what groups invaded europe in the 800s
Hello. Welcome to solsarin. This post is about “what groups invaded europe in the 800s“.
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages or Early Medieval Period, sometimes referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century.[note 1] They marked the start of the Middle Ages of European history. The alternative term Late Antiquity, for the early part of the period, emphasizes elements of continuity with the Roman Empire, while Early Middle Ages is used to emphasize developments characteristic of the earlier medieval period.
As such the concept overlaps with Late Antiquity, following the decline of the Western Roman Empire, and precedes the High Middle Ages (c. 11th to 13th centuries).
Dark Ages
The period saw a continuation of trends evident since late classical antiquity, including population decline, especially in urban centres, a decline of trade, a small rise in average temperatures in the North Atlantic region and increased migration. In the 19th century the Early Middle Ages were often labelled the Dark Ages, a characterization based on the relative scarcity of literary and cultural output from this time.[1] However, the Eastern Roman Empire, or Byzantine Empire, continued to survive, though in the 7th century the Rashidun Caliphate and the Umayyad Caliphate conquered swathes of formerly Roman territory.


Many of the listed trends reversed later in the period. In 800 the title of Emperor was revived in Western Europe with Charlemagne, whose Carolingian Empire greatly affected later European social structure and history. Europe experienced a return to systematic agriculture in the form of the feudal system, which adopted such innovations as three-field planting and the heavy plough. Barbarian migration stabilized in much of Europe, although the Viking expansion greatly affected Northern Europe.
What groups invaded Europe in the 800’s?
In the 800’s the Vikings invaded fromthe north, the Magyars and Muslims attacked from the east and south.
What obligations did the peasant have to the lord of the manor?
The obligationsthe peasants had to the lord of manor was raising and producing everything thatthey and their lord needed for daily life. Things like crops, milk, and cheese, fuel,cloth, leather goods, and lumber.
Who invaded Europe in the 9th and 10th centuries?
The Hungarian invasions of Europe (Hungarian: kalandozások, German: Ungarneinfälle) took place in the 9th and 10th centuries, the period of transition in the history of Europe in the Early Middle Ages, when the territory of the former Carolingian Empire was threatened by invasion from multiple hostile forces.
When was Europe invaded?
German Invasion of Western Europe, May 1940.

Where did the barbarians come from in Europe?
The word “barbarian” originated in ancient Greece, and was initially used to describe all non-Greek-speaking peoples, including Persians, Egyptians, Medes and Phoenicians.
Which country did the barbarians come from?
ancient Greece
Are Vikings barbarians?
These new barbarians came from Scandinavia and are known to us as the Vikings. Unlike the earlier barbarians, who were primarily small bands of nomads, the Vikings had already developed a fairly complex agricultural society.
Are Goths and Vikings related?
Vikings came from Norway and Sweden, then spread to Iceland and Denmark (and Britain). Goths came from Sweden, and spread to mainland Europe.
Are Goths Germanic?
The Goths were a nomadic Germanic people who fought against Roman rule in the late 300s and early 400s A.D., helping to bring about the downfall of the Roman Empire, which had controlled much of Europe for centuries. The ascendancy of the Goths is said to have marked the beginning of the medieval period in Europe.
What are goths called now?
Along with the Burgundians, Vandals and others they belong to the East Germanic group. Roman authors of late antiquity did not classify the Goths as Germani. In modern scholarship the Goths are sometimes referred to as being Germani.
Why are goths called Goths?
Goth is a subculture that began in the United Kingdom during the early 1980s. It was developed by fans of gothic rock, an offshoot of the post-punk music genre. The name goth was derived directly from the genre. Styles of dress within the subculture draw on punk, new wave, and New Romantic fashion.
What do Goths do for fun?
Goth humour Dressing up, dancing, hanging out with like-minded friends – Goths enjoy similar leisure activities to young (and not-so-young) people the world over.
Is Goth still a thing 2021?
The fashion Goth has been trending for a few seasons now. Just take a look at the spring 2021 collections of Sacai, Rick Owens, and Yohji Yamamoto and of course, mainstays like Noir Kei Ninomiya. But online, too, the Goth is making a comeback with spiked collars, mismatched leg warmers, chains, platforms, and plaid.
