Facet Anteio Thecal Sac Disc Mat
Hello friends. This topic is about “Facet Anteio Thecal Sac Disc Mat” which is really helpful for health’s body. Please stay with us, comment your opinion and introduce solsarin to your friends.
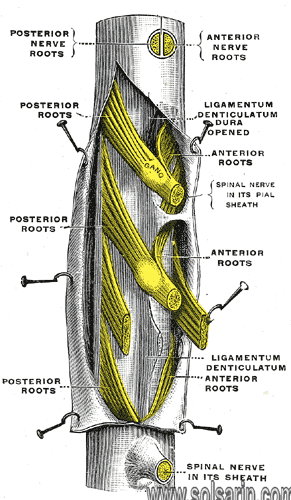

Thecal sac
The thecal sac or dural sac is the membranous sheath (theca) or tube of dura mater that surrounds the spinal cord and the cauda equina. The thecal sac contains the cerebrospinal fluid which provides nutrients and buoyancy to the spinal cord. From the skull the tube adheres to bone at the foramen magnum and extends down to the second sacral vertebra where it tapers to cover over the filum terminale. Along most of the spinal canal it is separated from the inner surface by the epidural space. The sac has projections that follow the spinal nerves along their paths out of the vertebral canal which become the dural root sheaths.
Clinical significance
The lumbar cistern is part of the subarachnoid space. It is the space within the thecal sac which extends from below the end of the spinal cord (the conus medularis), typically at the level of the first to second lumbar vertebrae down to tapering of the dura at the level of the second sacral vertebra. The dura is pierced with a needle during a lumbar puncture (spinal tap).
For epidural anesthesia an anesthetic agent is injecting into the space just outside the thecal sac and diffuses through the dura to the nerve roots where they exit the thecal sac. For spinal anaesthesia in general, an injection can be given intrathecally into the subarachnoid space, or into the spinal canal. This route of administration may also be used for the delivery of drugs which will evade the blood–brain barrier.
Disruption of the dural sac may occur as a complication of a medical procedure, or as a consequence of trauma causing a cerebrospinal fluid leak; or spontaneously resulting in a spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak.
If the spinal cord is not free to move within the thecal sac due to abnormal tissue attachments, especially during growth, tethered spinal cord syndrome may occur.
In a split cord malformation, some portion of the spinal cord is divided into parallel halves. The thecal sac may be dividing and surround each half with a spike of cartilage or bone dividing the halves (Type I); or both halves may be present within the same sac where the dura is bound to a band of fibrous tissue (Type II).
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the cause of compression. The following are some of the signs and symptoms of thecal sac compression:
Most people experience pain in their lower spine. They also notice weakness in their muscles which affects their day to day activities.
When the cause is spinal stenosis, you feel severe leg weakness which affects your walking or standing upright. It can also cause loss of bowel control in some people especially when the nerves to the bowel or bladder are weakening.
Symptoms of herniated disc depend on the location of the disc on your spine. This condition may not cause any symptoms; but when it is large it can cause pain and numbness in your leg and thigh. This pain can worsen when you stand up and reduce when you lay down.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of thecal sac compression requires several tests depending on the underlying cause.
A physical examination can be done by your doctor to check for signs and symptoms. For herniated discs as the cause, your doctor will ask you about your symptoms such as pain in the leg when standing or sitting.
Blood test can also be conducting to find out if the cause in an infection.
