what is an asterism in astronomy?
Hello dear friends, thank you for choosing us. In this post on the solsarin site, we will talk about ”what is an asterism in astronomy”.
Stay with us.
Thank you for your choice.


In observational astronomy, an asterism is a pattern or group of stars that can be seen in the night sky. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky.
What is an asterism name 2 examples?
Its stars are part of the constellation Ursa Major, the Great Bear.
What is the meaning of asterisms?
asterism, a pattern of stars that is not a constellation.
How are asterisms formed?
Stars are born within the clouds of dust and scattered throughout most galaxies. … Turbulence deep within these clouds gives rise to knots with sufficient mass that the gas and dust can begin to collapse under its own gravitational attraction. As the cloud collapses, the material at the center begins to heat up.
Why are asterisms important?
The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. For example, the asterism known as the Big Dipper comprises the seven brightest stars in the constellation Ursa Major. … The stars within an asterism may be physically associated.
What is an asterism for kids?
An asterism is a pattern of stars in the sky that we can easily recognize. Stars appear to be moving through the sky because of the Earth’s rotation and orbit, and they also have proper movement.
What is an asterism name one?
the North Star an asterism?
Polaris is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Minor. It is designated α Ursae Minoris (Latinized to Alpha Ursae Minoris) and is commonly called the North Star or Pole Star.
Is Ursa Major an asterism?
The Big Dipper is an asterism in the constellation Ursa Major (the Great Bear). One of the most familiar star shapes in the northern sky, it is a useful navigation tool. Asterisms are prominent groups of stars that form patterns but are smaller than, or even part of, a constellation.
Is Draco an asterism?
Draco is a constellation in the far northern sky. Its name is Latin for dragon.


Do you want to know about “an empty-kcalorie food is one that contains“? Click on it.
What gems can have asterism?
Common examples of gems with asterism are ruby and sapphire with six-pointed stars caused by tiny exsolution rutile needles, or black diopside with four-pointed stars produced by exsolution inclusions of black magnetite. Rose quartz, garnets, moonstone and other gems can also have asterism effect.
Are Zodiacs asterisms?
The constellations of the zodiac are fairly easy to find because they either contain a conspicuous asterism or are located near one. Because the Sun appears to travel through these constellations, they do not rise in the night sky at certain times of the year, but are visible at other times.
What are some common asterisms in the northern hemisphere?
There are five of these in the Northern Hemisphere: Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, Draco, Cassiopeia and Cepheus. The Southern Hemisphere has three: Crux, Centaurus and Carina.
Have you heard anything about “how much is the coca-cola brand worth?“? Click on it.
Are there 88 constellations?
Today there are a total of 88 constellations that cover the entire night sky. 36 of these are located in the northen hemisphere of the sky while the remaining 52 are in the southern hemisphere. The official borders of these constellations were originally defined by the IAU in the 1920s.
How do you use asterism in a sentence?
The asterism’s appearance signified the coming of the rainy season and increase in food staple manioc, used at feasts to feed guests. Later, four more stars were added to this asterism, but the name remained unchanged. Its main asterism consists of 11 stars, and 108 stars in total are brighter than magnitude 6.5.
What do you think makes Polaris so special?
The reason Polaris is so important is because the axis of Earth is pointed almost directly at it. During the course of the night, Polaris does not rise or set, but remains in very nearly the same spot above the northern horizon year-round while the other stars circle around it.
What is the Little Dipper’s real name?
Ursa Minor
Why is the North Star always north?
Polaris, the North Star, appears stationary in the sky because it is positioned close
to the line of Earth’s axis projected into space. As such, it is the only bright star whose position relative
to a rotating Earth does not change.
All other stars appear to move opposite to the Earth’s rotation beneath them.
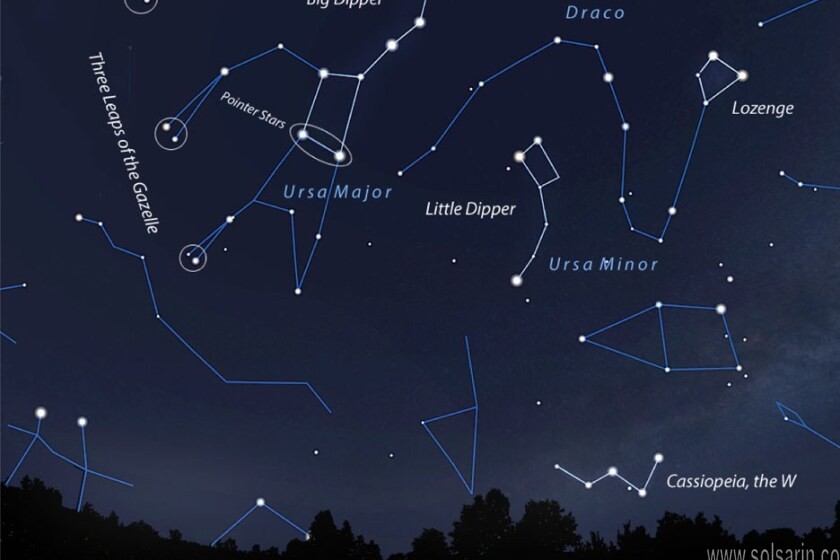

