what is produced during transcription
Hello. Welcome to solsarin. This post is about “what is produced during transcription”.
Transcription
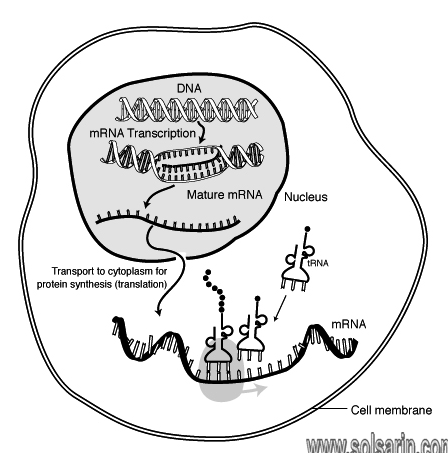
Transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). … The newly formed mRNA copies of the gene then serve as blueprints for protein synthesis during the process of translation.

Where is produced during transcription?
the nucleus
Transcription takes place in the nucleus. It uses DNA as a template to make an RNA molecule. RNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. Translation reads the genetic code in mRNA and makes a protein.
What is produced during translation?
The molecule that results from translation is protein — or more precisely, translation produces short sequences of amino acids called peptides that get stitched together and become proteins. Transfer RNA binds to amino acids and drags them over to the messenger RNA strand on the ribosome.
What is made during transcription and what is made during translation?
Transcription uses a strand of DNA as a template to build a molecule called RNA. The RNA molecule is the link between DNA and the production of proteins. During translation, the RNA molecule created in the transcription process delivers information from the DNA to the protein-building machines.
What is produced during transcription RNA polymerase?
The main enzyme involved in transcription is RNA polymerase, which uses a single-stranded DNA template to synthesize a complementary strand of RNA. Specifically, RNA polymerase builds an RNA strand in the 5′ to 3′ direction, adding each new nucleotide to the 3′ end of the strand.
What is produced during transcription quizlet?
In transcription, the RNA nucleotides are linked by the transcription enzyme, RNA polymerase. It produces primary transcript RNA.
What is produced in translation and where does it occur?
Translation is the process by which a protein is synthesized from the information contained in a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). … Translation occurs in a structure called the ribosome, which is a factory for the synthesis of proteins.
Which of the following molecules are produced during transcription?
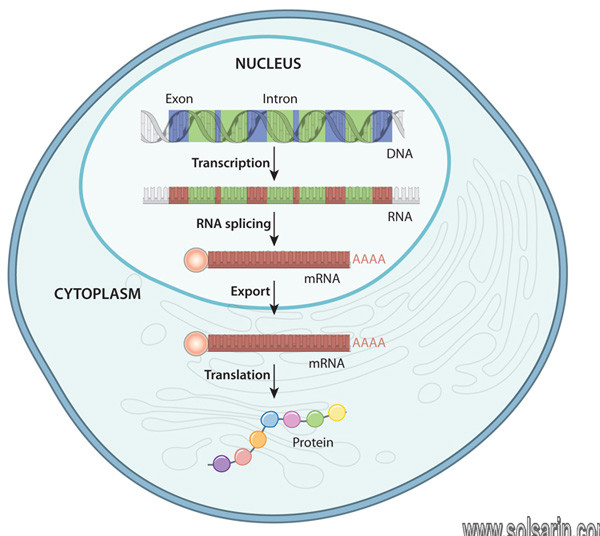
During transcription, the enzyme RNA polymerase (green) uses DNA as a template to produce a pre-mRNA transcript (pink). The pre-mRNA is processed to form a mature mRNA molecule that can be translated to build the protein molecule (polypeptide) encoded by the original gene.

What happens during transcription and translation quizlet?
is the synthesis of polypeptide which occurs under the direction of mRNA. The cell translates the base sequence of an mRNA molecule into the amino acid sequence of an mRNA molecule into the amino acid sequence of polypeptide. is the synthesis of RNA under the directions of DNA (template).
What happens during translation?
Translation is the process of translating the sequence of a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule to a sequence of amino acids during protein synthesis. … In the cell cytoplasm, the ribosome reads the sequence of the mRNA in groups of three bases to assemble the protein.
Which type of RNA is made during transcription?
messenger RNA
mRNA (messenger RNA): Produced during transcription. Carries the genetic instructions of a gene from the nucleus to the ribosome in the cytoplasm.
Where is the RNA molecule formed during transcription?
When RNA molecules are produced it happens inside the nucleus. The RNA molecule can then leave the nucleus and travel to ribosomes which are located in the cytoplasm and attached to endoplasmic reticulum. The RNA will be used to create proteins molecules.
What is the end product of transcription?
The product of transcription is RNA, which can be encountered in the form mRNA, tRNA or rRNA while the product of translation is a polypeptide amino acid chain, which forms a protein.
What is created between 2 amino acids during translation?
