What is facet arthropathy?
Hey guys! We return with an amazing topic about health. This topic is “what is facet arthropathy?”. As always, read the text, share it to your friends and comment us in solsarin.


How Is Facet Arthropathy Treated?
The facet joints are found between the vertebrae of each segment of your spinal column. Osteoarthritis can develop in these joints and may be called facet arthropathy or facet joint osteoarthritis. Learn about this condition and what treatments may be recommended.
What is Facet Arthropathy?
Facet Arthropathy (FA) is a painful, arthritic condition of the facet joints. These joints allow for bending, twisting, and alignment of the spine. The spinal nerves come off the spinal cord between the vertebra and the facet joints. At the front the vertebra rests on a spongy contained disc while at the back each of the two facet joints rest over the facet joint below it. In a healthy spine, the spinal disc and the facet joints support each other for healthy and safe movement.
Facet Arthropathy is often associated with chronic low back pain. Low back pain potential causes include defects of the ligaments that attach the muscles to the spinal discs, compression or pinching of the spinal cord roots, the hard, protective covering of the spinal cord known as the dura, muscle disorders of the lower spine and facet joints.
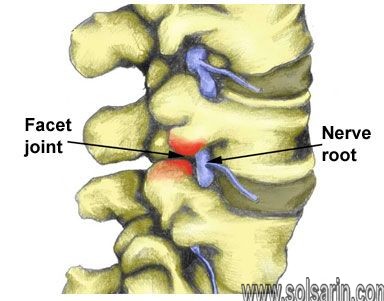
Anatomy of the Facet Joints
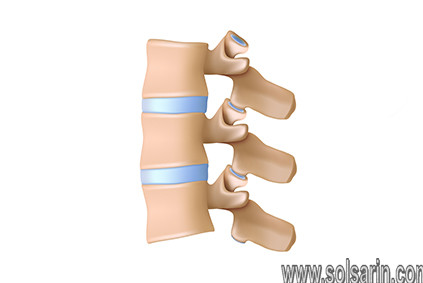
Facet joints are found in the posterior of the spine. There are 24 vertebrae that form the human spine above the sacrum (tailbone). There are two facet joints between the vertebrae of each spinal segment along the spinal column.
The facet joints and intervertebral disc form a three-joint complex between adjacent vertebrae. A facet joint has two bony surfaces with cartilage between them and a capsule of ligaments surrounding it.
Synovial fluid lubricates the joints, as is the case with other joints such as the knee. Facet joints help keep the normal alignment of the vertebrae and limit motion.
Facet Arthropathy Symptoms
Pain is the main symptom associating with facet arthropathy. The pain is typically worse in the afternoon and evening, and upon waking in the morning. Pain associated with facet arthropathy may be exacerbating by twisting or bending backward.
Low back pain is the most frequent complaint, but it does not typically radiate down the legs or buttocks unless spinal stenosis is also involved.

What Causes Facet Arthropathy?
Facet Arthropathy can be affecting by widespread arthritis of other joints seen in Ankylosing Spondylitis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Trauma such as small undiagnosed fractures, disc tears, cartilage splitting or haemorrhage in the area can be some associated findings.
We regularly observe patients with damaged and dysfunctional spinal discs presenting with facet joint damage at the same level in their spine. Loss of disc height and function places increased stress on the facet joints at that level, which can then cause wear and damage over time.
Osteoarthritis can cause lumbar facet pain. People with low back pain can also demonstrate X-Ray evidence of osteoarthritis. The severity of the symptoms also correlate with the degree of damage seen on the CT scan. Unusual orientation of the facet joints and enlarged ligaments can be associating with facet disease.
The synovial capsule may become distended and inflamed which puts pressure on the spinal nerves. When combined with degenerative arthritis and joint instability, pain in facet syndrome results in lower back pain. Rheumatoid arthritis is associating with damage to facets especially the mid-lumbar and lower lumbar areas.
Do you have facet arthropathy?
Make an appointment with your doctor if you’re experiencing continuous lower back pain. If you don’t already have a provider, our Healthline FindCare tool can help you connect to physicians in your area. Your doctor will determine the cause of your pain by first performing a physical examination. They will also ask you questions about your pain and your medical history.
Your doctor may also order one or more of the following tests to help find out if you have facet arthropathy:
- CT scan or MRI scan: These imaging tests can show evidence of facet joint degeneration, even in mild to moderate cases.
- Bone scan: This test, which reveals bone density, can show where there are active areas of inflammation in your spine.
- Anti-inflammatory steroid injection: If an injection of a steroid and anesthetic into your facet joints relieves your back pain, it’s likely you have facet arthropathy.
- Routine X-rays: These will help your doctor evaluate the condition of your spine.

