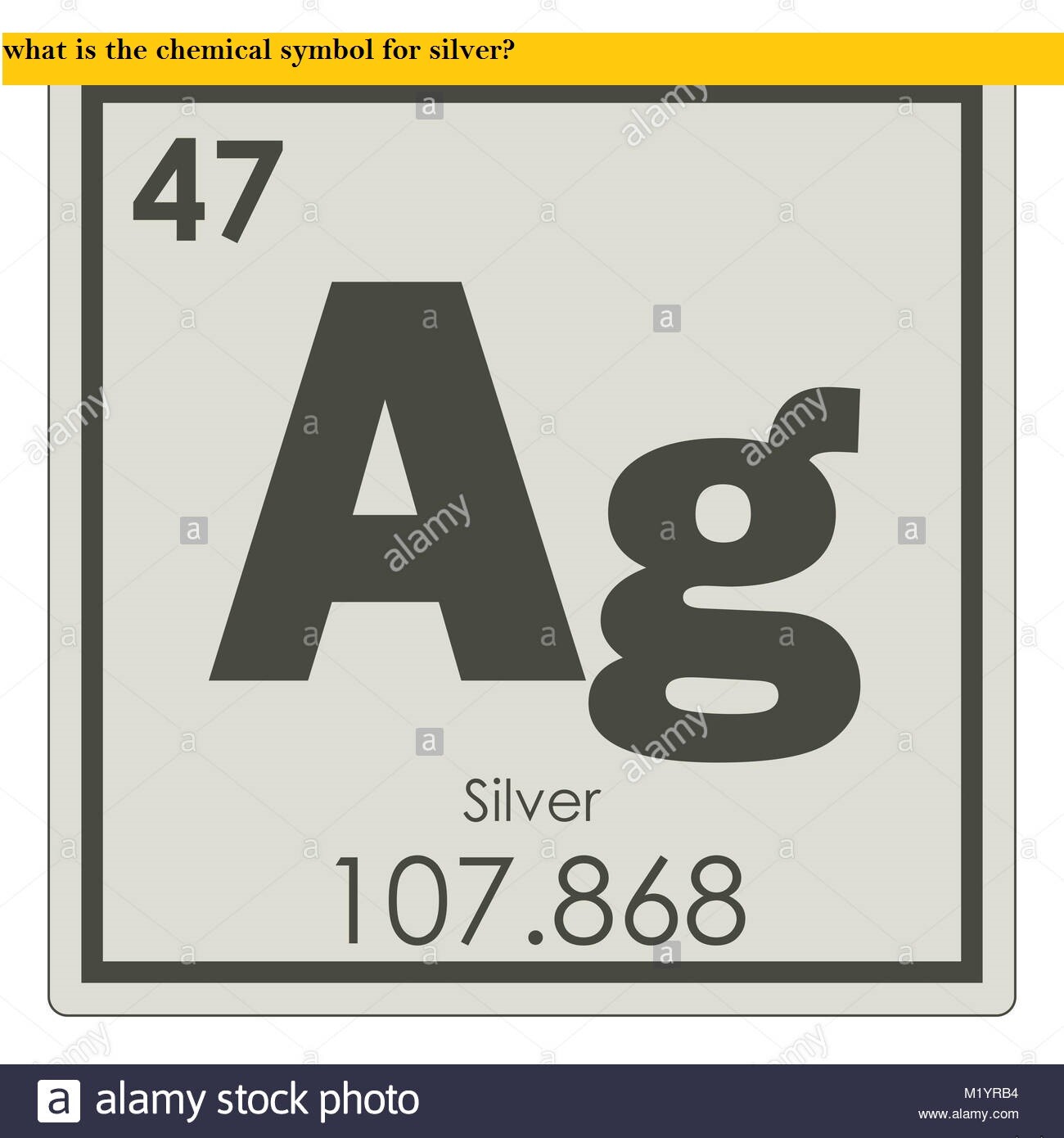
what is the chemical symbol for silver?
Hello dear friends, thank you for choosing us. In this post on the solsarin site, we will talk about “what is the chemical symbol for silver?”.
Stay with us.
Thank you for your choice.