What is the common name of the asterism that is part of Ursa Major?
The constellation Ursa Major contains the group of stars commonly called the Big Dipper.
The handle of the Dipper is the Great Bear’s tail and the Dipper’s cup is the Bear’s flank.
The Big Dipper is not a constellation itself, but an asterism, which is a distinctive group of stars.
Have you heard anything about “how much is the coca-cola brand worth?“? Click on it.
How did Big Dipper get its name?
In astronomy, the Big Dipper refers to an asterism that consists of the seven brightest stars of the constellation Ursa Major,
or the Great Bear. … The term Big Dipper is derived from the outline of the major stars,
an outline that suggests the form of a large ladle or dipper.
Is Polaris a binary star?
Polaris actually is part of a binary (two) star system. Of the stars nearest to our Sun,
about half are known to be in multiple systems (two or more stars).
Between 5 and 10 percent of the stars we can observe are “visible binaries”
— the star companions can be observed with a telescope.
Which star is the cat star?
Its brightest star, HD 85951, was named Felis by
the International Astronomical Union on 1 June 2018 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.


How can you tell a polar star?
How do you find the North Star? Locating Polaris is easy on any clear night.
Just find the Big Dipper. The two stars on the end of the Dipper’s “cup” point the way to Polaris,
which is the tip of the handle of the Little Dipper, or the tail of the little bear in the constellation Ursa Minor.
What are the 7 major constellations?
The largest constellations in the sky are Hydra, Virgo, Ursa Major, Cetus and Hercules.
The largest northern constellations are Ursa Major, Hercules, Pegasus, Draco and Leo,
and the southern ones are Hydra, Virgo, Cetus, Eridanus and Centaurus.
What type of star is eltanin?
K5 III
Gamma Draconis / Spectral type
Eltanin has the stellar classification K5 III, indicating a giant star appearing orange in colour.
The star has a mass 1.72 times that of the Sun and, as it evolved away from the main sequence,
it has expanded to a size of 48.15 solar radii.
How old is eltanin?
Eltanin is about 150 light-years away, while Rastaban is at 380 light-years.
So if you lined them up side by side, Rastaban would shine several times brighter than the dragon’s other eye.
Rastaban is only about 65 million years old, compared to four and a half billion years for the Sun.
Are star rubies rare?
Star rubies are the rarest rubies, according to Guernsey’s,
and they are among the most valuable types of colored gemstones available in the world.
Most are rarer and more valuable than diamonds of comparable size. For hundreds of years,
Myanmar was the world’s main source for rubies.
What is Star diopside?
Diopside is a calcium-magnesium-silicate and one of the most common minerals of the pyroxene-group.
It forms two complete series with Hedenbergite and Johannsenite.
The 4-rayed star is caused by reflection of light at needle-shaped inclusions of magnetite.
What is the difference between constellation and asterism?
Constellations are patterns of stars visible to the unaided eye,
What makes the North Star Polaris special?
Do you want to know about “an empty-kcalorie food is one that contains“? Click on it.



