cloudy ammonia chemistry
Hello. Welcome to solsarin. This post is about “cloudy ammonia chemistry“.
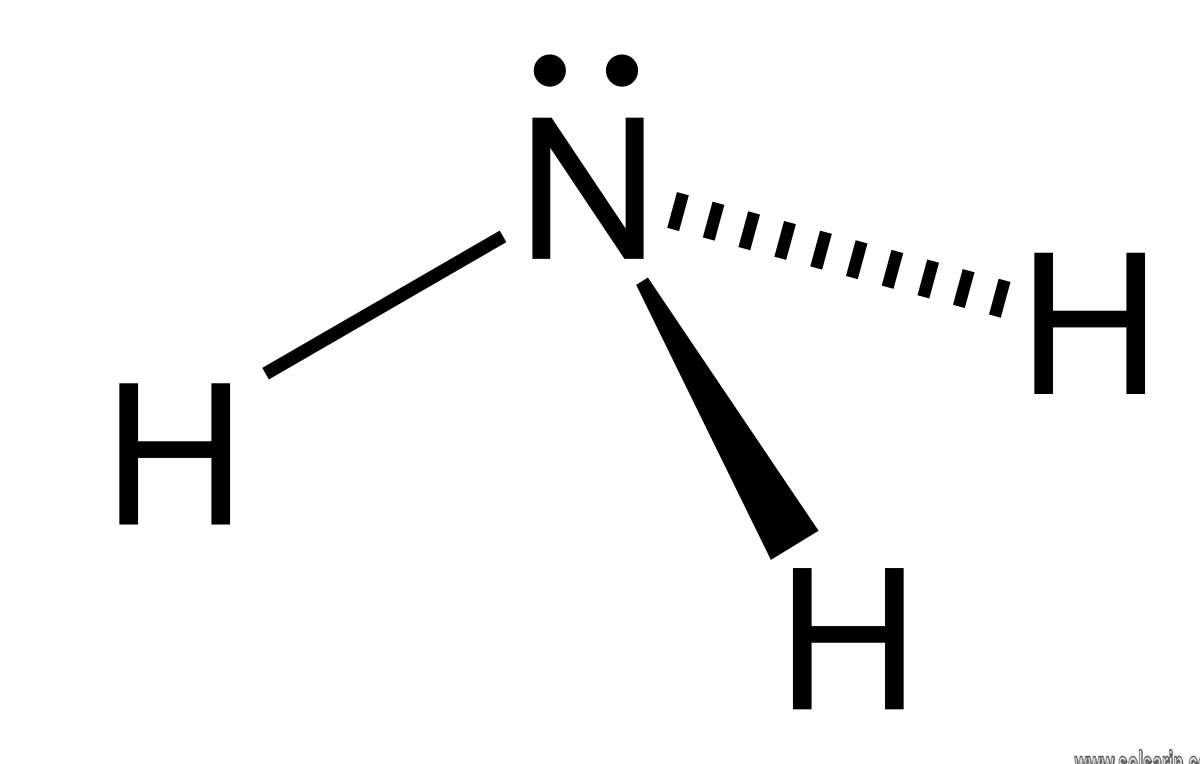
Ammonia solution
4][OH−
], it is actually impossible to isolate samples of NH4OH. The ions NH+
4 and OH− do not account for a significant fraction of the total amount of ammonia except in extremely dilute solutions.
Basicity of ammonia in water
In aqueous solution, ammonia deprotonates a small fraction of the water to give ammonium and hydroxide according to the following equilibrium:
- NH3 + H2O ⇌ NH4+ + OH−.
In a 1 M ammonia solution, about 0.42% of the ammonia is converted to ammonium, equivalent to pH = 11.63 because [NH4+] = 0.0042 M, [OH−] = 0.0042 M, [NH3] = 0.9958 M, and pH = 14 + log10[OH−] = 11.62. The base ionization constant is
- Kb = [NH4+][OH−] / [NH3] = 1.77×10−5.

Saturated solutions
Like other gases, ammonia exhibits decreasing solubility in solvent liquids as the temperature of the solvent increases. Ammonia solutions decrease in density as the concentration of dissolved ammonia increases. At 15.6 °C (60.1 °F), the density of a saturated solution is 0.88 g/ml and contains 35.6% ammonia by mass, 308 grams of ammonia per litre of solution, and has a molarity of approximately 18 mol/L. At higher temperatures, the molarity of the saturated solution decreases and the density increases. Upon warming saturated solutions, ammonia gas is released.
