Planet smaller than Earth
Hello and welcome to solsarin. Our discussion is “planet smaller than Earth”. Please stay with us until the end of the text.


Planet
A planet is a large astronomical body that is neither a star nor a stellar remnant. There are competing scientific definitions of a “planet”. In the dynamicist definition adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a planet is a non-stellar body that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, that directly orbits a star, and that has cleared its orbital zone of competing objects. The IAU has also declared that there are eight planets in the Solar System, independently of the formal definition. In the geological definition used by most planetologists, a planet is a rounded sub-stellar body, possibly a satellite. In addition to the eight Solar planets accepted by the IAU, these include dwarf planets such as Eris and Pluto and planetary-mass moons. Bodies meeting the geological definition are sometimes called “planetary-mass objects” or “planemos” for short.
The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, astrology, science, mythology and religion. Apart from the Moon, five planets are visible to the naked eye in the night sky. Planets were regarded by many early cultures as emissaries of deities or as divine themselves. As scientific knowledge advanced, human perception of the planets changed, and the invention of the telescope enabled the discovery of additional planetary objects that were diverse in size, shape and orbit. In 2006, the IAU adopted a resolution limiting the number of planets within the Solar System, though they are not followed by all astronomers, especially planetologists. The IAU resolution is controversial because it excludes many geologically active planetary-mass objects due to where or what they orbit.
Ptolemy thought that the planets orbited Earth in deferent and epicycle motions. Although the idea that the planets orbited the Sun had been suggested before, it wasn’t until the 17th century that this view was supported by the concrete evidence, in the form of telescopic observations performed by Galileo Galilei. About the same time, by careful analysis of pre-telescopic observational data collected by Tycho Brahe, Johannes Kepler discovered that the planets’ orbits were elliptical rather than circular. As observational tools improved, astronomers saw that, like Earth, each of the planets rotated around an axis tilted with respect to its orbital pole, and that some shared such features as ice caps and seasons. Since the dawn of the Space Age, close observations by space probes have found that Earth and other planets share additional characteristics such as volcanism, hurricanes, tectonics and even hydrology.
The eight Solar planets in the IAU definition are divided into two divergent types: large low-density giant planets and small rocky terrestrial planets. In order of increasing distance from the Sun, they are the four terrestrials: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars; and the four giants: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Six are orbited by natural satellites, the two exceptions being the innermost planets Mercury and Venus. Under geophysical definitions, the classification is more complex: the Moon and Jupiter’s moons Io and Europa are additional terrestrial planets, but a large number of small icy planets are also added, such as the dwarf planets Ceres and Pluto and the other large giant-planet moons such as Ganymede, Callisto, and Titan.
Beginning at the end of the twentieth century, several thousand planets have been discovered orbiting other stars. These are referred to as “extrasolar planets”, or “exoplanets” for short. As of 1 April 2022, 4,984 extrasolar planets have been discovered in 3,673 planetary systems. The count includes 815 multi-planetary systems. Known exoplanets range in size from gas giants about twice as large as Jupiter down to just over the size of the Moon.
More than 100 of these planets are approximately the same size as Earth, nine of which orbit in the habitable zone of their star. In 2011, the Kepler Space Telescope team reported the discovery of the first Earth-sized extrasolar planets orbiting a Sun-like star, Kepler-20e and Kepler-20f. A 2012 study, analyzing gravitational microlensing data, estimates a minimum of 1.6 bound planets on average for every star in the Milky Way. As of 2013, one in five Sun-like stars is thought to have an Earth-sized planet in its habitable zone.