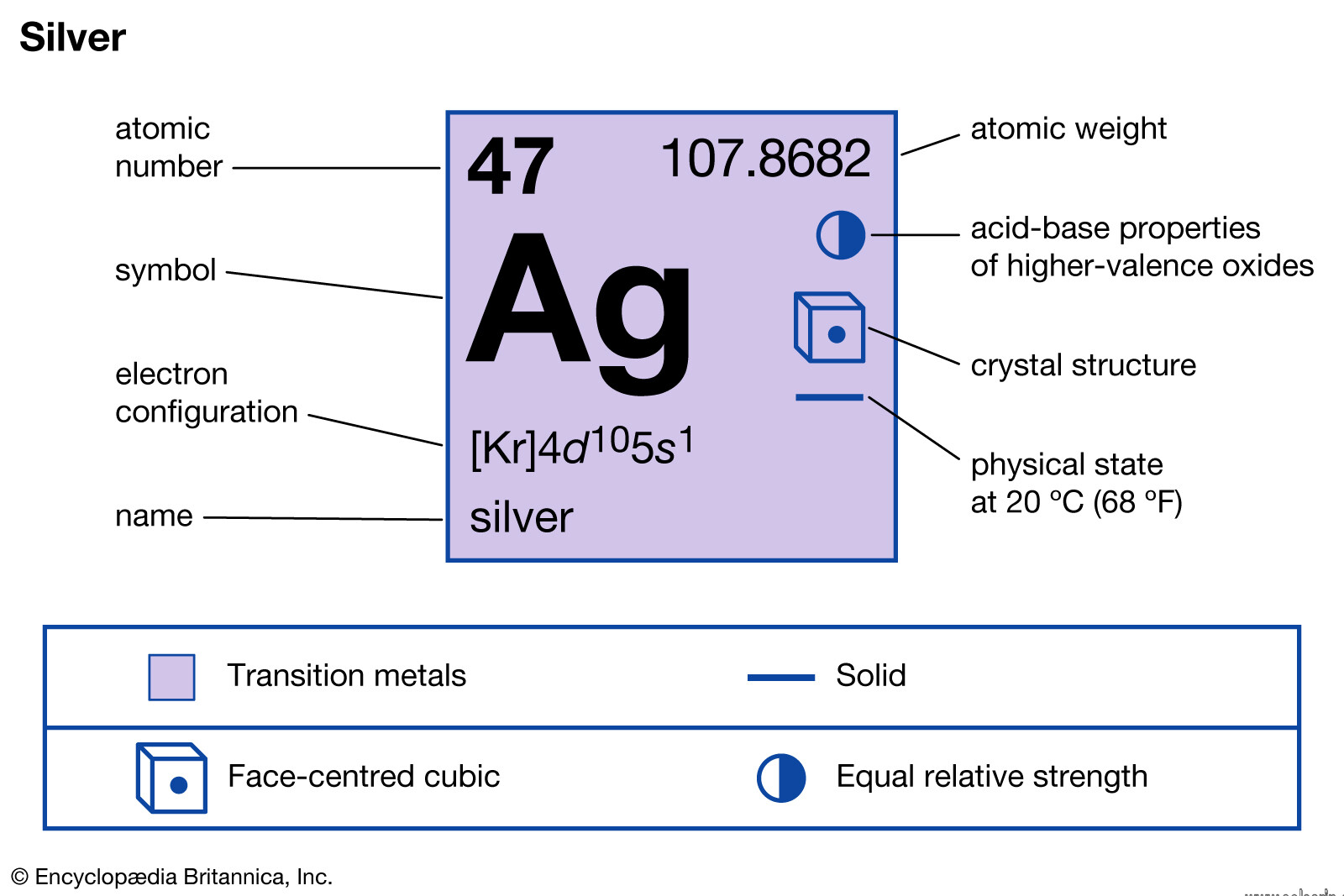

what is the chemical symbol for silver
Silver
Properties, uses, and occurrence
Together with gold and the platinum-group metals, silver is one of the so-called precious metals.
Silver also finds use as a catalyst for its unique ability to convert ethylene to ethylene oxide.
which is a precursor of many organic compounds. Silver is one of the noblest—that is, least chemically reactive—of the transition elements.
what is the chemical symbol for silver and gold
What is the Chemical Symbol for Silver?
The chemical symbol for silver is Ag, coming from the Latin word for silver – Argentum .
Interestingly, it is the same root word for the French word argent .
which means both silver and money, telling us a lot about the historical affinity between wealth and precious metals.
Precious Metals and Their Chemical Symbols
While it’s true that gold and silver hold monetary values, it’s also important to remember that.
at their essence, they are elements. Society has assigned a monetary value to them based on their rarity.
industrial and decorative use, and more, but at their essence, gold, silver, and other precious metals are elements.
