why is water considered to be abiotic?
Hi, welcome to solsarin site, today we want to talk about“why is water considered to be abiotic?”,
thank you for choosing us.
why is water considered to be abiotic?
Water is considered to be abiotic because it is a nonliving component of an ecosystem.
Water (H2O) is a very important Abiotic factor – it is often said that “water is life. ” All living organisms need water. Plants must have water to grow. Even plants that live in the desert need a little bit of water to grow. Without water, animals become weak and confused, and they can die if they do not rehydrate.
Is water considered to be abiotic?
An abiotic factor is a non-living part of an ecosystem that shapes its environment. In a terrestrial ecosystem, examples might include temperature, light, and water.
What is biotic and abiotic in water?
moreover, Abiotic factors refer to non-living physical and chemical elements in the ecosystem. Abiotic resources are usually obtained from the lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere. Examples of abiotic factors are water, air, soil, sunlight, and minerals. Biotic factors are living or once-living organisms in the ecosystem.
What Does Abiotic Mean?
An abiotic is a physical and non-living factor. This can include chemicals or parts of the ecosystem. moreover,Abiotics serve as components of degradation and corrosion by physical and chemical processes such as in hydrolysis.


Abiotic Factors
Evidently, the light and heat from the sun play an important role in providing suitable conditions. However, the water conditions also inevitably have an effect on life in the ecosystem.
A still body of water will inevitably be disturbed by various factors, which will affect the distribution of organisms in the water. Wind is considered to be the prime factor responsible for disturbing water, though changes in temperature can create convection currents where temperature is evened out across the body of water via this movement.
Naturally, a river will have water movement as water succumbs to gravity and moves downstream. These are relatively constant factors that affect water movement though, for example, human intervention can also cause water movement. The surface tension of the water will also affect the organisms that occupy the area, depending on the cohesion of water at the surface, it can affect the amount of oxygen that reaches organisms living below the water surface.
These factors all affect the way of life for organisms occupying such a freshwater ecosystem. On a more molecular level, the chemical compositions of the water, soil and surrounding air also play a part in determining the face of the ecosystem.
Oxygen
The oxygen concentration of the water and the surrounding air will have great bearing on which organisms can survive in a particular environment. Oxygen is required for aerobic respiration in animals, and the concentration of oxygen in an area is determined by many factors, including temperature and abundance of organisms for example.
Water temperature
Temperature will affect the ability of an organism to carry out metabolism; the warmer the conditions the better able enzymes can operate. You might expect lowland water to be warmer than that in upland. However, water does provide a stable temperature over short periods of time
This will vary not only along the length of the river but also through seasonal and even diurnal periods. The altitude, local climate and the extent of the vegetation at the side of the river will influence temperature. The external environment will determine their internal temperature and therefore metabolic activity. This varies enormously between species, especially their threshold of survival ability. For example, some insect eggs when laid in autumn will not hatch until the spring if the temperature is too low. Also warmer temperatures increase the rate at which the larvae feed and grow. moreover,There is always an upper limit above which all metabolism will slow down. 25∘C is the upper limit for many midge larvae although black fly can survive substantially above this.
Abiotic Factors in the Ocean
The ocean hosts some unique abiotic factors. Notably, the ocean contains salt. It also has the attribute of depth, which affects the amount of sunlight that sea life receives.
The saltiness of the ocean is important for the animals living there. All creatures must adapt to prevent the ocean’s salt from disrupting their biochemistry. Dolphins that swim in the ocean get all of their water from their prey animals because the saltwater would dehydrate them. Some fish can survive only in saltwater because they have adapted so well to the environment.
The ocean, like the rainforest, also has a number of different zones that receive different amounts of sunlight and host very different types of life. This is because water itself both blocks out and absorbs sunlight.
moreover, Life in the topmost zone of the ocean, called the epipelagic zone, receives a large amount of sunlight. This is where photosynthetic ocean life, like coral and seaweed, is found.
By contrast, the abyssopelagic zone at the bottom of the ocean receives almost no sunlight. This part of the ocean hosts strange sea creatures, some of which cannot survive at the surface because their body structures depend on the high water pressure at depth.
