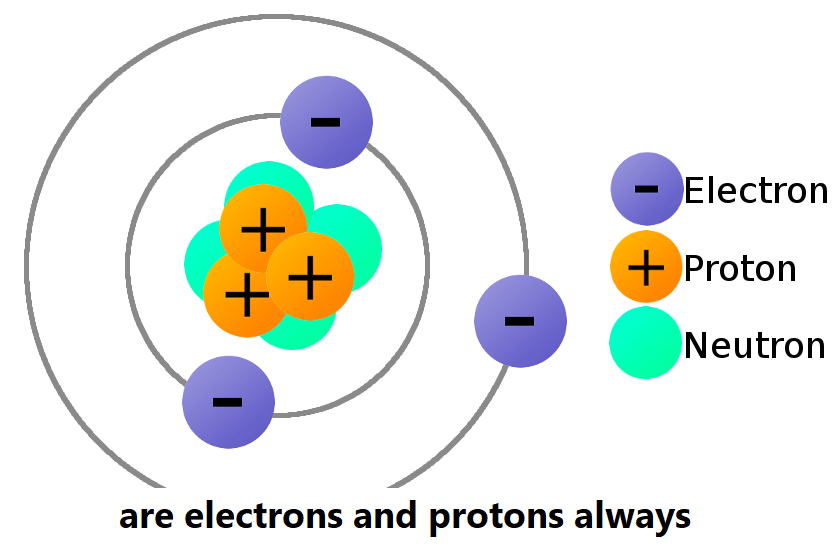
are electrons and protons always
Hello dear friends, In this post on Solsarin we’re mentioning “are electrons and protons always”. Stay with us to the end. Thanks for being with us.
Electrons
Electrons are one of three main types of particles that make up atoms. Unlike protons and neutrons, which consist of smaller, simpler particles, electrons are fundamental particles that do not consist of smaller particles. They are a type of fundamental particle called leptons. All leptons have an electric charge of −1−1 or 00. Electrons are extremely small. The mass of an electron is only about 1/2000 the mass of a proton or neutron, so electrons contribute virtually nothing to the total mass of an atom. Electrons have an electric charge of −1−1, which is equal but opposite to the charge of a proton, which is +1+1. All atoms have the same number of electrons as protons, so the positive and negative charges “cancel out”, making atoms electrically neutral.
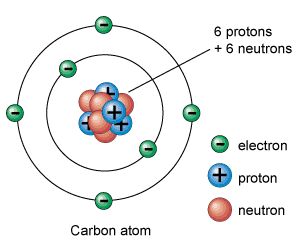

Unlike protons and neutrons, which are located inside the nucleus at the center of the atom, electrons are found outside the nucleus. Because opposite electric charges attract one another, negative electrons are attracted to the positive nucleus. This force of attraction keeps electrons constantly moving through the otherwise empty space around the nucleus. The figure below is a common way to represent the structure of an atom. It shows the electron as a particle orbiting the nucleus, similar to the way that planets orbit the sun. However, this is an incorrect perspective, as quantum mechanics demonstrates that electrons are more complicated.
Protons
A proton is one of three main particles that make up the atom. Protons are found in the nucleus of the atom. This is a tiny, dense region at the center of the atom. Protons have a positive electrical charge of one (+1)(+1) and a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (amu)(amu), which is about 1.67×10−271.67×10−27 kilograms. Together with neutrons, they make up virtually all of the mass of an atom.
MORE POSTS:
- jack russell terrier lifespan
- is garth brooks and trisha yearwood divorced
- where did samba originate?
- is george soros an american citizen
- hedgehogs natural immunity
Neutrons
Atoms of all elements—except for most atoms of hydrogen—have neutrons in their nucleus. Unlike protons and electrons, which are electrically charged, neutrons have no charge—they are electrically neutral. That’s why the neutrons in the diagram above are labeled n0n0. The zero stands for “zero charge”. The mass of a neutron is slightly greater than the mass of a proton, which is 1 atomic mass unit (amu)(amu). (An atomic mass unit equals about 1.67×10−271.67×10−27 kilograms.) A neutron also has about the same diameter as a proton, or 1.7×10−151.7×10−15 meters.
As you might have already guessed from its name, the neutron is neutral. In other words, it has no charge whatsoever and is therefore neither attracted to nor repelled from other objects. Neutrons are in every atom (with one exception), and they are bound together with other neutrons and protons in the atomic nucleus.
Before we move on, we must discuss how the different types of subatomic particles interact with each other. When it comes to neutrons, the answer is obvious. Since neutrons are neither attracted to nor repelled from objects, they don’t really interact with protons or electrons (beyond being bound into the nucleus with the protons).
Even though electrons, protons, and neutrons are all types of subatomic particles, they are not all the same size. When you compare the masses of electrons, protons, and neutrons, what you find is that electrons have an extremely small mass, compared to either protons or neutrons. On the other hand, the masses of protons and neutrons are fairly similar, although technically, the mass of a neutron is slightly larger than the mass of a proton. Because protons and neutrons are so much more massive than electrons, almost all of the mass of any atom comes from the nucleus, which contains all of the neutrons and protons.


Does number of protons always equal to number of electrons?
Number of protons always equal number of electron, but that’s the case with a neutral atom.
A neutral atom is an atom of any element that has no electric charge over it.
This implies that it has same number of protons and electrons in it.
It means it has same amount of positive and negative charge, which cancel each other, and the atom as a whole becomes electrically neutral.
But in case an atom tends to form an ionic Bond with any other atom, it either loses or gains electron(the number of electrons lost or gained depends on the number of electrons present in the valence shell of the atom) and becomes ionized. In this case, the number of electron and proton differ.
Thus, in an ionized atom or simply an ion, the number of protons and electrons are not the same but in a neutral atom they are.
Why do atoms always contain the same number of electrons and protons?
Atoms do not always contain the same number of electrons and protons, although this state is common. When an atom has an equal number of electrons and protons, it has an equal number of negative electric charges (the electrons) and positive electric charges (the protons). The total electric charge of the atom is therefore zero and the atom is said to be neutral. In contrast, when an atom loses or gains an electron (or the rarer case of losing or gaining a proton, which requires a nuclear reaction), the total charges add up to something other than zero. The atom is then said to be electrically charged, or “ionized”. There is a major difference between the neutral state and the ionized state. In the neutral state, an atom has little electromagnetic attraction to other atoms. Note that the electric field of a neutral atom is weak, but is not exactly zero because the atom is not a point particle. If another atom gets close enough to the atom, they may begin to share electrons. Chemically, we say that the atoms have formed bonds.

In contrast to neutral atoms, the field due to an ionized atom is strong, even at larger distances. The strong electric field of ions makes them strongly attracted to other atoms and molecules, to the point of being highly chemically reactive. Ionized atoms can be free radicals, which are atoms with a dangling bond that are highly reactive. In the human body, free radicals can react with DNA, leading to mutations and possibly cancer. Atoms become ionized when light with enough energy knocks off some of their electrons. Only light waves at the frequencies of X-rays and gamma rays have enough energy to ionize atoms and therefore lead to cancer. The cancer-causing power of only certain frequencies is why you can use your cell phone as much as you want, but you can only get an X-ray image taken on rare occasions. Free radicals occur naturally in your body. They only become dangerous when there are more free radicals than your body can handle.
But not all ions in the body are bad. Because of the charged nature of ions, the human body makes use of them to pass electric signals through nerves. The body also uses ions to control fluid levels and blood pressure. The most-used ions in the human body are sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium and chloride. Ions are also created whenever you electrostatically charge an object, such as when you rub a balloon on your hair. For this reason, your clothes dryer machine can be thought of as an ion maker. As clothes rub together in the machine, electrons get knocked from one atom to another. The result is the all-too familiar static cling. Electricity and strong electric fields do a good job of creating ions (think lightning).

The neutral state of an atom is typically the most stable configuration (unless molecular bonds and the chemical environment complicates the picture), so ions tend to discharge and return to their neutral state over time. The reason for this is that, as an ion, the atom has a strong electric field that attracts the needed electron or the needed atom to take its extra electron. But once the atom becomes neutral, it has an equal number of electrons and protons, it does not have a very strong field, and therefore has little possibility of changing.