Two amino acids are joined together through a condensation reaction that creates a peptide bond between the two amino acids. – The ribosome moves along the mRNA one codon shifting the tRNA that was attached to methionine to the E site.
What happens during translation quizlet?
What happens during translation? During translation, a ribosome uses the sequence of codons in mRNA to assemble amino acids into a polypeptide chain. The correct amino acids are brought to the ribosome by tRNA. … The decoding of an mRNA message into a protein is a process known carries out both these tasks.
How are proteins being synthesized during translation?
In translation, polypeptides are synthesized using mRNA sequences and cellular machinery, including tRNAs that match mRNA codons to specific amino acids and ribosomes composed of RNA and proteins that catalyze the reaction. The genetic code is degenerate in that several mRNA codons code for the same amino acids.

Where does the energy for translation come from?
Guanosine triphosphate (GTP), which is a purine nucleotide triphosphate, acts as an energy source during translation—both at the start of elongation and during the ribosome’s translocation.
How are polypeptide chains formed?
Polypeptide chains are formed by dehydration between the amino group of a L-amino acid4 with the carboxyl group of another. One hundred or more amino acids are linked together with covalent peptide bonds in various specific sequences in the polypeptide chain with polypeptide chains combining to form a protein.
Which of the following events occurs during transcription?
Which of the following events occurs during transcription? A molecule of RNA is formed based on the sequence of nucleotides in DNA. During transcription, RNA nucleotides line up with their complementary DNA partners, transcribing the information in DNA into RNA.
Which enzyme delivers new nucleotides to the DNA during transcription?
RNA Polymerase II (RNA Pol II) is the enzyme that adds nucleotides to a new DNA chain produced during transcription. It is recruited to the transcription start site of a gene by a cluster of transcription factors that bind the TATA box, which is a sequence of nucleotides near the starting line of the gene.
Which nucleic acid is translated to make A protein?
Which nucleic acid is translated to make a protein? mRNA is the message that is translated to make a protein.
What are the 4 steps in the process of transcription?
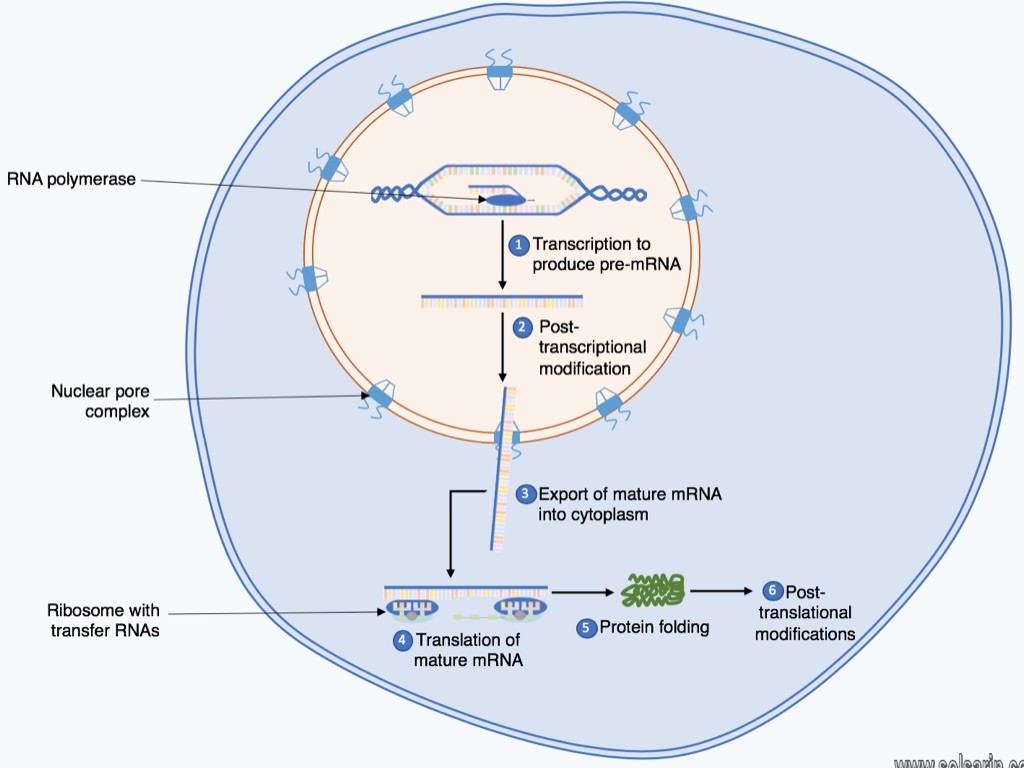
The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination.
What are the 6 steps of transcription?
Stages of Transcription
Initiation. Transcription is catalysed by the enzyme RNA polymerase, which attaches to and moves along the DNA molecule until it recognises a promoter sequence. …
Elongation. …
Termination. …
5′ Capping. …
Polyadenylation. …
Splicing.