As a result of these abiotic factors, there are different ocean ecosystems, such as shoreline ecosystems, coral reef ecosystems, and deep ocean ecosystems.
Water pH
pH can vary enormously between ponds and lakes, due to bedrock, topography and even the species of plant present. For example on heathlands where ponds form, there are likely to be Sphagnum or bog mosses present that increase acidity. Some animals are specific to calcium-rich, alkaline water like the crayfish. In addition, snails need calcium for their shells and so will be limited to waters rich in this mineral. The most significant aspect to pH is the amount of carbonic acid present. Carbon dioxide dissolves in water to produce carbonic acid so it is a measurement of the level of CO2 available for photosynthesis. The pH is often a limiting factor of enzyme-controlled reactions.
Examples of Abiotic Factors
moreover, Abiotic examples typically depend on the type of ecosystem. For instance, abiotic components in a terrestrial ecosystem include air, weather, water, temperature, humidity, altitude, the pH level of soil, type of soil and more.moreover, Abiotic examples in an aquatic ecosystem include water salinity, oxygen levels, pH levels, water flow rate, water depth and temperature.
What Defines a Biotic Component?
A bunch of red rocks? Craters? Little green aliens? Believe it or not, the closest answer actually is little green aliens. Scientists have yet to find any life on Mars (bacteria, little green aliens, or otherwise). As far as we know, the one thing that Earth has that no other planet has is life, otherwise known as biotic components.
moreover, Biotic components are all the living things in an ecosystem. They are the animals, the plants and the microorganisms. Biotic components also include the waste from living things and dead organisms. Even the harshest corners of our planet have biotic components. Earth is teaming with biotic beings.
However, ecosystems also contain abiotic components which are the non-living parts of an ecosystem. These can include everything from rocks to temperature, sunlight, clouds, and chemicals in the soil.
Examples of Biotic Factors
Examples of biotic resources include all the living components present in an ecosystem. moreover, These include producers, consumers, decomposers and detritivores.
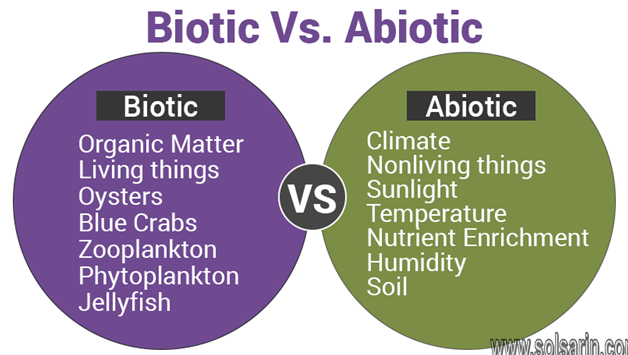

Difference between Abiotic and Biotic Resources
Following are the important difference between abiotic and biotic factors:
| Difference Between Biotic Resources and Abiotic Resources | |
| Biotic Resources | Abiotic Resources |
| Definition | |
| Biotic factors include all the living components present in an ecosystem | Abiotic factors refer to all the non-living, i.e. physical conditions and chemical factors that influence an ecosystem |
| Examples | |
| Examples of biotic resources include all flora and fauna | abiotic factors include sunlight, water, air, humidity, pH, temperature, salinity, precipitation, altitude, type of soil, minerals, wind, dissolved oxygen, mineral nutrients present in the soil, air and water, etc. |
| Dependence | |
| Biotic factors depend on abiotic factors for survival and reproduction | Abiotic factors are completely independent of biotic factors |
| Origin | |
| Biotic components originate from the biosphere | Abiotic components originate from the lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere |
Abiotic Factors vs Biotic Factors
Whereas abiotic factors are the non-living factors that influence an ecosystem, biotic factors are all the living components. Biotic factors include the organisms and any decaying organic matter present in the environment. There are various differences between biotic and abiotic factors, but both have profound effects on the balance of an ecosystem. To learn more, visit this article, which compares the features of abiotic and biotic factors.
MORE POSTS:




