what is the function of arp?
Welcom to solsarin site ,Keep reading and find the answer about “what is the function of arp?”.
Stay with us.
Thank you for your support.
What are functions of ARP?
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used to resolve an IP address into a physical address (Ethernet MAC address, for example). In an Ethernet LAN,
a switch uses ARP to resolve the IP address of the next hop to the corresponding MAC address.
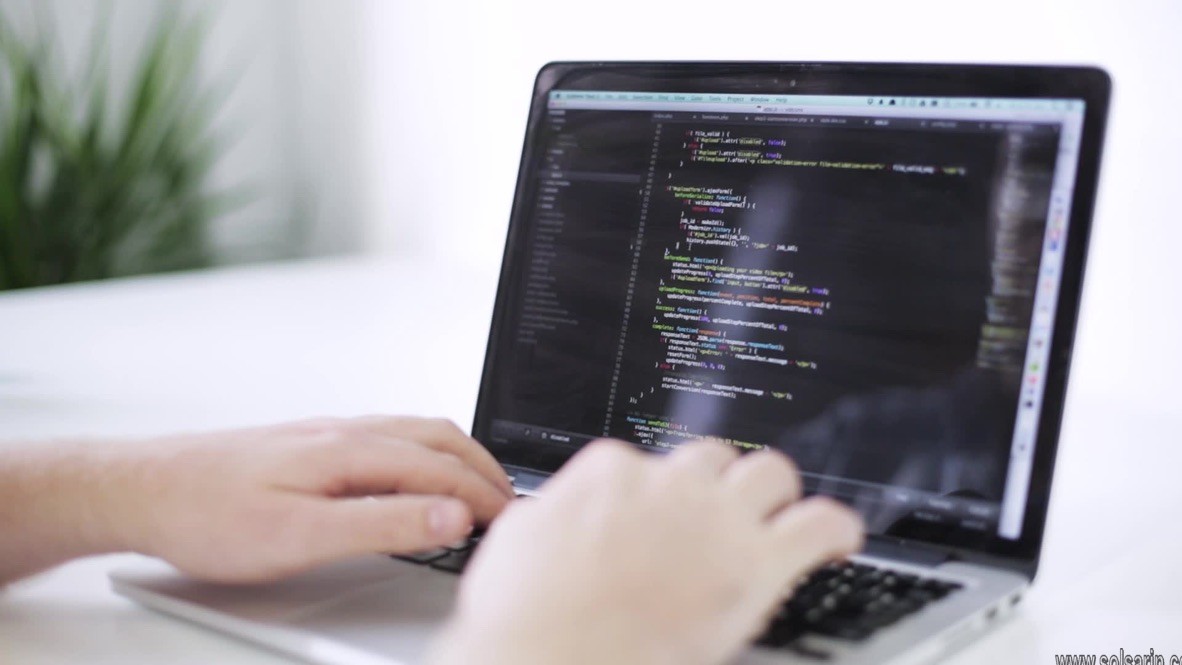


What is the function of ARP Mcq?
The basic purpose of the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is to resolve IP addresses to ethernet addresses.
ARP mediates between broadcast link-level protocols and IP protocols.
Specifically, it maps 32-bit IP addresses to 48-bit ethernet addresses. You can learn more about ARP in RFC 826.
Address Resolution Protocol
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol or procedure that connects an ever-changing Internet Protocol (IP) address to a fixed physical machine address,
also known as a media access control (MAC) address, in a local-area network (LAN).
This mapping procedure is important because the lengths of the IP and MAC addresses differ,
and a translation is needed so that the systems can recognize one another. The most used IP today is IP version 4 (IPv4).
An IP address is 32 bits long.
However, MAC addresses are 48 bits long.
ARP translates the 32-bit address to 48 and vice versa.
There is a networking model known as the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model.
First developed in the late 1970s, the OSI model uses layers to give IT teams a visualization of what is going on with a particular networking system.
This can be helpful in determining which layer affects which application, device, or software installed on the network, and further, which IT or engineering professional is responsible for managing that layer.
The MAC address is also known as the data link layer,
which establishes and terminates a connection between two physically connected devices so that data transfer can take place.
The IP address is also referred to as the network layer or the layer responsible for forwarding packets of data through different routers.