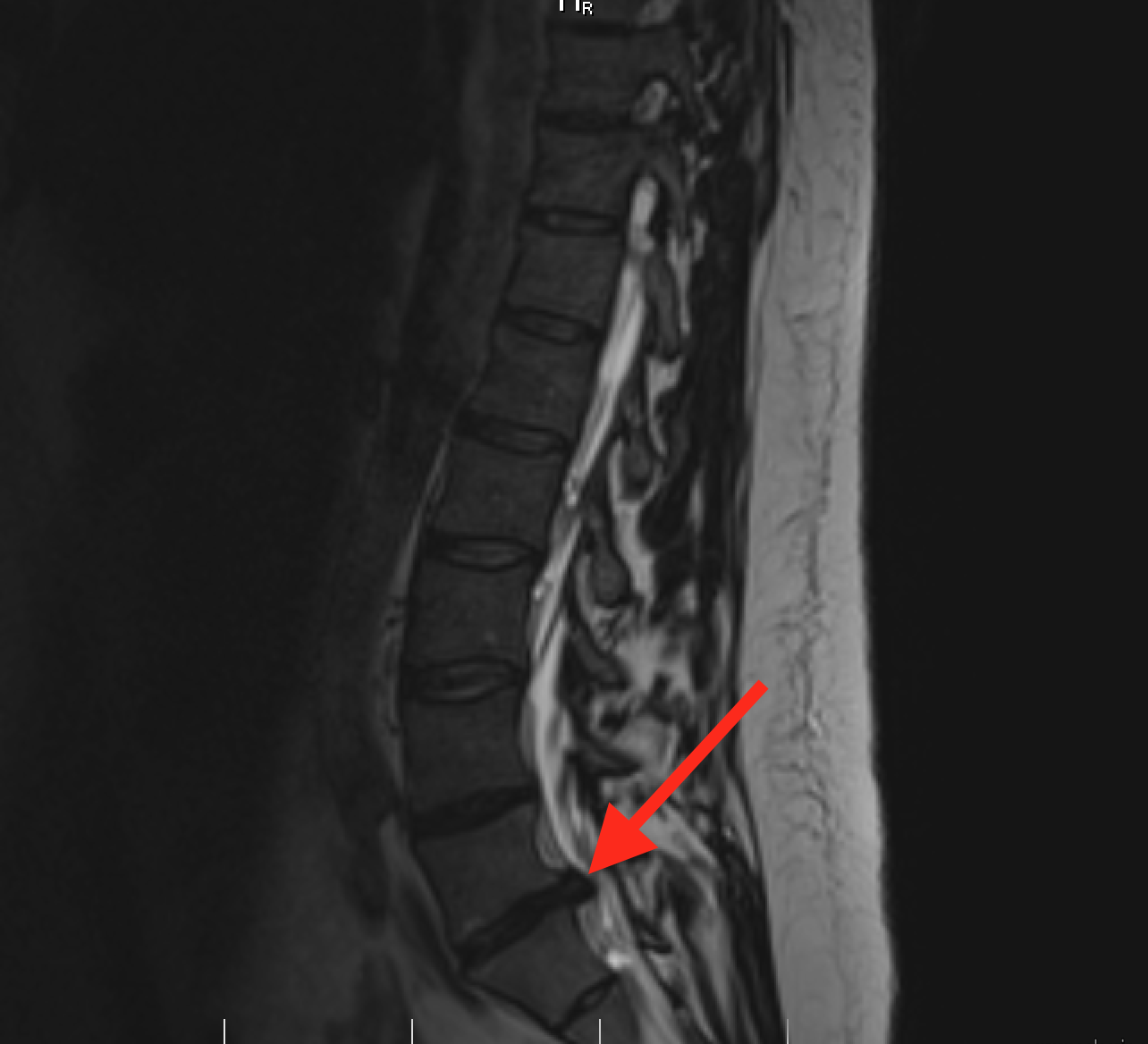
Other tests include use of imaging techniques such as Magnetic Resonance imaging scan (MRI) and computed tomography scan (CT). X-rays can be using to determine the extent of spine degeneration. Your doctor can also use an electromyogram to find out if spinal nerves are irritating.


What is Thecal Sac Impingement?
Impingement is a term which means that something is pressing against the structure. In most cases, this is done by a bulging disc; although osteophytes and general osteoarthritic change can also impinge on the thecal sac. Picture a finger pushing into a water balloon and you will get the visual idea here. There are other diagnostic terms that are identical or similar in their meaning and these may include:
Herniated disc providing a mass effect on the thecal sac and compressing the thecal sac.
