what is the end product of replication
hello dear friend thank you for choosing us.
in this post on the solsarin. site. we will talk a bout what is the end product of replication .
stay with us .
thank you for your choice
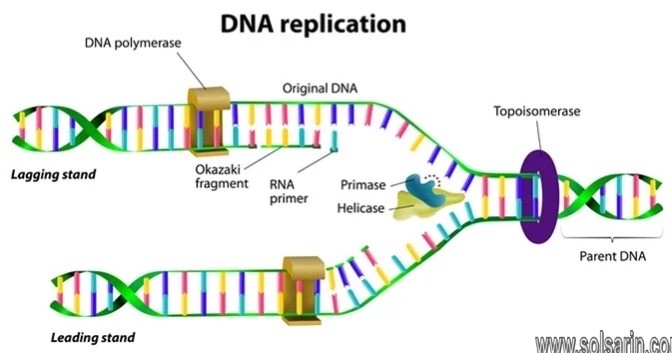

What is the end product of replication? Two identical DNA strands. Each one is made of one original strand and one new strand. What is the role of DNA polymerase in replication?
What is the end product of the replication process?
The result of DNA replication is two DNA molecules consisting of one new and one old chain of nucleotides.
What happens at the end of DNA replication?
DNA replication ends when converging replication forks meet. During this process, which is known as replication termination, DNA synthesis is completed, the replication machinery is disassembled and daughter molecules are resolved.
What is the end product of translation?
polypeptide
The amino acid sequence is the final result of translation, and is known as a polypeptide. Polypeptides can then undergo folding to become functional proteins.
Do you want to know about “an empty-kcalorie food is one that contains“? Click on it.
What is the end result of transcription?
The end product of transcription is RNA, a single-stranded molecule made up of RNA nucleotides. The three main types of RNA produced in the transcription are mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA.
How is the end replication problem solved?
Eukaryotes have solved the end-replication problem by locating highly repeated DNA sequence at the end, or telomeres, of each linear chromosome. In humans and other vertebrate organisms, the sequence of nucleotides in telomeres is TTAGGG, is repeated between 100 and 1000 times.
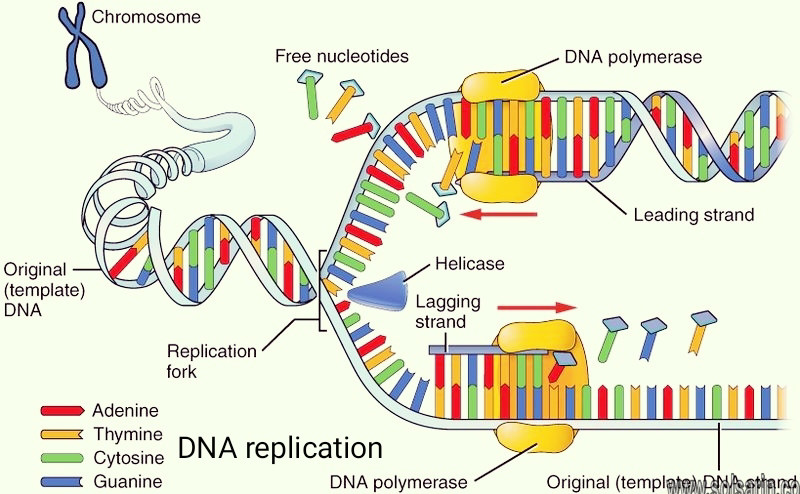

What are the 4 steps of replication?
Step 1: Replication Fork Formation. Before DNA can be replicated, the double stranded molecule must be “unzipped” into two single strands. …
Step 2: Primer Binding. The leading strand is the simplest to replicate. …
Step 3: Elongation. …
Step 4: Termination.
How many strands of DNA are produced at the end of replication?
At the end of DNA replication (two, four) new strands of DNA have been produced, giving a total of (four, six) strands of DNA. New DNA is replicated in strands complementary to old DNA because production of new DNA follows the rules of (base pairing/the double helix).
What is the end product of translation quizlet?
The final product of translation, and gene expression, is a protein.
What is the final product of translation apex?
The second step is called translation, where the sequence of mRNA is converted into a sequence of amino acids to form a polypeptide. This polypeptide can then go on to fold into a protein with a specific shape and function. So the final product of translation is given by answer choice (D), a polypeptide chain.
What is a product of translation?
The products of translation are proteins. During translation mRNA created during transcription is localized to the ribosome.
What is the end result and purpose of translation?
The end product of translation is a polypeptide chain which folds and undergoes post translational modifications to form a functional protein. The process of translation or protein synthesis.

What is the order of replication?
How is DNA replicated? Replication occurs in three major steps: the opening of the double helix and separation of the DNA strands, the priming of the template strand, and the assembly of the new DNA segment.
What molecule is produced at the end of transcription?
mRNA
The outcome of Transcription is a complimentary strand of messengerRNA (mRNA).
What is the end result of replication of a duplex DNA molecule?
Replication produces two identical DNA double helices, each with one new and one old strand.
What is the final product of translation Brainly?
Answer: The product of transcription is RNA, which can be encountered in the form mRNA, tRNA or rRNA while the product of translation is a polypeptide amino acid chain, which forms a protein.
Where does the finished product go in DNA replication?
Translation: Where does the finished product go? its going to go wherever its needed, depending on the function of the protein.
What happens at the end of translation?
Translation ends in a process called termination. Termination happens when a stop codon in the mRNA (UAA, UAG, or UGA) enters the A site. Stop codons are recognized by proteins called release factors, which fit neatly into the P site (though they aren’t tRNAs).
What is the polypeptide chain?
A polypeptide is an unbranched chain of amino acids that are linked together by peptide bonds. The peptide bond links the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amine group of the next amino acid to form an amide.
In translation, mRNA along with transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomes work together to produce proteins.
Have you heard anything about “how much is the coca-cola brand worth?“? Click on it.
What is produced by transcription?
Transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). DNA safely and stably stores genetic material in the nuclei of cells as a reference, or template.
Does replication come before transcription?
The mechanism of transcription has parallels in that of DNA replication. As with DNA replication, partial unwinding of the double helix must occur before transcription can take place, and it is the RNA polymerase enzymes that catalyze this process.

What is translation Bioninja?
Translation is the synthesis of polypeptides on ribosomes. The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is determined by mRNA according to the genetic code. Codons of three bases on mRNA correspond to one amino acid in a polypeptide.
What is the purpose and product of translation?
The genes in DNA encode protein molecules, which are the “workhorses” of the cell, carrying out all the functions necessary for life.
What are the 4 steps of translation?
The four steps of translation are:
Activation or charging of tRNA.
Initiation – recognition of start codon, binding of ribosomal subunits to mRNA and formation of initiation complex with Met-tRNA at the P site.
Elongation – peptide bond formation and growing of polypeptide chain.
Why does DNA replication stop?
Eukaryotes initiate DNA replication at multiple points in the chromosome, so replication forks meet and terminate at many points in the chromosome. Because eukaryotes have linear chromosomes, DNA replication is unable to reach the very end of the chromosomes.
the DNA cannot be extended and this creates the end replication problem
As we all know, with a linear chromosome, on the lagging strand (template 5′->3′) of DNA replication, when the last piece of RNA primer at the 3′ end is removed, the DNA cannot be extended and this creates the end replication problem.
Why can’t the ends of chromosomes be replicated?
DNA replication on the lagging strand in eukaryotes occurs through the production of many small pieces of DNA called Okazaki fragments.
How does telomerase solve the end replication problem quizlet?
What is the Telomerase cycle ? A lot of telomeres + sheltering proteins=degrade/take off the telomeres. When end replication problem arises again/continues the telomeres and sheltering are shorten so telomerase adds more telomeres.
What is the telomere replication problem?
Telomeres are complex nucleoprotein structures that protect the extremities of linear chromosomes.
Telomerase, a ribonucleoprotein, consists of protein and an RNA molecule that is complementary to the 3′ end of the DNA of a eukaryotic chromosome.
How does telomerase extend the 3 ends of chromosomes?
In Summary: Telomeres
Telomerase, an enzyme with a built-in RNA template, extends the ends by copying the RNA template and extending one end of the chromosome. DNA polymerase can then extend the DNA using the primer. In this way, the ends of the chromosomes are protected.
How does the enzyme telomerase meet the challenge of replicating the ends of linear chromosomes?
How does the enzyme telomerase meet the challenge of replicating the ends of linear chromosomes? It catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres, compensating for the shortening that occurs during replication. DNA is a self-replicating molecule.
What happens in the final step of DNA replication?
Once completed, the parent strand and its complementary DNA strand coils into the familiar double helix shape. In the end, replication produces two DNA molecules, each with one strand from the parent molecule and one new strand.
What does 5 end and 3 end mean?
Each end of DNA molecule has a number. One end is referred to as 5′ (five prime) and the other end is referred to as 3′ (three prime). The 5′ and 3′ designations refer to the number of carbon atom in a deoxyribose sugar molecule to which a phosphate group bonds.



