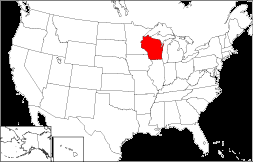
state directly north of illinois
Hello dear readers. In this post on Solsarin we are going to talk about ”state directly north of illinois“ .
Continue reading to find the answer.
Please write your comment, Thanks for your attention.
State directly north of Illinois
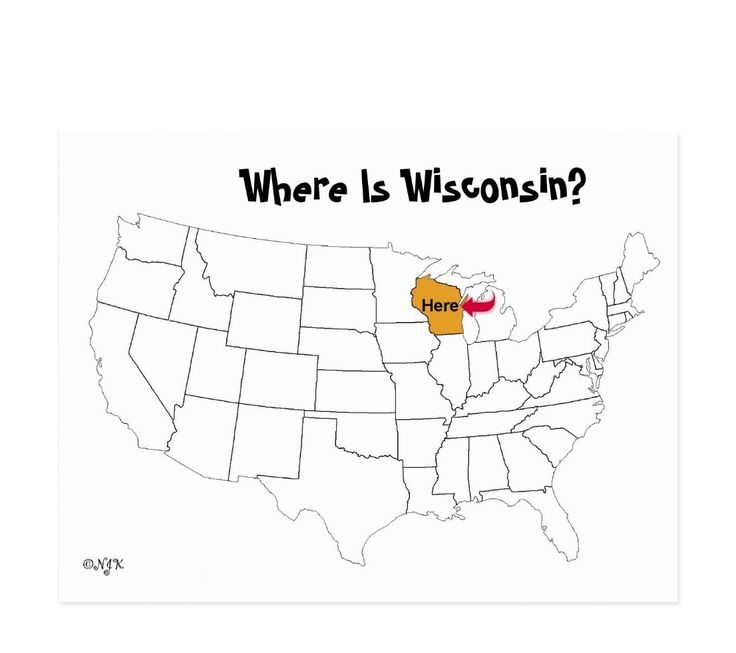

What is Wisconsin most known for?
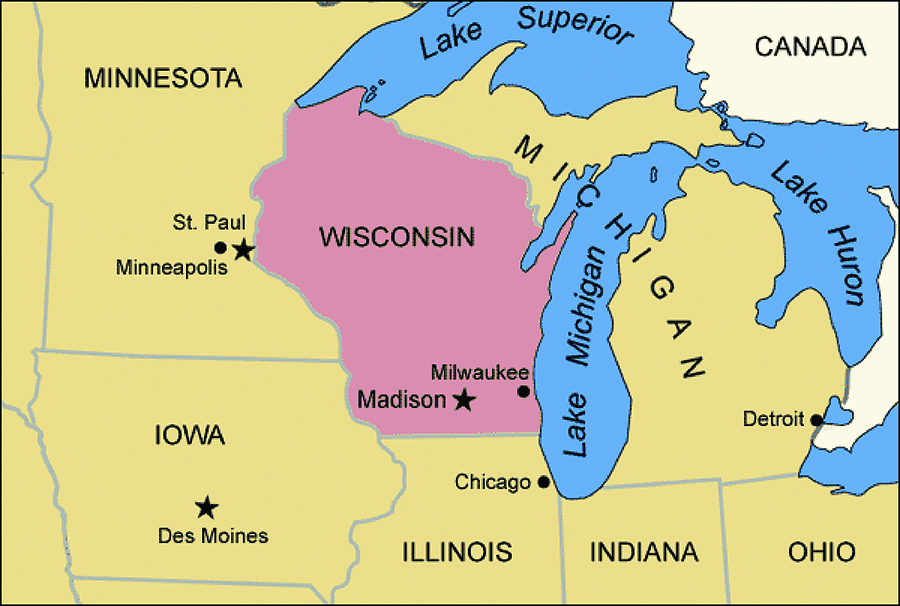
Wisconsin, constituent state of the United States of America. Wisconsin was admitted to the union as the 30th state on May 29, 1848. One of the north-central states, it is bounded by the western portion of Lake Superior and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to the north and by Lake Michigan to the east. The state of Illinois lies to the south, and Minnesota and Iowa lie to the west and southwest, respectively. The name Wisconsin is an Anglicized version of a French rendering of an Algonquin name, Meskousing, said to mean “this stream of red stone,” referring to the Wisconsin River. Madison, in south-central Wisconsin, is the state capital.
More than 12,000 years ago the area that is now Wisconsin was covered by enormous glaciers. During the Wisconsin Glacial Stage, when the ice sheet began to melt, it left behind scenic physical features, including outwash plains, terminal and kettle moraines, drumlins, eskers, and low-lying areas that became lakes.
The economy of Wisconsin is diversified, with three major sectors concentrated in specific regions. Wisconsin’s southeastern industrial belt—extending from the state line along Lake Michigan from Kenosha up to and beyond Milwaukee, the state’s largest city—is the primary factor in making Wisconsin one of the largest manufacturing states in the country. In the southern two-thirds of the state, a combination of favourable climate, soil, and topography makes possible dairy agriculture that allows Wisconsin to be the top producer of cheese in the country and one of the top producers of milk and butter. The sparsely settled northern evergreen-hardwood forest and lake country is a centre for tourism and recreational activity. Area 65,496 square miles (169,635 square km). Population (2020) 5,893,718.
Land
Relief
Wisconsin comprises six physical regions. The Northern Highland is a broad upland underlain by granitic bedrock. It contains the state’s highest point, Timms Hill (1,951 feet [595 metres]), in Price county. The Lake Superior Lowland is a narrow plain to which the surface of the Northern Highland drops abruptly. The upland slopes down gently southward to the Central Plain, or Central Sand Plain, a crescent-shaped region on sandstone stretching across the centre of the state.
The Western Upland lies in the southwest corner of the state and is etched into ridges and valleys by streams that cut into the limestones and sandstones. Glaciers largely bypassed the southwestern and western sections of the state along the Mississippi; this dry upland is known as the Driftless Area. Finally, the Eastern Ridges and Lowlands region is formed by three broad, parallel limestone ridges running north-south and separated by wide and shallow lowlands. The lowest elevation in the state is in this region, along the shoreline of Lake Michigan, about 580 feet (180 metres) above sea level.
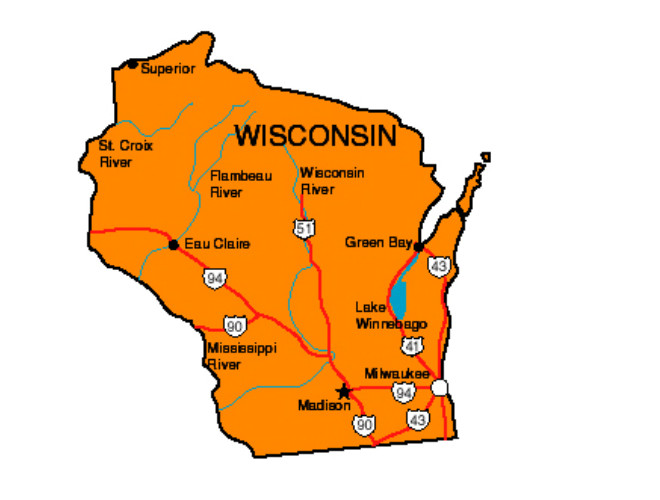

