carbon forms bonds with a maximum of how many other atoms?
Hi, welcome to solsarin site, in this post we want to talk about“carbon forms bonds with a maximum of how many other atoms?”,
stay with us.
carbon forms bonds with a maximum of how many other atoms?
The maximum number of covalent bond than an atom of carbon can form is 4
The atomic number of C is 6. Its electronic configuration is 1s22s22p2
Thus in the valence shell of C atom, 4 electrons are present which it can share with 4 other atoms to form 4 covalent bonds.
How many more electrons does carbon need to have a full outer energy level?
Carbon needs four more valence electrons, or a total of eight valence electrons, to fill its outer energy level. A full outer energy level is the most stable arrangement of electrons.
How can carbon achieve a full outer energy level?
Carbon can form four covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are chemical bonds that form between nonmetals. In a covalent bond, two atoms share a pair of electrons. By forming four covalent bonds, carbon shares four pairs of electrons, thus filling its outer energy level and achieving stability.
carbon
Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. This means that carbon atoms, bonded to other carbon atoms or other elements, form the fundamental components of many, if not most, of the molecules found uniquely in living things. Other elements play important roles in biological molecules, but carbon certainly qualifies as the “foundation” element for molecules in living things. It is the bonding properties of carbon atoms that are responsible for its important role.


Carbon Bonding
The four covalent bonding positions of the carbon atom can give rise to a wide diversity of compounds with many functions, accounting for the importance of carbon in living things.
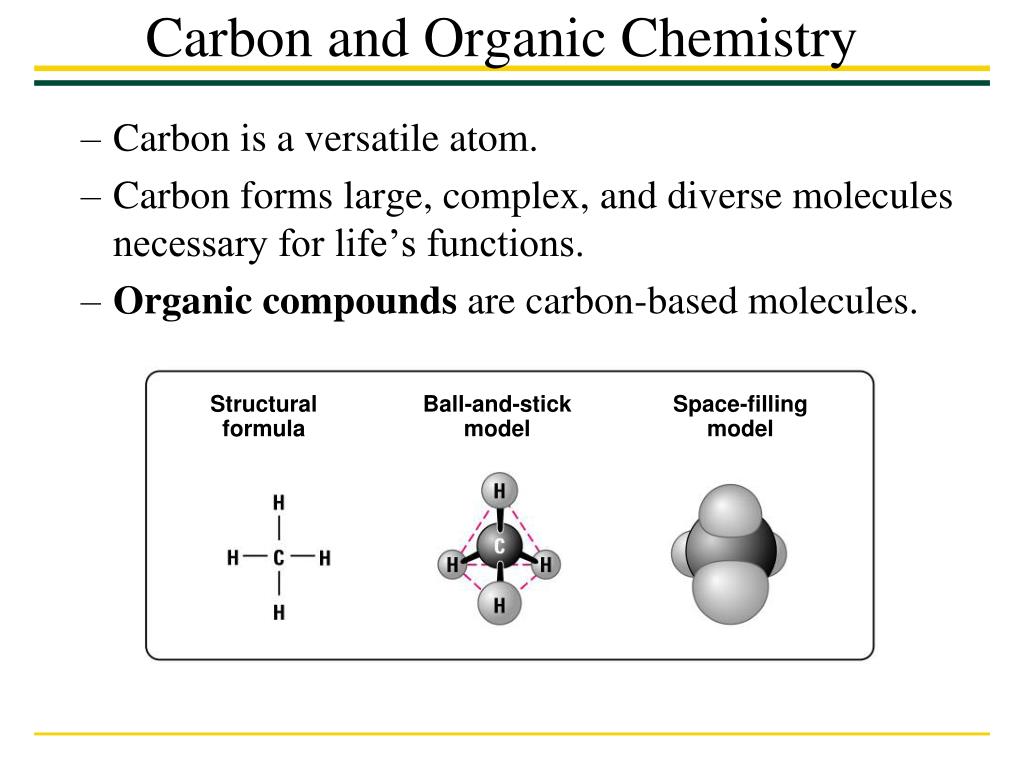
Carbon contains four electrons in its outer shell. Therefore, it can form four covalent bonds with other atoms or molecules. The simplest organic carbon molecule is methane (CH4), in which four hydrogen atoms bind to a carbon atom .
However, structures that are more complex are made using carbon. Any of the hydrogen atoms can be replaced with another carbon atom covalently bonded to the first carbon atom. In this way, long and branching chains of carbon compounds can be made (Figure 2a). The carbon atoms may bond with atoms of other elements, such as nitrogen, oxygen, and phosphorus . The molecules may also form rings, which themselves can link with other rings. This diversity of molecular forms accounts for the diversity of functions of the biological macromolecules and is based to a large degree on the ability of carbon to form multiple bonds with itself and other atoms.
How does carbon bond?
Carbon is a non-metal with an atomic number of 6, meaning it has six protons and six electrons. It has the electron configuration
Ignoring sub-shells, we can see in the image below that carbon has four electrons in its outer shell, also known as its valence shell.
This means that carbon can form up to four covalent bonds with other atoms. If you remember from Covalent Bond, a covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons. In fact, carbon is rarely found with anything other than four bonds because forming four covalent bonds means it has eight valence electrons. This gives it the electron configuration of a noble gas with a full outer shell, which is a stable arrangement.
These four covalent bonds can be between carbon and almost any other element, be it another carbon atom, an alcohol group (-OH) or nitrogen. However, in this article we are concerned with the various structures it forms when it bonds with other carbon atoms to make different allotropes. We refer to all these different allotropes as carbon structures. They include diamond and graphite. Let’s explore them both further.