What is made in translation quizlet?
Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mRNA template where the code in the mRNA is converted into an amino acid sequence in a protein. … Translation creates protein or polypeptide chain, and it’s created from tRNA bringing the amino acids to the ribosomes to create the protein.
What is made during translation biology quizlet?
mRNA is made during transcription/translation
What is a transcription quizlet?
Transcription. The process of making an RNA copy of a gene sequence. RNA polymerase. An enzyme that synthesizes the formation of RNA from a DNA template during transcription.

What is a transcription and translation?
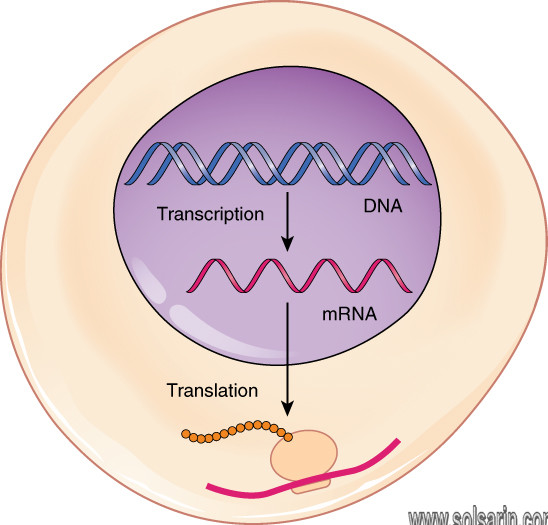
The process by which DNA is copied to RNA is called transcription, and that by which RNA is used to produce proteins is called translation.
What is the process of transcription and translation together?
Together, transcription and translation are known as gene expression.
What is the process of making proteins called?
Protein synthesis is the process in which cells make proteins. It occurs in two stages: transcription and translation. Transcription is the transfer of genetic instructions in DNA to mRNA in the nucleus. … Translation Goccurs at the ribosome, which consists of rRNA and proteins.
What is amino acid sequence?
Amino acid sequencing is the process of identifying the arrangement of amino acids in proteins and peptides. Numerous distinct amino acids have been discovered in nature but all proteins in the human body are comprised of just twenty different types.
Where are the 3 types of RNA made
Three RNAs
Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. mRNA is produced in the nucleus, as are all RNAs.
The other two forms of RNA, ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and transfer RNA (tRNA), are involved in the process of ordering the amino acids to make the protein.
What are the components of a operon?
An operon is a unit of the bacterial chromosome consisting of the following components:
A regulatory gene. The regulatory gene codes for a regulatory protein. …
An operator. The operator is the region of DNA of the operon that is the binding site for the regulatory protein.
A promoter. …
Structural genes.
What happens during transcription *?
Transcription is the first phase of the protein-making process, even though the actual protein synthesis doesn’t happen until the second phase. Essentially, what happens during transcription is that an mRNA “copies down” the instructions for making a protein from DNA.
How is mRNA formed by transcription in eukaryotes?
mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus using the nucleotide sequence of DNA as a template. This process requires nucleotide triphosphates as substrates and is catalyzed by the enzyme RNA polymerase II. The process of making mRNA from DNA is called transcription, and it occurs in the nucleus.
What are the products of transcription quizlet?
Messenger RNA.
Transfer RNA.
Ribosomal RNA.
What is the final product of transcription quizlet?
what is the end result of transcription? DNA is converted to a strand of mRNA to be translated in the ribosome.
What is the end product in translation?
The amino acid sequence is the final result of translation, and is known as a polypeptide. Polypeptides can then undergo folding to become functional proteins.
Which statement best summarizes what happens during transcription?
Which statement best summarizes what happens during transcription? A DNA template is used to create an mRNA strand. What is created between 2 amino acids during translation?
Is a polypeptide a sequence of proteins or amino acids?
A peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by peptide bonds; a polypeptide is a chain of many amino acids; and a protein contains one or more polypeptides. … The order of deoxyribonucleotide bases in a gene determines the amino acid sequence of a particular protein.
Which step begins the process of transcription?
Transcription Initiation. The first step in transcription is initiation, when the RNA pol binds to the DNA upstream (5′) of the gene at a specialized sequence called a promoter
What is wobble and what makes it necessary in protein synthesis?
Wobble base pairs are fundamental in RNA secondary structure and are critical for the proper translation of the genetic code. Wobbling allows faster dissociation of tRNA from mRNA and also protein synthesis.
What is a codon and what does it code for quizlet?
a three base mRNA sequence that codes for ONE amino acid. The term is also used for a DNA bases triplet on the non-template strand. As codons are triplets of bases, the number of nucleotides that make up the genetic message must be three times the number of amino acids specified in the protein.
- nerve specialist called
- lilac flower meaning
- advantages of java beans
- what color are tendons
- madagascar points of interest