ARP works between these layers.
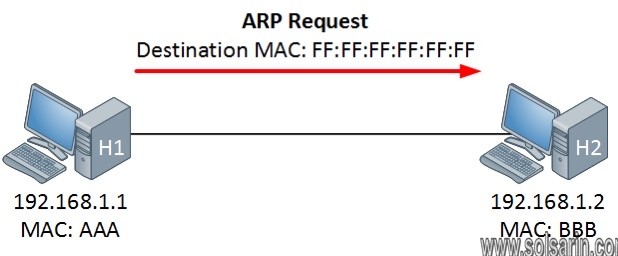

What Does ARP Do and How Does It Work?
When a new computer joins a local area network (LAN), it will receive a unique IP address to use for identification and communication.
Packets of data arrive at a gateway, destined for a particular host machine.
The gateway, or the piece of hardware on a network that allows data to flow from one network to another,
asks the ARP program to find a MAC address that matches the IP address.
The ARP cache keeps a list of each IP address and its matching MAC address.
The ARP cache is dynamic, but users on a network can also configure a static ARP table containing IP addresses and MAC addresses.
If it exists, then a new request is unnecessary.
What is address resolution protocol’s relationship with DHCP and DNS? How do they differ?
ARP is the process of connecting a dynamic IP address to a physical machine’s MAC address.
As such, it is important to have a look at a few technologies related to IP.
However changes on IP addresses should not be completely random.
There should be rules that allocate an IP address from a defined range of numbers available in a specific network.
This helps prevent issues,
such as two computers receiving the same IP address.
The rules are known as DHCP or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
IP addresses as identities for computers are important because they are needed to perform an internet search.
When users search for a domain name or Uniform Resource Locator (URL), they use an alphabetical name.
Computers, on the other hand, use the numerical IP address to associate the domain name with a server.
To connect the two,
What Are the Types of ARP?(what is the function of arp?)
There are different versions and use cases of ARP. Let us take a look at a few.
Proxy ARP
Proxy ARP is a technique by which a proxy device on a given network answers the ARP request for an IP address that is not on that network.
The proxy is aware of the location of the traffic’s destination and offers its own MAC address as the destination.
Gratuitous ARP(what is the function of arp?)
Gratuitous ARP is almost like an administrative procedure, carried out as a way for a host on a network to simply announce or update its IP-to-MAC address. this. is not prompted by an ARP request to translate an IP address to a MAC address.
Reverse ARP (RARP)
Host machines that do not know their own IP address can use the Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) for discovery.
Inverse ARP (IARP)
Whereas ARP uses an IP address to find a MAC address, IARP uses a MAC address to find an IP address.
What is ARP in Networking Useful For?
ARP is necessary because the software address (IP address) of the host or computer connected to the network needs to be translated to a hardware address (MAC address).
Without ARP, a host would not be able to figure out the hardware address of another host.
The LAN keeps a table or directory that maps IP addresses to MAC addresses of the different devices, including both endpoints and routers on that network.
This table or directory is not maintained by users or even by IT administrators.
Instead, the ARP protocol creates entries on the fly. If a user’s device does not know the hardware address of the destination host, the device will send a message to every host on the network asking for this address.
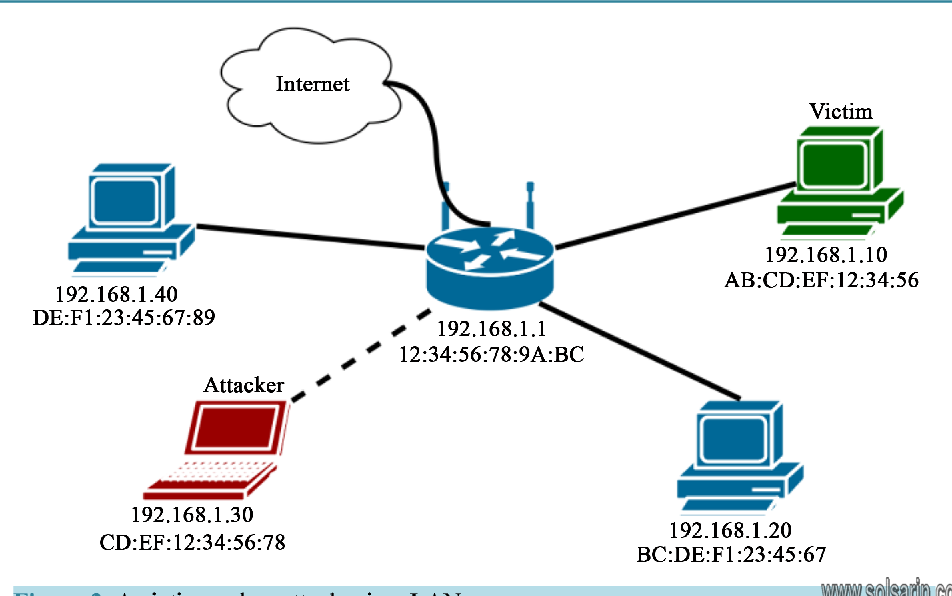
What Is ARP Spoofing/ARP Poisoning Attack?(what is the function of arp?)
