what is the opposite of socialism
Welcom to solsarin site ,Keep reading and find the answer about “ what is the opposite of socialism”.
Stay with us.
Thank you for your support.


What Is Socialism?
Socialism is a populist economic and political system based on public ownership (also known as collective or common ownership) of the means of production. Those means include the machinery, tools, and factories used to produce goods that aim to directly satisfy human needs.
Communism and socialism are umbrella terms referring to two left-wing schools of economic thought; The government determines the output and pricing levels of these goods and services.
Socialists contend that shared ownership of resources and central planning provide a more equal distribution of goods and services and a more equitable society.
Understanding Socialism
Common ownership under socialism may take shape through technocratic, oligarchic, totalitarian, democratic, or even voluntary rule. A prominent historical example of a socialist country is the Soviet Union.
Contemporary examples include Cuba, Venezuela, and China.
Due to its practical challenges and poor track record, socialism is sometimes referred to as a utopian or “post-scarcity” system, although modern adherents believe it could work if only properly implemented.
They argue socialism creates equality and provides security—a worker’s value comes from the amount of time they work, not in the value of what they produce—while capitalism exploits workers for the benefit of the wealthy.
Socialist ideals include production for use, rather than for profit;
an equitable distribution of wealth and material resources among all people; no more competitive buying and selling in the market; and free access to goods and services. Or, as an old socialist slogan describes it, “from each according to ability, to each according to need.”


Origins of Socialism
Socialism developed in opposition to the excesses and abuses of liberal individualism also capitalism. Under early capitalist economies during the late 18th and 19th centuries, western European countries experienced industrial production and compound economic growth at a rapid pace. Some individuals and families rose to riches quickly, while others sank into poverty, creating income inequality and other social concerns.
The most famous early socialist thinkers were Robert Owen
The most famous early socialist thinkers were Robert Owen, Henri de Saint-Simon, Karl Marx, and Vladimir Lenin. It was primarily Lenin who expounded on the ideas of earlier socialists and helped bring socialist planning to the national level after the 1917 Bolshevik Revolution in Russia.
Following the failure of socialist central planning in the Soviet Union and Maoist China during the 20th century,
many modern socialists adjusted to a high regulatory and redistributive system sometimes referred to as market socialism or democratic socialism.
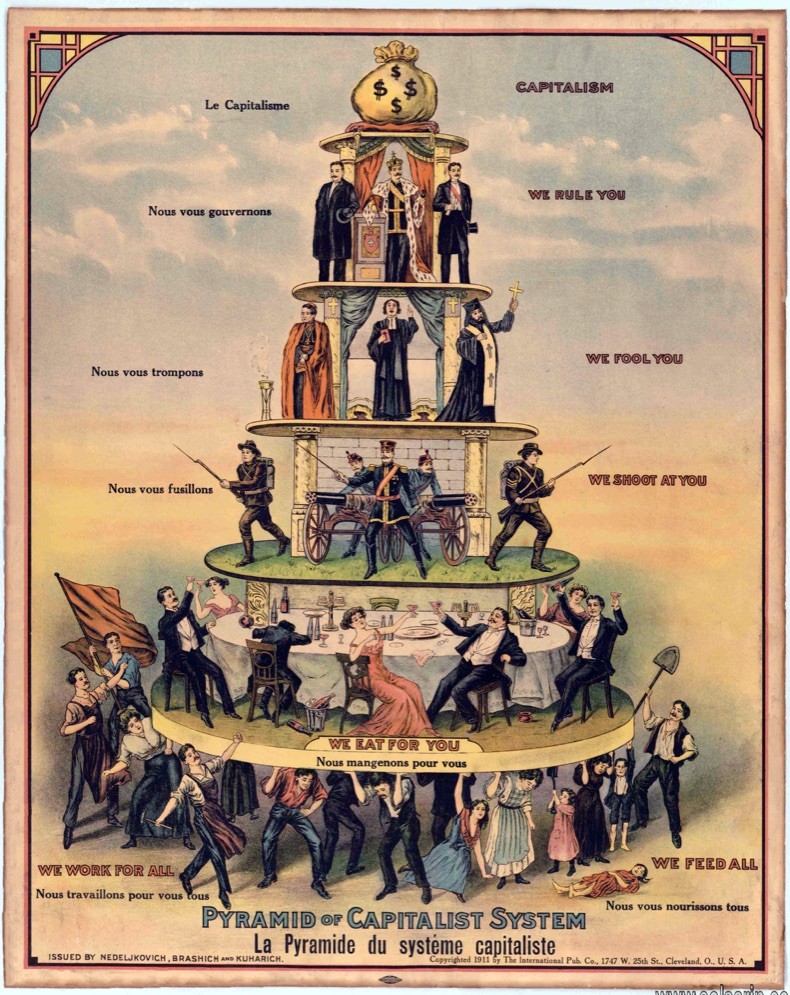