Herniated disc encroaching on the thecal sac and displacing the thecal sac.
In all cases, this means that the bulging portion of the disc is making contact to some degree with the thecal membrane and enacting some force against the side wall of the structure. This will produce a noticeable deformity which can be visualizing on diagnostic imaging. However, this occurrence does not mean that any nerve tissue is inherently affecting.
What Are The Treatment Options For Thecal Sac Impingement?
To give you an idea of what you can expect when dealing with thecal sac impingement. We will give you an outline of the most common courses of treatment. Since there can be many causes for this condition (some of them being serious diseases themselves), there is no one-shoe-fits-all solution to this.
Here are the most common treatment options, presented from mildest to the most radical.
Depending on the particulars of your case, your doctor may recommend you to either:
a) Treat the underlying condition first, and the symptoms of thecal sac impingement may go away in time, after the problem is solved;
b) Go to physiotherapy and practice a stretching form of mild exercise or alternative treatment, like tai chi or yoga;
c) Visit a chiropractor for regular treatments
d) Get epidural injections (for the more serious cases)
e) Have spinal surgery (for the most serious of cases) and only as a last resort.
The last option of treatment should only be considering if all else fails. Usually, doctors prescribe at least 3 months of chiropractic treatment and massages before going ahead with the surgery, even for the difficult cases.
read about qvc host does lisa robertson cause of death
facet anterio thecal sac disc mat
The spinal cord is comprising of a bundle of nerves that connects the brain to the tissues and muscles of the body. It is protecting within the vertebral column and branches out from openings in the vertebrae to specific parts of the body. The vertebrae and intervertebral discs that cushion each vertebra can degenerate due to age, diet; lifestyle or injury, providing less support and protection for the spinal cord within and compressing the sensitive nerves. In severe cases, the nervous tissue may be pinching, interfering with the brain’s ability to send and receive messages from a particular part of the body.
Compression of the spinal cord is a spinal condition that can occur at any section of the spine and may cause pain; muscle weakness, or numbness. An expert surgeon can diagnose the cause of spinal or nerve compression and develop a comprehensive treatment plan to help alleviate the symptoms, repair the damage; and/or stop the condition from worsening.
The board-certified neurosurgeons at ProMedSPINE have undergone extensive training in the most advanced, minimally invasive surgical procedures. To learn more about our treatments or to schedule your initial consultation at one of our three locations – Beverly Hills, Encino, or Valencia – please contact us today!

1. Introduction
Synovial facet cyst is an abnomal fluid-filled lesion of the spine that often associated with degenerative changes of the spine. They commonly see in lumbar spine, rarely in cervical and thoracic spine. In lumbar spine, 60% to 89% occur at L4/L5 level, 14% at L3/L4 level and 12% at L5/S1 level. L4/L5 level is the most mobile segment at the lumbar spine which predisposing to facet joint osteoarthritits and cyst formation.
The pathogenesis is poorly uunderstanding, but they are often associating with spinal trauma, microinstability and degenerative facet disease. Spinal facet cysts are usually asymptomatic and incidentally found on MRI, however they may present with back pain, radicular pain; neurologic claudication and rarely with cauda equine syndrome and myelopathy.
A herniated cervical dics is one of the most common causes of neck pain and upper limb radiculopathy as a result of direct impingement of nerve roots and asociated with inflammatory processes. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) is a common surgical procedure for cervical spine surgery. In recent decades, new techniques developed with the advancement of technology allowed minimally invasive surgery to achieve similar clinical outcomes compared with conventional procedures.
This procedure was describing by Hijikata and Kambin, who introduced the concept of percutaneous lumbar discectomy, while the first description of the percutaneous endoscopic cervical discectomy (PECD) was reporting in 1989. PECD has shown good clinical outcomes with low rate of complications and now becoming more popular. We report a case with double pathology of the spine which was treating by endoscopic approach with good result.