ARP spoofing is also known as ARP poison routing or ARP cache poisoning.
This is a type of malicious attack in which a cyber criminal sends fake ARP messages to a target LAN with the intention of linking their MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate device or server within the network.
ARP spoofing also enables other forms of cyberattacks, including the following:
Man-in-the-Middle (MTM) Attacks
A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack is a type of eavesdropping in which the cyberattacker intercepts, relays, and alters messages between two parties—who have no idea that a third party is involved—to steal information.
The attacker may try to control and manipulate the messages of one of the parties, or of both,
to obtain sensitive information.
Because these types of attacks use sophisticated software to mimic the style and tone of conversations—
including those that are text- and voice-based—a MITM attack is difficult to intercept and thwart.
A MITM attack occurs when malware is distributed and takes control of a victim’s web browser.
The browser itself is not important to the attacker, but the data that the victim shares very much is because it can include usernames, passwords, account numbers,
and other sensitive information shared in chats and online discussions.
Once they have control, the attacker creates a proxy between the victim and a legitimate site, usually with a fake lookalike site, to intercept any data between the victim and the legitimate site.
online banking
Attackers do this with online banking and e-commerce sites to capture personal information and financial data.
Denial-of-Service Attacks
A denial-of-service (DoS) attack is one in which a cyberattacker attempts to overwhelm systems
, servers, and networks with traffic to prevent users from accessing them.
These types of attacks exploit known vulnerabilities in network protocols.

Session Hijacking(what is the function of arp?)
Session hijacking occurs when a cyberattacker steals a user’s session ID, takes over that user’s web session,
and masquerades as that user.
With the session ID in their possession,
the attacker can perform any task or activity that user is authorized to do on that network.
Authentication occurs when a user tries to gain access to a system or sign in to a restricted website or web service.
The session ID is stored in a cookie in the browser,
and an attacker engaged in session hijacking will intercept the authentication process and intrude in real time
in cryptography and computer security(what is the function of arp?)
in cryptography and computer security, a man-in-the-middle, monster-in-the-middle,machine-in-the-middle, monkey-in-the-middle,meddler-in-the-middle (MITM) or person-in-the-middle (PITM) attack is a cyberattack where the attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communications between two parties who believe that they are directly communicating with each other,
as the attacker has inserted themselves between the two parties.


One example of a MITM attack is active eavesdropping,
in which the attacker makes independent connections with the victims and relays messages between them to make them believe they are talking directly to each other over a private connection,
when in fact the entire conversation is controlled by the attacker.
The attacker must be able to intercept all relevant messages passing between the two victims and inject new ones.
This is straightforward in many circumstances; for example, an attacker within the reception range of an unencrypted Wi-Fi access point could insert themselves as a man-in-the-middle.
As it aims to circumvent mutual authentication,
a MITM attack can succeed only when the attacker impersonates each endpoint sufficiently well to satisfy their expectations.
Most cryptographic protocols include some form of endpoint authentication specifically to prevent MITM attacks. For example,
TLS can authenticate one or both parties using a mutually trusted certificate authority.
- open area free of woods and buildings
- what color is a boat’s sternlight?
- which fruit was the first eaten on the moon
- the study of how the body functions is called
- do butterflies have a backbo



