is about all a lizard has for brain function. It is in charge of fight, flight, feeding, fear, freezing up, and fornication.
What is the primary motor cortex?
The primary function of the motor cortex is to generate signals to direct the movement of the body. It is part of the frontal lobe and is anterior to the central sulcus. … The primary motor cortex, situated in Brodmann area 4, sends most electrical impulses coming out of the motor cortex.
How is the primary somatosensory cortex organized Inquizitive?
How is the primary somatosensory cortex organized? … The cortex has more space devoted to the face than to the back. Sensitive areas on the body take up more space in the cortex.
What is another word for somatosensory?
somatic sense
In this page you can discover 8 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for somatosensory system, like: somatic sense, somesthesia, somesthesis, somaesthesia, somaesthesis, somatesthesia, somataesthesis and somatic sensory system.
What is S1 and M1 brain?
The wrinkled outer surface that covers the majority of the brain is the cerebral cortex. In panel (a) labels illustrate some of the areas of localized function including primary motor cortex on the precentral gyrus (M1) and primary somatosensory cortex on the postcentral gyrus (S1).
What is the relationship between the primary motor cortex and somatosensory cortex?
Neurons within the primary motor cortex control voluntary movement by controlling somatic motor neurons in the deep brain and spinal cord, while neurons within the primary sensory cortex receive somatic sensory information from afferent neurons located within the skin and muscle that detect changes in pressure
How did Broca and Wernicke determine the location of key language areas in the brain?
How did Broca and Wernicke determine the location of key language areas in the brain? By looking at the different lesions on the brain, and how it affected their skills to communicate.
Did Dr Penfield get married?
In June 1917, in Hudson, Wisconsin, Penfield married Helen Kermott, a physician’s daughter. They were a devoted couple. They had two daughters and two sons: Ruth Mary, Priscilla, Wilder Graves Jr., and Amos Jefferson.
What is Dr Penfield famous for?
Wilder Graves Penfield OM CC CMG FRS (January 26, 1891 – April 5, 1976) was an American-Canadian neurosurgeon. He expanded brain surgery’s methods and techniques, including mapping the functions of various regions of the brain such as the cortical homunculus.