What were some of the themes of medieval literature?
Some themes of medievalliterature were Epic Poetry, Love poems and songs.
What were some of the matters covered by canon law?
How did Otto the great make the crown stronger than the German nobles?
Why did lay investiture cause a struggle between kings and popes?
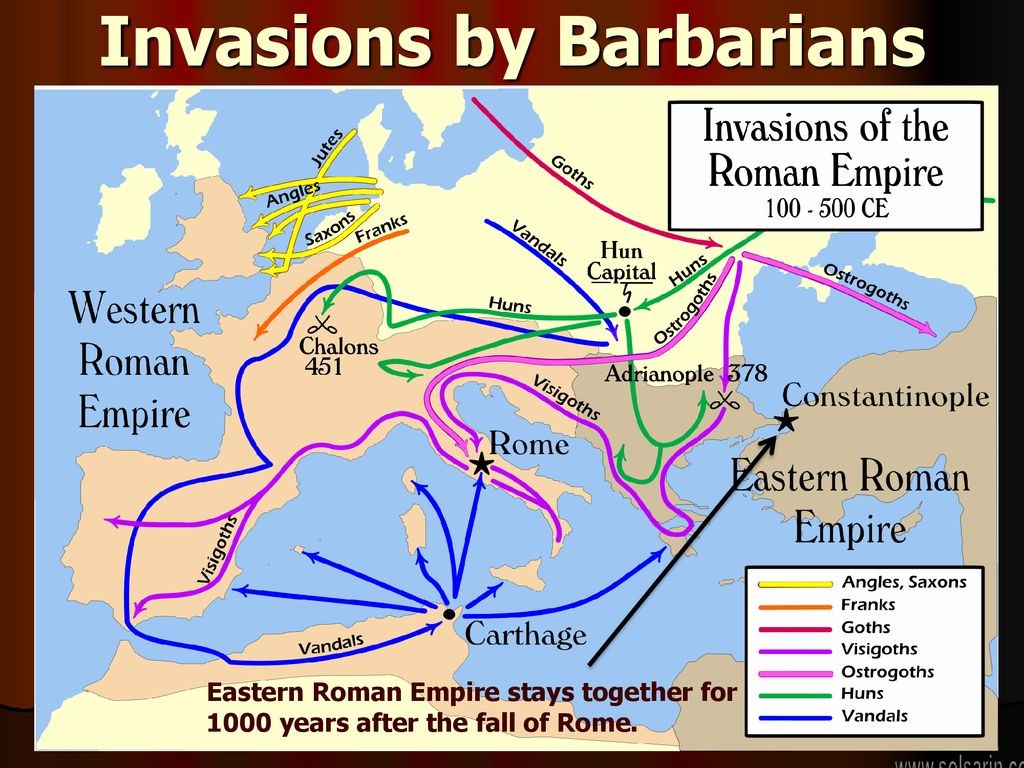
Barbarian migrations and invasions
The Germans and Huns
The wanderings of the Germanic peoples, which lasted until the early Middle Ages and destroyed the Western Roman Empire, were, together with the migrations of the Slavs, formative elements of the distribution of peoples in modern Europe. The Germanic peoples originated about 1800 BCE from the superimposition, on a population of megalithic culture on the eastern North Sea coast, of Battle-Ax people from the Corded Ware Culture of middle Germany.
During the Bronze Age the Germanic peoples spread over southern Scandinavia and penetrated more deeply into Germany between the Weser and Vistula rivers. Contact with the Mediterranean through the amber trade encouraged the development from a purely peasant culture, but during the Iron Age the Germanic peoples were at first cut off from the Mediterranean by the Celts and Illyrians. Their culture declined, and an increasing population, together with worsening climatic conditions, drove them to seek new lands farther south.
Before 200 BCE
Thus, the central European Celts and Illyrians found themselves under a growing pressure. Even before 200 BCE the first Germanic tribes had reached the lower Danube, where their path was barred by the Macedonian kingdom. Driven by rising floodwaters, at the end of the 2nd century BCE, migratory hordes of Cimbri, Teutoni, and Ambrones from Jutland broke through the Celtic-Illyrian zone and reached the edge of the Roman sphere of influence, appearing first in Carinthia (113 BCE), then in southern France, and finally in upper Italy. With the violent attacks of the Cimbri, the Germans stepped onto the stage of history.
