The difference between tuberculosis and gel
Hello. Welcome to solsarin. This post is about “The difference between tuberculosis and gel”.
How can you distinguish Mycobacterium tuberculosis from other Mycobacterium?
Growth of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTC) is inhibited by rho-nitrobenzoic acid (PNB), whereas non-tuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) are resistant.
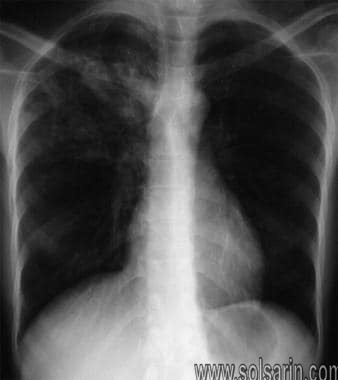

What is the difference between Mycobacterium tuberculosis and tuberculosis?
The bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes tuberculosis (TB), a contagious, airborne infection that destroys body tissue. Pulmonary TB occurs when M. tuberculosis primarily attacks the lungs. However, it can spread from there to other organs.
Why is tuberculosis called Mycobacterium?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tb) is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, M. tuberculosis has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acid.
What are the differences between gel electrophoresis and capillary electrophoresis what are they meant to detect and how is this detection achieved?
Featured Article
But in contrast to conventional gel electrophoresis, which separates molecules as they migrate through a slab gel matrix, capillary electrophoresis separates molecules as they travel along the inside of a small capillary tube that is filled with a conductive, liquid buffer, rather than a gel.
Why capillary electrophoresis is preferred over gel electrophoresis?
Capillary electrophoresis offers practical as well as technical advantages over gel electrophoresis. Capillary electrophoresis offers higher throughput both for electrophoresis (96 samples run in about 1 hour) and reading of results, once familiar with the software.
Which Mycobacterium can cause TB?
In the United States, the majority of tuberculosis (TB) cases in people are caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis). Mycobacterium bovis (M. bovis) is another mycobacterium that can cause TB disease in people.
What disease is similar to tuberculosis?
There are more than 25 different species of mycobacteria that cause nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. One of the most common is Mycobacterium avium, which can cause symptoms similar to tuberculosis, such as cough, fever, fatigue, and weight loss.
TB transmitted by droplet?
tuberculosis is carried in airborne particles, called droplet nuclei, of 1– 5 microns in diameter. Infectious droplet nuclei are generated when persons who have pulmonary or laryngeal TB disease cough, sneeze, shout, or sing. TB is spread from person to person through the air.
What are the 3 types of tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection that usually infects the lungs. It may also affect the kidneys, spine, and brain. Being infected with the TB bacterium is not the same as having active tuberculosis disease. There are 3 stages of TB—exposure, latent, and active disease.
Is Mycobacterium tuberculosis a virus?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but TB bacteria can attack any part of the body such as the kidney, spine, and brain.
TB?
The vaccine was developed over a period of 13 years, from 1908 to 1921, by French bacteriologists Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin, who named the product Bacillus Calmette-Guérin, or BCG. The vaccine is administered shortly after birth only in infants at high risk of tuberculosis.

Do you want to know about “an empty-kcalorie food is one that contains“? Click on it.
What color is Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
The purple rod-shaped organism is a TB bacterium. This name, meaning ‘fungus-bacteria’ refers to shape of the bacillus when it grows in a laboratory: when seen through a microscope it forms heaps of small rods with protective layers around them, and thus looks like a fungus.
there a vaccine for tuberculosis?
Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is a vaccine for tuberculosis (TB) disease. This vaccine is not widely used in the United States, but it is often given to infants and small children in other countries where TB is common. BCG does not always protect people from getting TB.
What does capillary electrophoresis detect?
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is the primary methodology used for separating and detecting short tandem repeat (STR) alleles in forensic DNA laboratories worldwide. This chapter examines the general principles and components of injection, separation, and detection of STR alleles using CE.