What is an example of a socialism country?
Many countries around the world claim to be socialists. Current states that follow the Marxist-Leninist principles include the Laos People’s Democratic Republic,
the People’s Republic of China, the Republic of Cuba, and the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
What is Communism vs socialism?
The main difference is that under communism, most property and economic resources are owned also controlled by the state (rather than individual citizens); under socialism, all citizens share equally in economic resources as allocated by a democratically-elected government.
What is capitalism?
Capitalism is an economic ideology in which the means of production is controlled by private business. This means that individual citizens run the economy without the government interfering in production or pricing.
Instead, pricing is set by the free market. This means that value is based on supply and demand also the relationship between producers and consumers.
Capitalism is very different from socialism and communism,
in which the government maintains tight control of the economy. The United States is arguably the most well-known country with a capitalist economy, which many citizens see as an essential part of democracy and building the “American Dream.”
Capitalism also taps into the American spirit, being a more “free” market when compared to the more government-controlled alternatives.

Socialism vs. Capitalism
Capitalist economies (also known as free-market or market economies) and socialist economies differ by their logical underpinnings, stated or implied objectives, and structures of ownership and production. Socialists and free-market economists tend to agree on fundamental economics—the supply and demand framework, for instance—while disagreeing about its proper adaptation.
Several philosophical questions also lie at the heart of the debate between socialism and capitalism:
What is the role of government?
What constitutes a human right?
What roles should equality and justice play in society?
Bones of Contention
There are many points of contention between these two systems. Socialists consider capitalism and the free market to be unfair and possibly unsustainable.
For example, most socialists contend that market capitalism is incapable of providing enough subsistence to the lower classes. They contend that greedy owners suppress wages and seek to retain profits for themselves.
Proponents of market capitalism counter that it is impossible for socialist economies to allocate scarce resources efficiently without real market prices.
They claim that the resultant shortages, surpluses, and political corruption will lead to more poverty, not less. Overall, they say, that socialism is impractical and inefficient, suffering in particular from two major challenges.
The first challenge, widely called the “incentive problem,” says no one wants to be a sanitation worker or wash skyscraper windows.
That is, socialist planners cannot incentivize laborers to accept dangerous or uncomfortable jobs without violating the equality of outcomes.
Far more serious is the calculation problem, a concept originating from economist Ludwig von Mises’ 1920 article “Economic Calculation in the Socialist Commonwealth”.
Socialists, wrote Mises, are unable to perform any real economic calculation without a pricing mechanism.
Without accurate factor costs, no true accounting may take place. Without futures markets, capital can never reorganize efficiently over time.
How Mixed Economies Develop
Mixed economies are still relatively young and theories around them have only recently codified.
The Wealth of Nations, Adam Smith’s pioneering economic treatise, argued that markets were spontaneous and that the state could not direct them, or the economy.
Later economists including John-Baptiste Say, F.A. Hayek, Milton Friedman, also Joseph Schumpeter would expand on this idea.
However, in 1985, political economy theorists Wolfgang Streeck and Philippe C. Historically, mixed economies have followed two types of trajectories. The first type assumes that private individuals have the right to own property, produce, and trade. State intervention has developed gradually, usually in the name of protecting consumers, supporting industries crucial to the public good (in fields like energy or communications), providing welfare, or other aspects of the social safety net. however Most western democracies, such as the United States, follow this model.
The second trajectory involves states that evolved from pure collectivist or totalitarian regimes. Individuals’ interests are considered a distant second to state interests, but elements of capitalism are adopted to promote economic growth. China and Russia are examples of the second model.
Transitioning From Socialism
in like manner a nation needs to transfer the means of production to transition from socialism to free markets.
Privatization occurs whenever ownership rights transfer from a coercive public authority to a private actor, whether it is a company or an individual. Different forms of privatization include contracting out to private firms, awarding franchises, and the outright sale of government assets, or divestiture.
In some cases
In some cases, privatization is not really privatization.
Case in point: private prisons. It is important to remember that not all transfers of government control result in a free market.
Privatizing a Socialist Economy
Some nationwide privatization efforts have been relatively mild, while others have been dramatic. The most striking examples include the former satellite nations of the Soviet Bloc after the collapse of the U.S.S.R. and the modernization of the post-Mao Chinese government.
The privatization process involves several different kinds of reforms, not all of them completely economic.
Should these transfers be gradual or immediate?
What are the impacts of shocking an economy built around central control? Can firms be effectively depoliticized? As the struggles in Eastern Europe in the 1990s show, it can be very difficult for a population to adjust from complete state control to suddenly having political and economic freedoms.
what countries are a mix of socialism and capitalism?
- open area free of woods and buildings
- what color is a boat’s sternlight?
- which fruit was the first eaten on the moon
- the study of how the body functions is called
- do butterflies have a backbo