The Three Covalent Bonds
Single bonds are a type of covalent bond formed from the sharing of two electrons between two atoms, one electron from each atom. Now this is quite different from double bonds. Double bonds are a type of covalent bond where four electrons are shared between two atoms. This leads us to the last type of bond, a triple bond. A triple bond is a type of covalent bond where six electrons are shared between two atoms. The take away with each of these bonds is the word ‘sharing.’ Remember this is the basis for covalent bonding.
Covalent Bonding and Covalent Compounds
A covalent bond is the interatomic bond formed by the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. The electrostatic attraction of the nuclei of the two atoms for the identical electrons causes the bonding in covalent compounds.
A covalent compound is a molecule produced by covalent bonds in which one or more pairs of valence electrons are shared by the atoms.
Types of Covalent Bonds
All bonds are represented as single lines in the ethane Lewis formula shown.Each bond is made up of two electrons, known as bonding electrons. It is also feasible for two atoms to share four electrons if they are bound together. This bonding structure, known as a double bond, is illustrated by two lines representing two electrons.

Why does carbon form covalent bonds?
Bonding in carbon
- Carbon is a non-metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Like other group 14 elements, carbon has four valence electrons. Carbon can form four covalent bonds.
- Covalent bonds are chemical bonds that form between non-metals. In a covalent bond, two atoms share a pair of electrons.
- By forming four covalent bonds, carbon shares four electrons’ pairs, thus filling its outer energy level and achieving stability.
- Electrons in a covalent bond are shared equally between the atoms.
- The only pure covalent bonds occur between identical atoms. Compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. An example is Methane (CH4 )
- In methane, a single carbon atom forms covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms. Carbon can form single, double, or even triple bonds with other carbon atoms.
Why Carbon Is An Important Element?
Hands down, carbon is perhaps one of the most important elements fundamental to living. A highly abundant element found on earth, you can find carbon’s presence everywhere. It is located in the compound, chlorophyll, giving plants its green color. It is the building block for numerous organic compounds within our body, such as proteins, DNA, and amino acids (to name a few).
Of course, it is also found in numerous simple and complex organic compounds that are synthesized to make so many of the commercial products we use on a daily basis. What contributes to carbon’s vast abundance throughout the earth? One reason may stem from the versatility of bonding with carbon. Before we address these different bond types, let’s go over the molecular shape of carbon.

What happens when the bonds are formed?
Remember that hydrogen’s electron is in a 1s orbital – a spherically symmetric region of space surrounding the nucleus where there is some fixed chance (say 95%) of finding the electron. When a covalent bond is formed, the atomic orbitals (the orbitals in the individual atoms) merge to produce a new molecular orbital which contains the electron pair which creates the bond.
Four molecular orbitals are formed, looking rather like the original sp3 hybrids, but with a hydrogen nucleus embedded in each lobe. Each orbital holds the 2 electrons that we’ve previously drawn as a dot and a cross.
The principles involved – promotion of electrons if necessary, then hybridisation, followed by the formation of molecular orbitals – can be applied to any covalently-bound molecule.
Properties of Covalent Bonds
- They are extremely strong chemical bonds formed between atoms.
- They don’t generate additional electrons. The link just connects them.
- They seldom dissolve spontaneously after formation.
- They are directional, meaning the linked atoms have distinct orientations relative to one another.
- Most covalently bound chemicals have relatively low melting and boiling points.
- Covalently bound compounds often have lower enthalpies of vaporisation and fusion.
- Due to a lack of free electrons, covalent molecules do not conduct electricity.
- Water does not dissolve covalent compounds.
MORE POSTS: