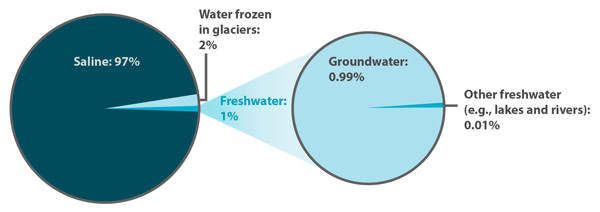
what percent of the earth’s hydrosphere is fresh versus salt water
Hello dear friends, thank you for choosing us. In this post on the solsarin site, we will talk about “ what percent of the earth’s hydrosphere is fresh versus salt water“.
Stay with us.
Thank you for your choice.

Distribution and quantity of Earth’s waters
hydrosphere
Ocean waters and waters trapped in the pore spaces of sediments make up most of the present-day hydrosphereThis water, however, plays an important role in the water cycle.
Earth’s water earth’s hydrosphere is fresh versus salt water
At present, ice locks up a little more than 2 percent of Earth’s water and may have accounted for as much as 3 percent or more during the height of the glaciations of the Pleistocene Epoch (2.6 million to 11,700 years ago). Although water storage in rivers, lakes, and the atmosphere is small, the rate of water circulation through the rain-river-ocean-atmosphere system is relatively rapid. The amount of water discharged each year into the oceans from the land is approximately equal to the total mass of water stored at any instant in rivers and lakes.
Soil moisture earth’s hydrosphere is fresh versus salt water
Soil moisture accounts for only 0.005 percent of the water at Earth’s surface. It is this small amount of water, however, that exerts the most direct influence on evaporation from soils. The biosphere, though primarily H2O in composition, contains very little of the total water at the terrestrial surface, only about 0.00004 percent, yet the biosphere plays a major role in the transport of water vapour back into the atmosphere by the process of transpiration.
Thus, the masses of water at Earth’s surface are major receptacles of inorganic and organic substances, and water movement plays a dominant role in the transportation of these substances about the planet’s surface.
Biogeochemical properties of the hydrosphere

Rainwater
About 107,000 cubic km (nearly 25,800 cubic miles) of rain fall on land each year. The total water in the atmosphere is 13,000 cubic km, and this water, owing to precipitation and evaporation, turns over every 9.6 days. Rainwater is not pure but rather contains dissolved gases and salts, fine-ground particulate material, organic substances, and even bacteria. The sources of the materials in rainwater are the oceans, soils, fertilizers, air pollution, and fossil fuel combustion.
oceanic islands
It has been observed that rains over oceanic islands and near coasts have ratios of major dissolved constituents very close to those found in seawater. The discovery of the high salt content of rain near coastlines was somewhat surprising because sea salts are not volatile, and it might be expected that the process of evaporation of water from the sea surface would “filter” out the salts.
nitrogen
For the nitrogen gases nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) released from fossil fuel burning, their atmospheric reactions lead to the production of nitric acid (HNO3) and its dissociation to hydrogen ions (H+) and nitrate (NO3−). These reactions are responsible for the acid rain conditions that occurred in the northeastern United States, southeastern Canada, and western Europe during the second half of the 20th century (see below Acid rain). The high sulfate values of the rain in the northeastern United States reflect the acid precipitation conditions of this region.