Size of Planets in Order
The planets in our solar system are each very unique for various reasons. When it comes to their measurable sizes in diameter, the planets vary greatly. Jupiter, for example, is approximately 11 times the diameter of the Earth. Mercury, on the other hand, is 2.6 times smaller in diameter than the Earth. Below you will find a list of the planet’s mean diameters from largest to smallest. We have included Pluto as further reference point for additional information.
1. Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system at 139,822 km in diameter. This means that Jupiter is actually more than 28.5 times larger in diameter than the smallest planet, Mercury.
2. Saturn measures out to be 116,464 km in diameter. This makes Saturn over 9 times bigger in diameter than the Earth. This number does not include the actual rings of the planet as they are considered a separate entity.
3. Uranus comes in at third on the list with a maximum diameter of 50,724 km, making the planet almost 4 times the diameter of Earth and over 10 times the diameter of Mercury.
4. Neptune, often described as Uranus’s “twin planet” due to their many similar characteristics, is also very close in size to Uranus. Neptune is 49,248 km in diameter, making Uranus only 1.3 times larger in diameter.
5.Our home planet Earth is the fifth largest of the eight planets and measures in at 12,756 km in diameter. This means that Earth is actually approximately 2.6 times the diameter of the smallest planet, Mercury. Another size comparison puts Earth at 3.67 times the diameter of the Moon.
6.Earth’s “twin planet” Venus is only slightly smaller than Earth with a diameter of 12,104 km. Venus also has a similar gravitational pull of 8.87m/s2 to that of Earth’s 9.81m/s2 .
7. The red planet of Mars has a diameter of only 6,780 km. This makes it 20.5 times smaller in diameter than Jupiter. Mars is 53% of the diameter of planet Earth, but only has approximately 38% of the surface area of our planet.
8. Mercury, the smallest planet, has a diameter of 4,780 km. This makes Jupiter, the largest planet, over 28.5 times bigger in diameter than Mercury.
9. Pluto, now designated as a dwarf planet, has a diameter of 2,400 km. This means that Pluto is over 59 times smaller in diameter than the massive Jupiter.
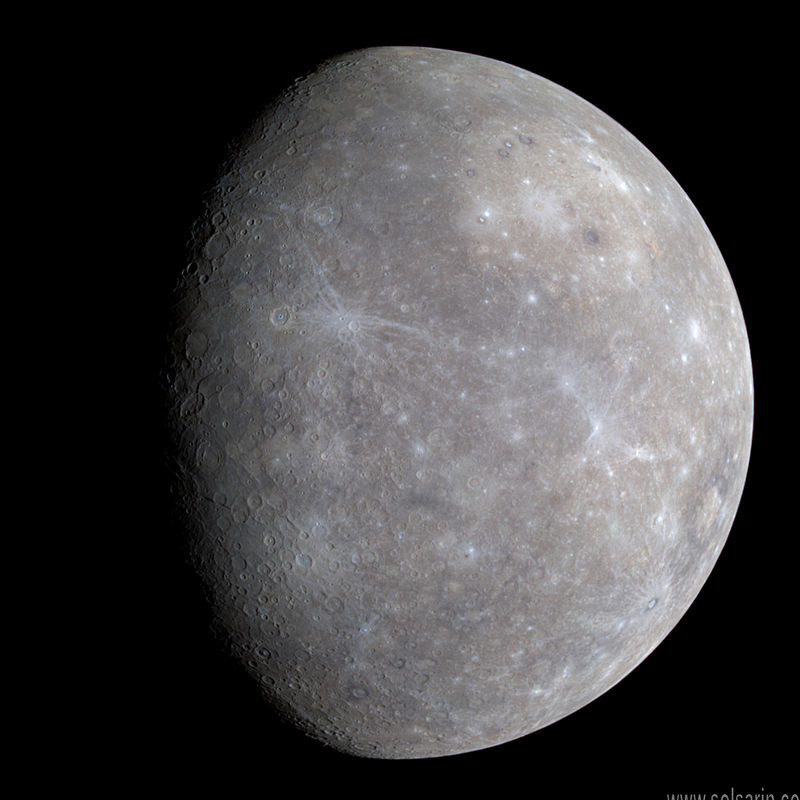

Are there any planets smaller than Earth?
Smallest Planet: Mercury The smallest planet in regards to both mass and volume is Mercury — at 4,879 km across and 3.3010 x 1023 kg, this tiny world is nearly 20 times less massive than Earth, and its diameter is about 2½ times smaller. In fact, Mercury is closer in size to our Moon than to Earth.
How much bigger are the planets than Earth?
Earth is nearly 13,000 kilometers across. The smallest terrestrial planet, Mercury, has a diameter about 40 percent of that size. Jupiter, the biggest planet, is more than ten times larger than Earth. The maximum possible size for a planet is a few times larger than Jupiter – about the same size as the smallest stars.
Which planets are smaller than earth?
Thus, Venus, Mars and Mercury are smaller than Earth. Mercury is at 4,879 km across and 3.3010 x 1023 kg, this tiny world is nearly 20 times less massive than Earth, and its diameter is about 2½ times smaller. The red-planet is the second smallest planet in the solar system.
Which planet is smaller than earth’s core?
The two smallest major planets, Mercury and Mars, are both smaller than the estimated size of the Earth’s core (combined inner and outer core). Mercury has a diameter of about 4879 km and Mars is about 6792 km, compared to the Earth’s core which is a sphere about 6972 km in diameter. All of the dwarf planets (Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, and Ceres) are smaller in diameter than even the Earth’s solid inner core (~2440 km in diameter), although Eris is almost as large and Pluto only slightly smaller than Eris. -The Earth’s inner core has a thickness (radius) of about 1220 km. -The Earth’s outer core has a thickness (radius) of about 2266 km.
NASA’s Kepler Finds Extra-Solar Planets Smaller Than Earth
Over the past year, NASA’s Kepler mission has found hundreds of possible planets outside of our solar system, and even a few candidates for Earth-like planets.
This week, astronomers revealed that a new system has been found that contains planets smaller than Earth. The new data has been presented in a paper published recently in the journal Nature.
The planets orbit around a star called Kepler-37, located around 210 light-years from our solar system. The smallest of the planest found, known as Kepler-37b, is only one-third the size of Earth – smaller than the planet Mercury and just slightly larger than Earth’s moon. The planet is not presumed to have an atmosphere, and scientists predict that life on the planet isn’t likely.
“Even Kepler can only detect such a tiny world around the brightest stars it observes,” said Jack Lissauer, planetary scientist at NASA‘s Ames Research Center. “The fact we’ve discovered tiny Kepler-37b suggests such little planets are common, and more planetary wonders await as we continue to gather and analyze additional data.”
Two other planets were found in the Kepler-37 system. Kepler-37c orbits further out and is slightly smaller than Venus, or around three-quarters the size of Earth. Kepler-37d is the furthest planet out, and is around twice the size of Earth. Kepler-37 itself is slightly smaller and cooler than the sun.
All three of the planets orbit Kepler-37 at less than than the distance between the sun and Mercury. They each also orbit their star in 40 days or less. The surface temperature of Kepler-37b is estimated to be higher than 800 degrees Fahrenheit.
“We uncovered a planet smaller than any in our solar system orbiting one of the few stars that is both bright and quiet, where signal detection was possible,” said Thomas Barclay, lead author of the paper and a Kepler scientist at the Bay Area Environmental Research Institute. “This discovery shows close-in planets can be smaller, as well as much larger, than planets orbiting our sun.”
Random Posts




