normal ph range of blood
Hello. Welcome to solsarin. This post is about “normal ph range of blood“.
Acidosis
Acidosis is a process causing increased acidity in the blood and other body tissues (i.e., an increase in hydrogen ion concentration). If not further qualified, it usually refers to acidity of the blood plasma.
The term acidemia describes the state of low blood pH, while acidosis is used to describe the processes leading to these states. Nevertheless, the terms are sometimes used interchangeably. The distinction may be relevant where a patient has factors causing both acidosis and alkalosis, wherein the relative severity of both determines whether the result is a high, low, or normal pH.
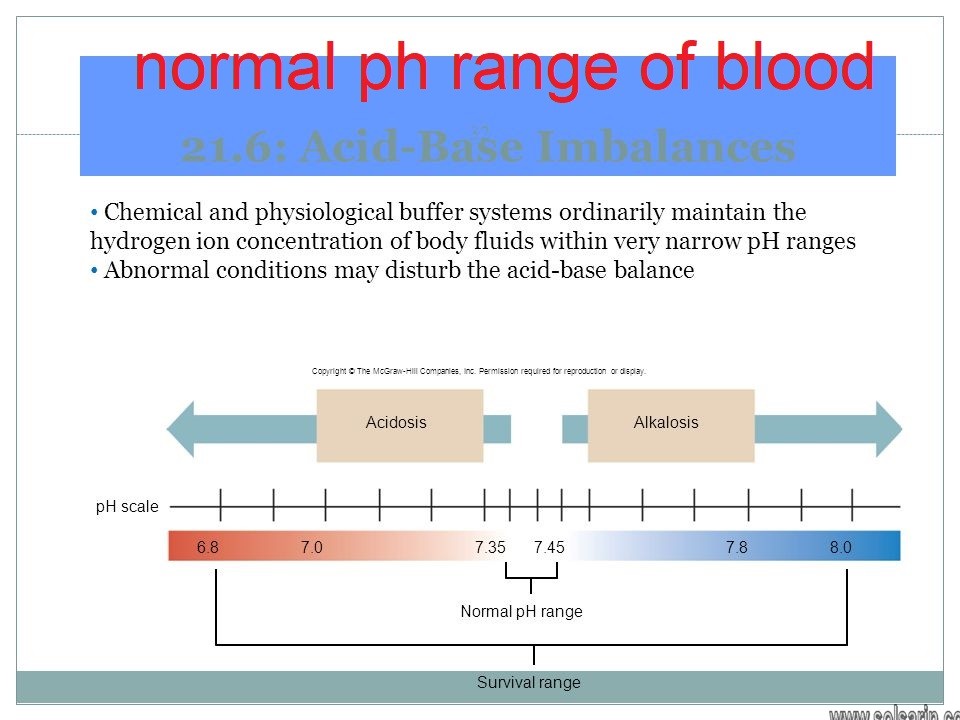
Below 7.35
Acidemia is said to occur when arterial pH falls below 7.35 (except in the fetus – see below), while its counterpart (alkalemia) occurs at a pH over 7.45. Arterial blood gas analysis and other tests are required to separate the main causes.
The rate of cellular metabolic activity affects and, at the same time, is affected by the pH of the body fluids. In mammals, the normal pH of arterial blood lies between 7.35 and 7.50 depending on the species (e.g., healthy human-arterial blood pH varies between 7.35 and 7.45). Blood pH values compatible with life in mammals are limited to a pH range between 6.8 and 7.8. Changes in the pH of arterial blood (and therefore the extracellular fluid) outside this range result in irreversible cell damage.
Have you heard anything about “is melanin a protein” ? Click on it.
Signs and symptoms
Respiratory acidosis
Respiratory acidosis results from a build-up of carbon dioxide in the blood (hypercapnia) due to hypoventilation. It is most often caused by pulmonary problems, although head injuries, drugs (especially anaesthetics and sedatives), and brain tumors can cause this acidemia. Pneumothorax, emphysema, chronic bronchitis, asthma, severe pneumonia, and aspiration are among the most frequent causes. It can also occur as a compensatory response to chronic metabolic alkalosis.
If you want to know about “what cell type produces antibodies“, click on it.
One key to distinguish between respiratory and metabolic acidosis is that in respiratory acidosis, the CO2 is increased while the bicarbonate is either normal (uncompensated) or increased (compensated). Compensation occurs if respiratory acidosis is present, and a chronic phase is entered with partial buffering of the acidosis through renal bicarbonate retention.