What is gel electrophoresis used for?
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory method used to separate mixtures of DNA, RNA, or proteins according to molecular size. In gel electrophoresis, the molecules to be separated are pushed by an electrical field through a gel that contains small pores.
What are 2 main advantages of using capillary electrophoresis?
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) provides a number of advantages for analysts, including high separation efficiency, short analysis times, low waste generation, and a diverse range of applications.
What are the advantages of gel electrophoresis?
This allows one to exploit differences in particle size, charge and shape, and results in the following advantages: (i) Charge and size isomers of proteins can be detected. It is possible to separate components of similar size, but different surface net charge density.
What does each stained band in the gel represent?
When a gel is stained with a DNA-binding dye, the DNA fragments can be seen as bands, each representing a group of same-sized DNA fragments.
What was used before gel electrophoresis?
Initially, agar, a natural carbohydrate, was used as a separation medium for electrophoresis, but this was replaced in the late 1960s by agarose, a polysaccharide which is one of the main components of agar. Gel electrophoresis for nucleic acids became even more sophisticated in the 1970s.
How common is Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
Worldwide, TB is a major health problem with as many as four million new cases and three million deaths each year. The impact of TB is felt most by older and poorer people. Cases usually occur in individuals who were infected years ago, particularly the elderly.
Is Mycobacterium tuberculosis Gram positive or negative?
tuberculosis belongs to the high G+C Gram-positive bacteria that form a monophyletic group with the low G+C Gram-positive bacteria such as Bacillus subtilis.
Although you may feel better
Although you may feel better, if you don’t finish treatment the TB bacteria are still in your body. You could become seriously ill, develop drug-resistant TB or pass TB on to others. Remember – TB can be fatal. Finishing treatment is the only way to cure tuberculosis completely.
Mycobacterium avium contagious?
MAC infection is a serious condition that can cause damage to the lungs. MAC infection is not contagious. Common signs and symptoms of MAC lung disease include fatigue, chronic cough, shortness of breath, night sweats, coughing up blood and weight loss.
What is the cousin to tuberculosis?
Can you tell me more about this disease and if there are other possible cures? – W.B. Dear Reader: Mycobacterium avium complex – MAC – germs are distant cousins of the tuberculosis germ, Mycobacterium tuberculosis. MAC is not tuberculosis, but like T.B. it can infect the lungs. in water, soil, dust, air and dry plants.
What is the fastest way to cure TB?
The usual treatment is:
2 antibiotics (isoniazid and rifampicin) for 6 months.
2 additional antibiotics (pyrazinamide and ethambutol) for the first 2 months of the 6-month treatment period.
Does Mycobacterium tuberculosis have DNA or RNA?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis contains at least nine small RNA families in its genome. The small RNA (sRNA) families were identified through RNomics – the direct analysis of RNA molecules isolated from cultures of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.

Have you heard anything about “how much is the coca-cola brand worth?“? Click on it.
a TB cough wet or dry?
Cough lasting more than three weeks is often a first symptom of active tuberculosis (TB). It can start as a dry irritating cough. It tends to continue for months and get worse. In time the cough produces a lot of phlegm (sputum), which may be bloodstained.
Sputum
Sputum, or phlegm, is often used to test for Mycobacterium tuberculosis, to find out if a patient has TB. This bacterium is completely acid-fast, which means the entire cell holds onto the dye.
What happens if MAC goes untreated?
The fibrocavitary (FC) type usually develops in middle-aged male smokers and accompanies apical fibrocavitary lesions. If left untreated, it can progress within a relatively short time period, leading to extensive lung destruction and respiratory failure
MAC lung disease terminal?
In some people, MAC lung disease can cause respiratory failure and death, but this generally happens over a long period of time. Approximately 1 in 4 people with weakened immune systems who develop the cavitary type of MAC lung disease die within five years of the initial MAC lung disease diagnosis.
What is the difference between MAI and MAC?
A: “Mycobacterium avium intracellulare” (MAI) or “Mycobacterium avium Complex” (MAC) is an atypical NON-TB germ (micro-organism). MAC is related to the tuberculosis germ, but is not contagious and the MAC microbes live in the environment. It comprises more than one type of microorganism (both M. avium and M.
does BCG leave a scar?
Most people develop a sore at the injection site. Once healed, the sore may leave a small scar. This is normal and nothing to worry about. More serious complications, such as abscesses, bone inflammation and widespread TB are rare.
How long does BCG last?
BCG vaccination given to babies and young children provides consistent protection (up to 80%) against severe forms of childhood TB, such as TB meningitis. It can be less effective against TB affecting the lungs in adults. The protection from the BCG vaccine can last up to 15 years.
When was the tuberculosis pandemic?
Although relatively little is known about its frequency before the 19th century, its incidence is thought to have peaked between the end of the 18th century and the end of the 19th century.
What is the size of Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a fairly large nonmotile rod-shaped bacterium distantly related to the Actinomycetes. Many non pathogenic mycobacteria are components of the normal flora of humans, found most often in dry and oily locales. The rods are 2-4 micrometers in length and 0.2-0.5 um in width.
bacteria?(The difference between tuberculosis and gel)
Being hydrophobic, they tend to grow as fungus-like pellicles on liquid culture media: hence the name Mycobacterium – ‘fungus bacterium.