These migrations were in no way nomadic; they were the gradual expansions of a land-hungry peasantry. Tribes did not always migrate en masse. Usually, because of the loose political structure, groups remained in the original homelands or settled down at points along the migration route. In the course of time, many tribes were depleted and scattered. On the other hand, different tribal groups would sometimes unite before migrating or would take up other wanderers en route. The migrations required skilled leadership, and this promoted the social and political elevation of a noble and kingly class.
Which groups invaded Europe during the Middle Ages and where did they settle?
The Muslims, Magyars and Vikings invaded Europe in the 800s.
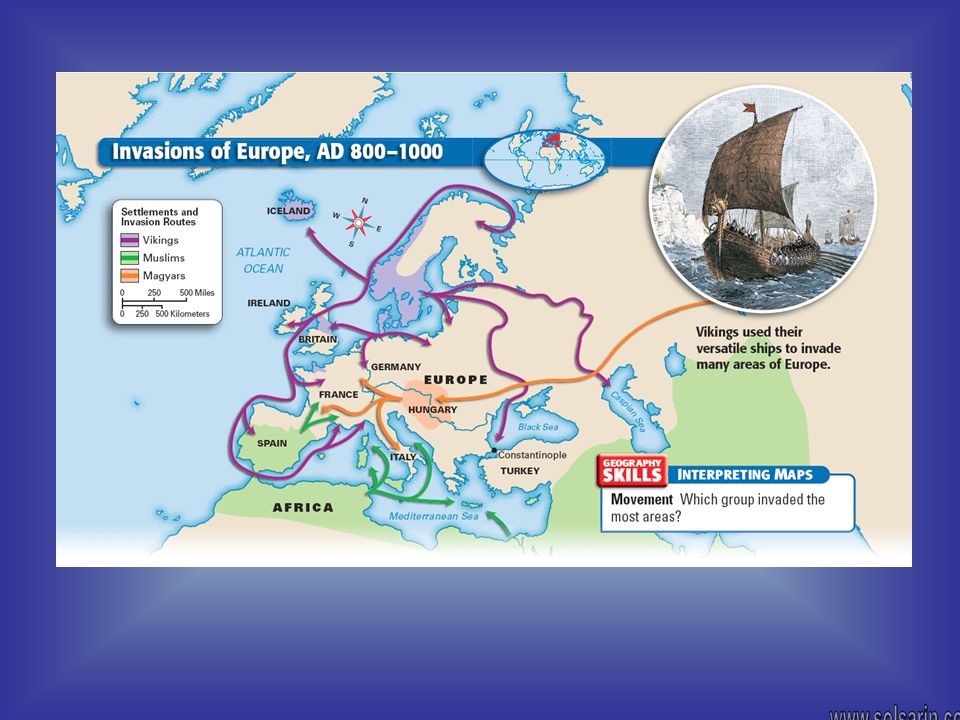

Who were the most feared invaders of Europe during the Middle Ages?
Of the groups who invaded Europe in the 700s and the 800s, which was the most feared? The Vikings.
Who was the greatest threat to Europe in the Middle Ages?
The plague was one of the biggest killers of the Middle Ages. It had a devastating effect on the population of Europe in the 14th and 15th centuries. Also known as the Black Death. The plague (caused by the bacterium called Yersinia pestis) was carried by fleas most often found on rats.
When did the barbarian invasion of Europe start?
Barbarian Invasion of Europe. The Migration Period, also called Barbarian Invasions or Völkerwanderung (German for “wandering of peoples”), is a name given by historians to a human migration which occurred within the period of roughly AD 300–700 in Europe,[1] marking the transition from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages.
Where was the first Arab invasion of Europe?
The Caucasus ( also referred to as North Caucasus) is a geopolitical region located between Europe Asia & Middle East At the same time, Arabs invaded Europe via Gibraltar, conquering Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula) from the Visigoths in 711 before finally being halted by the Franks at the Battle of Tours in 732.
Thank you for staying with this post “what groups invaded europe in the 800s” until the end.