Emphysema
However, in cases where chronic illnesses that compromise pulmonary function persist, such as late-stage emphysema and certain types of muscular dystrophy, compensatory mechanisms will be unable to reverse this acidotic condition. As metabolic bicarbonate production becomes exhausted, and extraneous bicarbonate infusion can no longer reverse the extreme buildup of carbon dioxide associated with uncompensated respiratory acidosis, mechanical ventilation will usually be applied.
Fetal respiratory acidemia
In the fetus, the normal range differs based on which umbilical vessel is sampled (umbilical vein pH is normally 7.25 to 7.45; umbilical artery pH is normally 7.20 to 7.38). In the fetus, the lungs are not used for ventilation. Instead, the placenta performs ventilatory functions (gas exchange). Fetal respiratory acidemia is defined as an umbilical vessel pH of less than 7.20 and an umbilical artery PCO2 of 66 or higher or umbilical vein PCO2 of 50 or higher.
pH in the Human Body
The pH of the human body lies in a tight range between 7.35-7.45, and any minor alterations from this range can have severe implications.
pH of Different Body Fluids
Although the pH of blood ranges from 7.35-7.45, the pH of other body fluids is different. pH indicates the level of H+ ions, where low pH indicates too many H+ ions and high pH indicates too many OH- ions. If the pH levels drop below 6.9, it can lead to coma. However, different body fluids have different pH values. The pH of saliva is ranges from 6.5 to 7.5. After swallowing, the food reaches the stomach where upper and lower parts of stomach have different pH values. The upper part has a pH of 4−6.5, while the lower part is highly acidic with a pH of 1.5−4.0. It then enters the intestine which is slightly alkaline, with a pH of 7−8.5. Maintaining the pH values of different regions is critical for their function.
Impact of Altering the pH Balance
Different organs function at their optimal level of pH. For example, the enzyme pepsin requires low pH to act and break down food, while the enzymes in intestine require high pH or alkaline environment to function. Similarly, any increase or decrease in the blood pH can lead to several disorders.

Maintaining the Body pH
pH is maintained in the body using primarily three mechanisms: buffer systems, respiratory control, and renal control.
Buffer Systems
Proteins form a part of the buffer system to regulate the pH levels. These proteins can act as H+ acceptors or donors because of the presence of basic or acidic groups. Similarly phosphate buffers also help in moderating the levels of pH. Buffers may help in regulating pH during minor physiological changes, such as during breath holding (which increases the CO2 in the blood), exercise (which increases lactic acid in the blood), or when gastric acid is secreted.
Respiratory Control
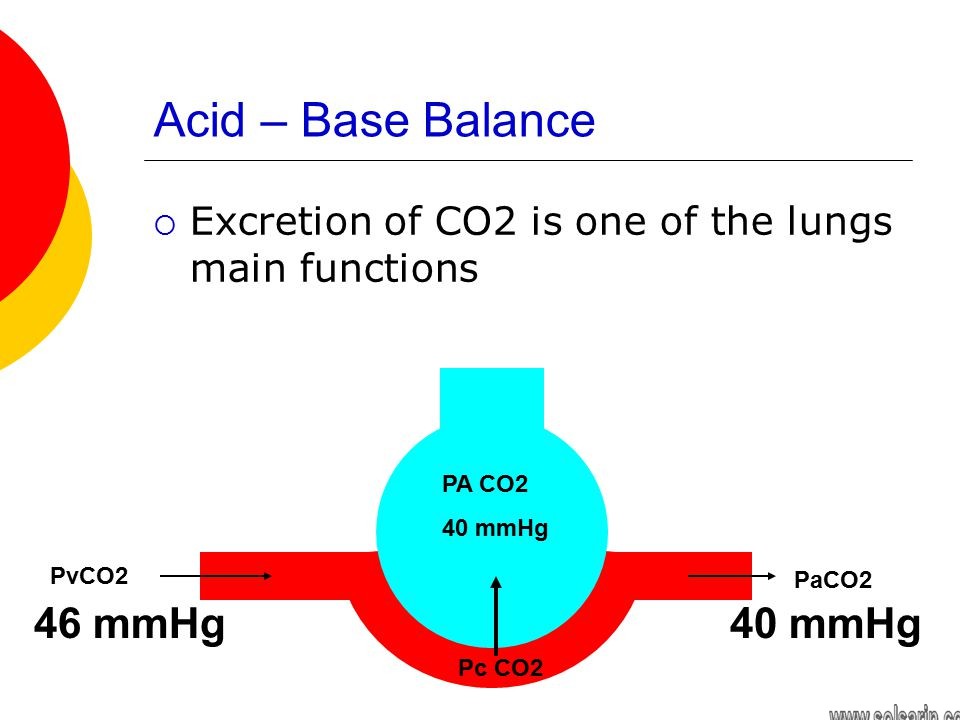
The pH of blood during normal conditions is 7.4. However, CO2 dissociates into carbonic acid in the tissues. Thus, presence of more CO2 makes the blood more acidic. That is the reason when we hold the breath for long durations, the CO2 levels increase in the blood lowering our pH leading to fainting. On the other hand during alkalosis or increased pH, the breathing may get slow in order to increase the CO2 levels and reduce the alkalinity. However, low breathing rate could also lead to low oxygen levels which could be detrimental. Thus, respiration provides an important control to regulate the pH levels.