Distinctive geographic formations include the Apostle Islands in Lake Superior; the rocky Door Peninsula between Lake Michigan and Green Bay; the broad gorges of the Mississippi and lower Wisconsin rivers, cut 300 to 500 feet (90 to 150 metres) below the general surface; ancient mountain remnants such as the Baraboo Range, Rib Mountain, and the Gogebic Range; the Kettle Moraine area west of Milwaukee; the narrow sandstone river gorge known as the Wisconsin Dells; and the sandy beaches of Lakes Michigan and Superior, which also have spectacular rocky shorelines.
Drainage
Wisconsin is one of the few states in which essentially all drainage is outflowing. The principal river is the scenic, island-studded Wisconsin River, 430 miles (700 km) long, which originates on the Michigan boundary and flows southward to near Madison, where it skirts the Baraboo Range before turning west to cross the Western Upland and enter the Mississippi near Prairie du Chien. A system of reservoirs regulates its flow. Untamed rivers include the upper St. Croix, the Namekagon, the upper Wolf, the Pine-Popple, the Brule, and the Pike, all of which are in northern Wisconsin. The lower St. Croix was designated a national scenic riverway by the U.S. Department of the Interior.
MORE POSTS:
- 180 celsius to fahrenheit
- brands of gasoline without ethanol
- how many pieces are in backgammon?
- formed the basic moral laws of many nations
- did karl marx create socialism

la vaca vegetariana
Northern Wisconsin, with a section of neighbouring Minnesota, has one of the largest concentrations of lakes in the world. Wisconsin has nearly 15,000 inland lakes of more than 20 acres (8 hectares), for a total of more than 1,500 square miles (4,000 square km), yet only one-fifth of these lakes are accessible to the public because of restrictions by private property owners. The largest is Lake Winnebago (215 square miles [550 square km]) in the Fox River valley.
Included in Wisconsin’s boundary waters and under its jurisdiction are 7,387 square miles (19,132 square km) of Lake Michigan and 2,675 square miles (6,928 square km) of Lake Superior. Wisconsin has about 400 miles (640 km) of shoreline along Lake Michigan and some 150 miles (240 km) along Lake Superior. The Mississippi River flows along the lower half of Wisconsin’s western border for about 230 miles (370 km). There are also thousands of streams throughout the state; streams and lakes may be frozen from December to mid-April, however.
Soils
The best soils for agricultural use are the black prairie soils and gray-brown forest soils of the Eastern Ridges and Lowlands and the Western Upland; these coincide rather well with the areas having the warmer and longer growing seasons. Soils less favourable for agricultural use are found in the predominantly forested regions of the Northern Highland and the Central Plain. But through the use of irrigation, drainage, and fertilization, even some of these soils have been made highly productive for special crops of vegetables, potatoes, and cranberries. On the steep slopes of the Western Upland, contour plowing and strip cropping of corn (maize) and hay reduce soil erosion, and in the Central Plain the sandy soils are protected from wind erosion by shelter belts of trees around fields and farmsteads.