Found on the periodic table and represented by their two-letter abbreviations.
it’s important to remember these precious metals are truly precious since they’re naturally occurring and finite in their quantity.
Their limited quantities are precisely what makes them attractive to collectors.
Gold: Au
Arguably the most treasured precious metal for thousands of years, gold’s chemical symbol Au originates from the Latin word “aurum,” which means golden or glowing.
It’s not surprising that the chemical symbol for gold is rooted in its bright yellow, glowing color.
Gold has a rich history across the globe and throughout the centuries.
It has long been associated with the sun, most notably by the ancient Egyptians.
Gold has always played an essential role in history.
As a much sought-after metal, alchemists tried to produce gold from other natural substances, including lead.
The attempt to manufacture the metal led to the Spanish word for goldsmith, which originates from the Latin “auri faber.”
Today, gold is known for being a wise investment for portfolios, an engaging hobby for collectors of its coins.
and more including currency, jewelry, and technology. As it’s a very soft metal, gold is often alloyed with other metals for strength.
Silver: Ag
Across the globe, gold was associated with the sun, while silver was associated with the moon.
Much like gold, silver’s chemical symbol is based off of its physical appearance.
Its color earned it the symbol Ag from the Latin word “argentum,” meaning off-white.
During the Roman Empire in the 4th century.
Spain supplied the Romans with silver in sheets called “plattum argentum.” That’s precisely where the Spanish word for silver, plata, comes from.


Platinum: Pt
First discovered by Spanish explorers in modern-day Columbia, and thought to be a variant of silver because of its grey-white color.
the name platinum and its chemical symbol of Pt comes from the Spanish word “platina,” which translates to little silver.
The Spaniards were perplexed when they attempted to melt this supposed silver.
and found it would not melt. Eventually, they determined this was a new metal, and it would indeed melt at a much higher temperature.
Unlike gold and silver, platinum is a very dense, hard metal.
When it is alloyed, it’s combined with a softer metal like iridium to make it more malleable to craft jewelry.
While not as popular in metal as silver or gold, platinum still represents an attractive choice for investors and collectors alike.
Nickel Provides Enormous Value Beyond the 5-Cent Piece
While many of us are familiar with a nickel we might find as pocket change, the metal itself is much different.
Nickel is actually a chemical element and features “Ni” as its symbol and 28 as its atomic number.
Uses
it has a place in food production as well.
Raney nickel, a fine-grained solid, is used for hydrogenation of unsaturated oils in order to make margarine.
what is the atomic symbol for silver worksheet


what is chemical symbol for silver nitrate
AgNO3
Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin argentum, derived from the Proto-Indo-European h₂erǵ: “shiny” or “white”) and atomic number 47
which of the following is the chemical symbol for silver
What is the chemical symbol for silver in the periodic table of elements?
Silver is the metallic element with the atomic number 47. Its symbol is Ag, from the Latin argentum.
The metal occurs naturally in its pure, free form (native silver).
Silver
Pure silver is nearly white, lustrous, soft, very ductile, malleable, it is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity.
forming silver sulfide (tarnish). This is why silver objects need regular cleaning. Silver is stable in water.
Soluble silver salts, specially AgNO3, are lethal in concentrations of up to 2g (0.070 oz). Silver compounds can be slowly absorbed by body tissues, with the consequent bluish or blackish skin pigmentation (argiria).
Eye contact: may cause severe corneal injury if liquid comes in contact with the eyes.
Skin contact: may cause skin irritation. Repeated and prolonged contact with skin may cause allergic dermatitis. Inhalation hazards:
exposure to high concentrations of vapors may cause dizziness, breathing difficulty, headaches or respiratory irritation. Extremely high concentrations may cause drowsiness, staggering, confusion, unconsciousness, coma or death.
Environmental effects of silver
For information on:
– Environmental levels
– Effects of organisms in the laboratory and field
– Aquatic environment: Toxicity of silver compounds to aquatic species
– Terrestrial environment
– Effects evaluation
Liquid or vapor may be irritating to skin
Liquid or vapor may be irritating to skin, eyes, throat, or lungs. Intentional misuse by deliberately concentrating and inhaling the contents of this product can be harmful or fatal.
Ingestion hazards: moderately toxic. May cause stomach discomfort, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and narcosis. Aspiration of material into lungs if swallowed or if vomiting occurs can cause chemical pneumonitis which can be fatal.