why are enzymes important to biological systems?
Hi, welcome to solsarin site, in this post we want to talk about“why are enzymes important to biological systems?”,

What is the biological importance of enzymes?
Enzymes are proteins that help speed up chemical reactions in our bodies. Enzymes are essential for digestion, liver function and much more. Too much or too little of a certain enzyme can cause health problems. Enzymes in our blood can also help healthcare providers check for injuries and diseases.
What is a biological catalyst called?
Enzymes are substances found in biological systems that are catalysts for specific biochemical processes.
What is enzyme catalysis with example?
Examples of enzyme-catalyzed reactions
Conversion of starch into maltose: Diastase is an enzyme that converts starch to maltose. Conversion of maltose into glucose: Maltase is an enzyme that converts maltose to glucose.
What is meant by the two terms biological catalyst?
A biological catalyst is an enzyme. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions inside cells.
Are enzymes biological catalysts?
Biological catalysts are called enzymes. There is, for instance, an enzyme in our saliva which converts starch to a simple sugar, which is used by the cell to produce energy, and another enzyme which degrades the excess lactic acid produced when we overexert ourselves.
How do enzymes act as a catalyst?
Enzymes are biological catalysts. Catalysts lower the activation energy for reactions. The lower the activation energy for a reaction, the faster the rate. Thus enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
How enzymes are used in catalysis process?
A single molecule of the enzyme catalyst can transform up to a million molecules of the reactant per second. Hence, enzyme catalysts are said to be highly efficient. These biochemical catalysts are unique to certain types of reactions, i.e. the same catalyst cannot be used in more than one reaction.
What is enzyme catalysis example?
Examples of enzyme-catalyzed reactions
Conversion of glucose into ethyl alcohol: The zymase enzyme breaks down glucose to produce ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide. Conversion of starch into maltose: Diastase is an enzyme that converts starch to maltose.
Why is an enzyme called a catalyst?
Enzymes are proteins that have a specific function. They speed up the rate of chemical reactions in a cell or outside a cell. Enzymes act as catalysts; they do not get consumed in the chemical reactions that they accelerate.
What are the 4 functions of enzymes?
Enzymes catalyze all kinds of chemical reactions that are involved in growth, blood coagulation, healing, diseases, breathing, digestion, reproduction, and many other biological activities. On biological aspects, enzymes are instrumental substances to many functions in living organisms.
What is the role of an enzyme?
Enzymes are proteins that help speed up chemical reactions in our bodies. Enzymes are essential for digestion, liver function and much more. Too much or too little of a certain enzyme can cause health problems. Enzymes in our blood can also help healthcare providers check for injuries and diseases.
What are uses for enzymes?
Enzymes are used in the food, agricultural, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries to control and speed up reactions in order to quickly and accurately obtain a valuable final product. Enzymes are crucial to making cheese, brewing beer, baking bread, extracting fruit juice, tanning leather, and much more.
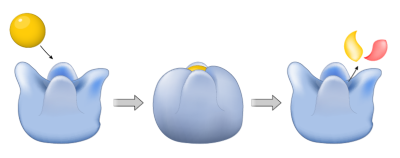

How does enzyme work?
How do enzymes work? Enzymes are not living organisms, they are biological substances that catalyse very specific biochemical reactions. When enzymes find their designated substrate, they lock on and transform them, and then continue to the next substrate molecule
What are three functions of enzymes?
The function of enzymes is to carry out critical tasks. These involve muscle growth, removing toxins, and tearing down the molecules in food throughout digestion.
What relationship exists between an enzyme and catalysts?
Enzymes are biological catalysts. Catalysts lower the activation energy for reactions. The lower the activation energy for a reaction, the faster the rate. Thus enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy.
Which industrial process uses enzymes as a catalyst?
Enzymes are used in industrial processes, such as baking, brewing, detergents, fermented products, pharmaceuticals, textiles, leather processing.
Why are enzymes useful industrial catalyst?
Like all catalysts, enzymes work by lowering the activation energy for a reaction, thus dramatically increasing the rate of the reaction. As a result, products are formed faster and reactions reach their equilibrium state more rapidly.
What is a catalyst in chemistry?
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, or lowers the temperature or pressure needed to start one, without itself being consumed during the reaction. Catalysis is the process of adding a catalyst to facilitate a reaction.
What is a catalyst in biology?
A catalyst is a molecule which can facilitate a chemical reaction without being consumed or changed. Virtually all chemical reactions taking place in a living cell require catalysts. Such biocatalysts are called enzymes.
Are all enzymes catalysts?
Posted January 29, 2021. Both, enzymes and catalysts affect the rate of a reaction without being consumed in the reactions themselves. All known enzymes are catalysts, but not all catalysts are enzymes.
What are the six functions of the enzymes?
According to the International Union of Biochemists (I U B), enzymes are divided into six functional classes and are classified based on the type of reaction in which they are used to catalyze. The six kinds of enzymes are hydrolases, oxidoreductases, lyases, transferases, ligases and isomerases.
Can enzymes catalyze multiple reactions?
It has been well documented that ROs catalyze a variety of other reactions, including mono-oxygenation, desaturation, O- and N-dealkylation, sulfoxidation etc. NDO itself catalyzes a variety of these reactions.
How does an enzyme perform catalytic activity with substrate molecule?
An enzyme can perform catalytic activity on the substrate by either arranging the substrate in a manner that is favorable for reaction, separate charge across a molecule, or induce strain to force the molecule to react with another in the active site.
What types of enzymes are used in industry?
The main industrial enzymes can be classified in three groups: carbohydrases, proteases, and lipases. Amylases are comprised in the carbohydrase group, together with cellulases, glucose isomerase, glucose oxidase, pectinases, xylanases, invertase, galactosidase, and others
How are enzymes used in manufacturing?
Some Examples Of Industrial Uses Of Enzymes: Rennin for coagulation of milk to make cheese. Invertase from yeast and lactase in the food industry. Cellulase and amylase to remove waxes, oils, and starch coatings on fabrics and to improve the look of the final product.
What are the 3 types of catalysis?
Catalysts and their associated catalytic reactions come in three main types: homogeneous catalysts, heterogeneous catalysts and biocatalysts (usually called enzymes). Less common but still important types of catalyst activities include photocatalysis, environmental catalysis and green catalytic processes.