Can facet arthropathy cause other conditions to develop?
Facet arthropathy can cause bone spurs, which are tiny bone projections or outgrowths. Bone spurs can decrease the space available for nerve roots, possibly leading to a condition called spinal stenosis.
Spinal stenosis can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in your buttocks and legs. It’s often associating with other conditions that can contribute to facet arthropathy symptoms, such as arthritis.
Arthritis in other parts of your spine or degenerative disk disease, which occur naturally with age, cause the disks between your vertebrae to lose their flexibility, elasticity, and ability to absorb shock from walking and other activities. This can all cause a lot of pain in your back and other parts of your body.
How is Facet Arthropathy Treated?
There are several options for treating the pain and symptoms caused by facet arthropathy:
1. Medications:Such as NSAIDs, Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Naproxen, and Toradol are helpful to reduce pain as are cyclo-oxygenase-2 Inhibitors such as Celecoxib, and analgesics Acetomenophen, known as Paracetamol or Tylenol.
2. Non-surgical treatments:Physical therapy, strengthening exercises, avoiding movements that aggravate the symptoms, and medications such as NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen can be used.
Intra-joint injections and medial branch blocks of steroids/numbing medication under radiographic guidance and radiofrequency (RF) ablation to block the sensation of pain are two standard therapies. It appears that medial branch blocks and RF ablation are the best options with the lowest complication rates.
Shockwave therapy is another therapy that appears to be better than steroid injections and as effective as RF ablation with better long-term outcomes. Shockwave therapy uses the same technology that breaks up kidney stones. The idea of this therapy
Our German Spine Specialists experience with “Total Lumbar Facet Replacement”, which is a new motion-preserving solution where the facet joints are removing and replacing with artificial joints. This restores healthy height and movement to the damaged part of the spine.
For mild to moderate Facet Arthropathy presenting with a degenerative spinal disc at the same level, Artificial Disc Replacement is also an option. The controlled movement of the New-Generation ESP & M6 Artificial Discs protect the facet joints, and when natural height and movement is re-introduced to the damaged spinal level with ADR, then we observe cases where Facet Joint rehabilitation is possible.
If the patient is not a candidate for a motion-preserving solution, then a spinal fusion can be offering as a ‘last line of defence’. In most forms of a spinal fusion, the surgeon removes the facet joints between the levels of the spine that are to be fusing together, which effectively eliminates the facet joints as a source of future symptoms.

Lumbar Facet Arthropathy
Continuing Education Activity
The lumbar zygapophysial joint, otherwise known as facet joint, is a common generator of lower back pain. The facet joint is forming via the posterolateral articulation connecting the inferior articular process of a given vertebra with the superior articular process of the below adjacent vertebra. The facet joint is a true synovial joint, containing a synovial membrane, hyaline cartilage surfaces, and surrounded by a fibrous joint capsule. There is a meniscoid structure forming within the intra-articular folds. The facet joint is dually innervating by the medial branches arising from the posterior ramus at the same level and one level above the joint. This activity describes the pathophysiology, evaluation; and management of lumbar facet arthropathy and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in improving care for affected patients.
Objectives:
-
Describe the pathophysiology of lumbar facet arthropathy.
-
Outline the components of a proper evaluation and assessment of a patient presenting with lumbar facet arthropathy, including any indicated imaging studies.
-
Explain treatment and management options available for lumbar facet arthropathy.
-
Review the role of improving coordination amongst the interprofessional team to streamline diagnosis, joint reduction, and/or surgery for patients with lumbar facet arthropathy.