Do you want to know about “static friction definition“? Click on it.
What is the Ph of Blood?
In humans, an arterial blood pH level anywhere between 7.35 and 7.45 is considered normal.
That number is just slightly above neutral on the pH, or potential hydrogen, scale. The scale goes from 0 to 14 and measures whether a solution is acid or alkaline. Neutral is 7, which indicates that a substance is an equal mix of acids and bases. A substance with a pH value from 0 to 7 is acidic; anything with a score above 7 to 14 is considered a base. So, with blood, a pH higher than 7.45 the blood’s acidity is too low, and below 7.35 means the blood’s acid level is too high.
Healthy kidneys and lungs work hard to help our bodies maintain a balance of 7.4, but there are a number of reasons that blood pH levels can rise and fall. When they do, it’s called either acidosis or alkalosis.
CO2
Acidosis occurs when blood pH levels dip below 7.35. There are two types of acidosis: metabolic and respiratory. During metabolic acidosis, your body either isn’t producing enough acid, or it can’t get rid of enough acid. During respiratory acidosis, your body lacks the bases to balance out the amount of acid in your system.
Metabolic acidosis stems from problems with the kidneys. Several kidney issues can lead to metabolic acidosis, including poorly controlled diabetes, extreme diarrhea or vomiting, and kidney failure. A buildup of lactic acid as a result of issues including heart failure, cancer, chronic alcohol use, seizures, liver failure or low blood sugar can also lead to metabolic acidosis.
Respiratory acidosis occurs when there is too much carbon dioxide (CO2) in the body. This can happen for a number of reasons, including chronic breathing conditions like asthma, a chest injury or nervous system problems.
So, what’s a normal blood pH?
Your blood has a normal pH range of 7.35 to 7.45. This means that blood is naturally slightly alkaline or basic.
In comparison, your stomach acid has a pH of around 1.5 to 3.5. This makes it acidic. A low pH is good for digesting food and destroying any germs that get into the stomach.
What makes blood pH change or become abnormal?
Health problems that make your body too acidic or too alkaline are usually linked to the pH of blood. Changes in your normal blood pH might be a sign of certain health conditions and medical emergencies. These include:
- asthma
- diabetes
- heart disease
- kidney disease
- lung disease
- gout
- infection
- shock
- hemorrhage (bleeding)
- drug overdose
- poisoning


Blood pH balance
Acidosis is when your blood pH drops below 7.35 and becomes too acidic. Alkalosis is when your blood pH is higher than 7.45 and becomes too alkaline. The two main organs that help balance the pH of blood are the:
- Lungs. These organs remove carbon dioxide through breathing or respiration.
- Kidneys. These organs remove acids through urine or excretion.
The different types of blood acidosis and alkalosis depend on the cause. The two main types are:
- Respiratory. This type occurs when the change in blood pH is caused by a lung or breathing condition.
- Metabolic. This type occurs when blood pH changes are due to a kidney condition or issue.
Testing blood pH
A blood pH test is a normal part of a blood gas test or arterial blood gas (ABG) test. It measures how much oxygen and carbon dioxide is in your blood.
Your doctor might test your blood pH as part of a regular health checkup or if you have a health condition.
Blood pH tests involve having your blood drawn with a needle. The blood sample is then sent to a lab to be tested.
Can you test at home?
An at-home blood finger-prick test won’t be as accurate as a blood pH test at your doctor’s office.
A urine pH litmus paper test won’t show your blood’s pH level, but it may help show that something is off-balance.
Thank you for staying with this post “normal ph range of blood” until the end.