when does fog usually form in inlets and bays?
Hello dear friends, thank you for choosing us. In this post on the solsarin site, we will talk about “when does fog usually form in inlets and bays?”.
Stay with us.
Thank you for your choice.
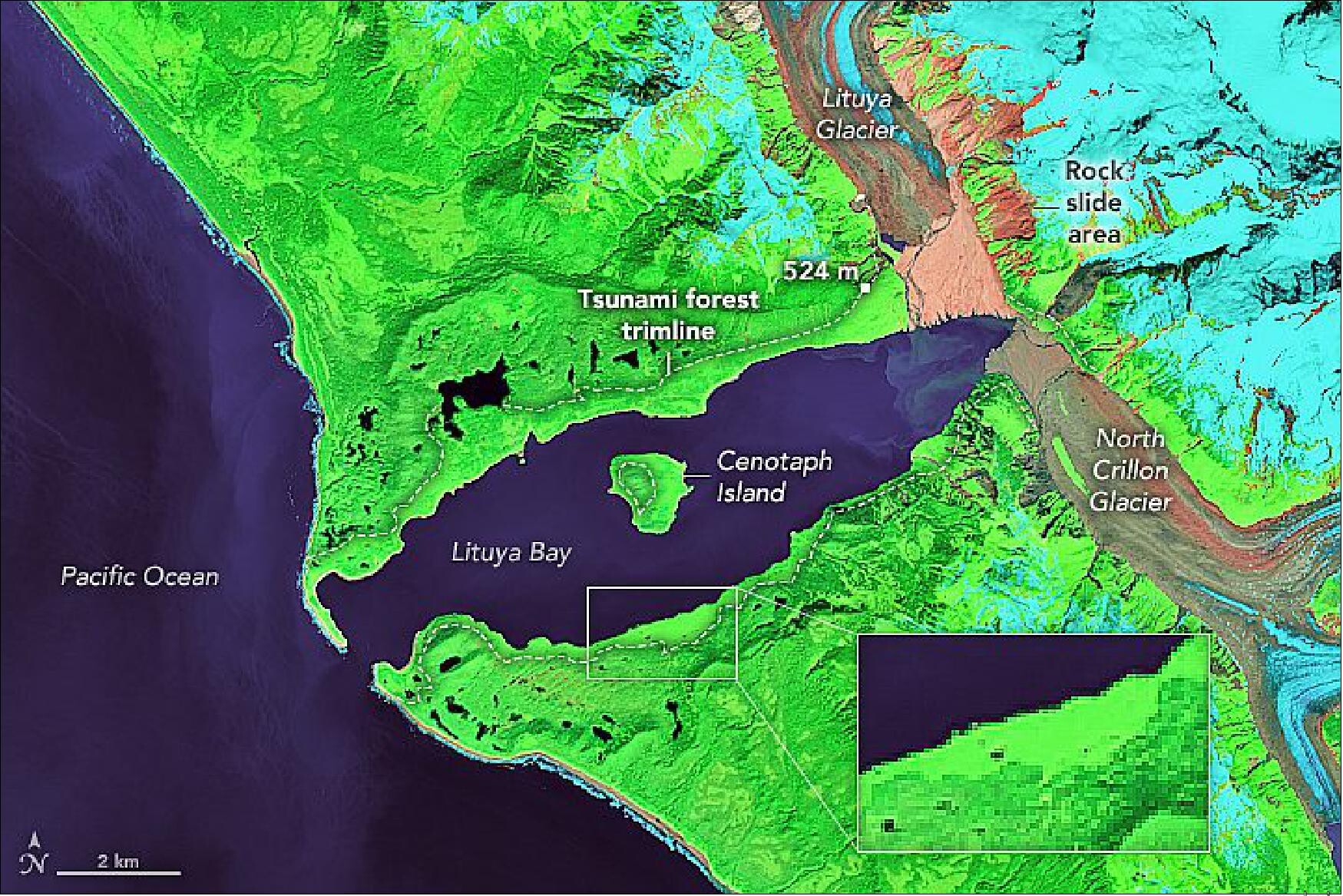

when does fog usually form in inlets and bays
when does fog usually form in inlets and bays boat ed
Fog will form if the air temperature drops below the dew point, which is the capacity of the air to hold moisture in suspension. If the temperature drop far enough the moisture content will exceed saturation point, causing it to form visible water vapour.
when does fog normally form in inlets and bays
How to Avoid Severe Weather (cont.)
Be alert to weather conditions, watching especially for the possibility of fog, squalls, thunderstorms, sudden wind, and ice. Accumulating dark clouds, shifting winds, and graying skies all may be indications of danger. Listen for distant thunder.
Track changes in barometer readings. A rising barometer indicates fair weather. A falling barometer indicates foul weather is approaching.
Watch for wind direction shifts, which usually indicate a weather change.
Watch for lightning and rough water. If not electrically grounded, pleasure craft (particularly sailboats) are vulnerable to lightning.
Be observant of weather from all directions; however, closely watch the weather to the west, the direction from which most bad weather arrives.
Watch for fog that restricts visibility and creates problems in inlets and bays. Typically, fog will form during the temperature changes of the early morning or evening hours and can persist for lengthy periods.
Head toward the nearest safe shore if a thunderstorm is approaching.
Fog Over Water
Fog that forms over water is commonly referred to as sea fog or lake fog. It forms when warm, moist air flows over relatively colder waters. Sea or lake fog can occur over the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, the Gulf of Mexico, the Great Lakes and other bodies of water.
Fog is common along the U.S. Pacific coastline year round because the water is typically much colder than the nearby land. Sea fog is a type of advection fog, and therefore can move into land areas and result in hazards to motorists.

Sometimes radiation fog that forms over land can move over bays, harbors, inlets, the intra-coastal and nearby ocean waters.
While this is not pure sea fog, it can also be a concern for mariners. The National Weather Service issues Dense Fog Advisories when fog over water reduces visibility to 1 mile or less.