How are catalysts made?
Manufacturing of Industrial Catalysts. Industrial catalyst manufacturing involves several process steps such as preparation and mixing of solutions or suspensions, crystallization, filtration, washing, mixing and kneading of powders, shaping drying, impregnation and calcination.
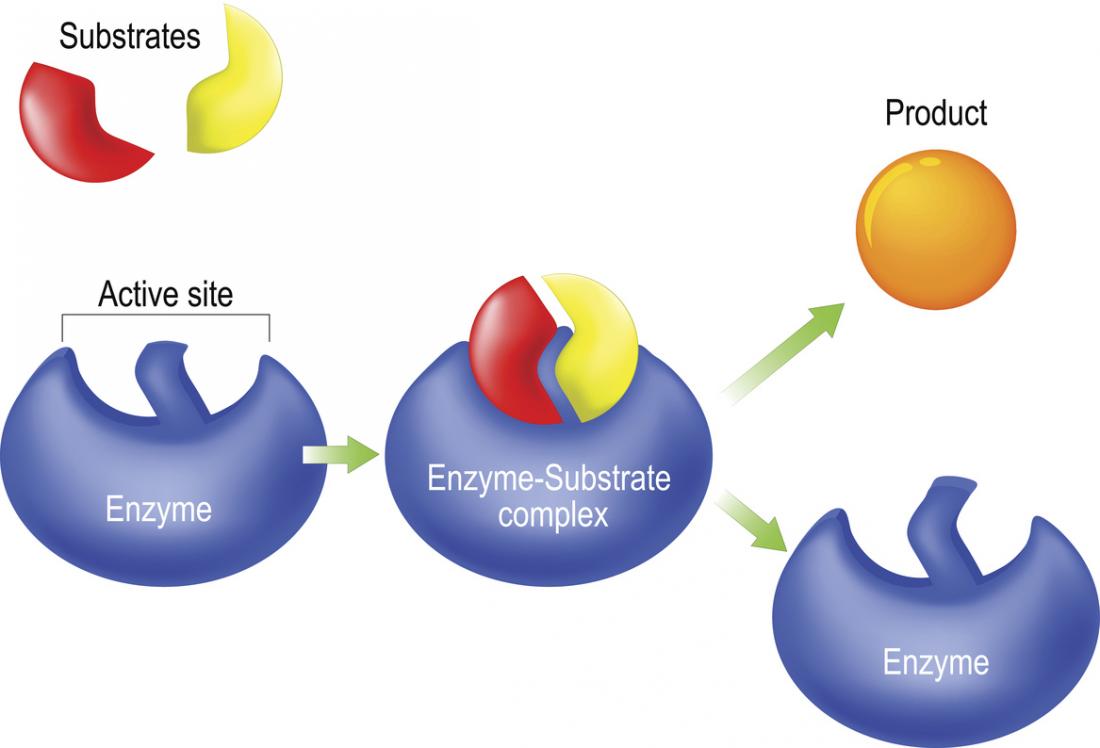
What happens to an enzyme after it has catalyzed a reaction?
Enzymes are not reactants and are not used up during the reaction. Once an enzyme binds to a substrate and catalyzes the reaction, the enzyme is released, unchanged, and can be used for another reaction. This means that for each reaction, there does not need to be a 1:1 ratio between enzyme and substrate molecules.
What happens in the final step of enzymatic catalysis?
the products are released and the enzyme is free to bind other substrates. requires the inorganic coenzyme zinc. An increase in either substrate or enzyme concentration will increase the reaction rate.
What are enzymes made of?
Enzymes are proteins comprised of amino acids linked together in one or more polypeptide chains. This sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is called the primary structure. This, in turn, determines the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme, including the shape of the active site.
Who discovered enzyme catalysis?
By the late 17th and early 18th centuries, the digestion of meat by stomach secretions and the conversion of starch to sugars by plant extracts and saliva were known but the mechanisms by which these occurred had not been identified. French chemist Anselme Payen was the first to discover an enzyme, diastase, in 1833.
What is the most important enzyme?
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, better known by the name Rubisco, is the key enzyme responsible for photosynthetic and chemoautotrophic carbon fixation and oxygen metabolism. Scientists believe it is the most abundant enzyme on the planet.
What would happen if there were no catalysts?
“Without catalysts, there would be no life at all, from microbes to humans,” he said. “It makes you wonder how natural selection operated in such a way as to produce a protein that got off the ground as a primitive catalyst for such an extraordinarily slow reaction.”
What is catalase mean?
Definition of catalase
: a red crystalline enzyme that consists of a protein complex with hematin groups and catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.

Is enzyme a catalyst?
An enzyme is a biological catalyst and is almost always a protein. It speeds up the rate of a specific chemical reaction in the cell. The enzyme is not destroyed during the reaction and is used over and over.