Key Difference – Ammonia vs Cloudy Ammonia
Ammonia is a chemical that is manufactured in larger quantities in the chemical industry and the key difference between ammonia and cloudy ammonia is the composition. Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen and the cloudy ammonia is a soap added ammonia. Cloudy ammonia, basically, is used for domestic cleaning purposes. But ammonia has a large variety of uses as a chemical; to produce pharmaceuticals, as a cleaning agent, etc.
What is Ammonia?
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH3. The gaseous form of ammonia is colourless with a pungent odor. Ammonia is a caustic and hazardous chemical. Ammonia is one of the main chemicals which is manufactured in larger quantities in the chemical industry. It is used in both liquid and gaseous forms for various uses and is widely used as a Nitrogen fertilizer. It is also used to synthesize many pharmaceuticals and is present in most of commercially available cleaning products. The pure form of ammonia is called anhydrous ammonia. High concentrated ammonia causes irritation and burns. When regular ammonia is used as a cleaner; it does not stain and is great for cleaning windows and mirrors. Some uses of Ammonia are,
- To produce ammonia fertilizer.
- As a refrigerator gas
- To purify water supplies.
- To manufacture plastics, explosives, fabrics, pesticides, dyes and other chemicals.
- As a domestic cleaner.
What is Cloudy Ammonia?
Cloudy ammonia is made by mixing ammonia with soap; it is also called as “sudsy ammonia”. It is a cloudy white or grey coloured solution. Cloudy ammonia is used as a cleaning agent as it is a perfect cleaner for grime and dirt. One of the most common uses of ammonia is as a domestic cleaning agent.
Make Clear Ammonia From Cloudy Ammonia
Whatever you do or how you do it, do it outside or in a well working fume chamber with proper exhaust!!!
The concentrations are high enough to create “ammonia fog” when mixing – a dangerous mix of hydrochloric acid and ammonium chloride.
This “fog” is no vapor but in fact extreme fine dust for most of it.
If you want to know about “the disaccharides include:“, click on it.
This dus will settle and creep everywhere in reach.
Stainless steel will start to rust under exposure and with moisture present.
Other metals will be affected in a similar way, so please avoid making the mess anywhere inside!
Disclaimer
This process produces quite high concentrations of clear Ammonia.
Ammonia is dangerous for your respitory system, bad on your skin and burns in your eyes if the concentration in the air is too high.
On the skin and especially your eyes liquid ammonia can cause severe damages.
I strongly recommend to do this outside and with protective clothing, gloves and a face shield.
In this Instructable I only provide a way to “remove” the sopa from cloudy ammonia, what you do with it is your responsibilty!


This is nothing for kids to play with!
When you decide to use the provided informations you acknowledge the risk involved.
I will take no responsibilty for anything that goes wrong on your end or any damages caused by the process or the final product!
Before you even attempt to do this check if the possession of Ammonia in concentrations higher than supermarket Ammonia is legal!
How does it work?
The cloudy Ammonia is of quite low concentration and has a small amount of soap added.
Around 20grams per liter.
The soap is good for your cleaning purposes but makes the stuff utterly useless for everthing else.
Ammonia has much lower boiling point than water, so when you destill it the first thing to come out is Ammonia vapor.
The soap is left in the pot and if you want you can use the leftover to clean your floors, works good.
Unless you have highly efficient reflux still you won’t be able to collect any Ammonia as a gas and this is good!
Ammonia is highly soluble in water wich means in a normal still is binds instantly to the water condesing in the cooling coil, only a very small amount will make it out as vapor.
At the beginning of the process you should start with some water in the first container so that the gas can get into the water.
Smell tester
Later in the process there will be water coming out that already has ammonia in it.
The jars should be connected air tight!
A little guide for the hoses: From the condenser to the bottom of the first jar, from the top of the first jar to the bottom of the second, the second lid only has a hole for the air to escape.
For the first run add a small amount of water to both jars so the longer hose is submerged a bit.
The water is to make sure no (or only very small amounts of Ammonia escape the system). The second jar is a “smell tester” – if you are able to smell Ammonia coming out of it your temperature is far too high, this jar should not collect any Ammonia at all.
It helps to have the first jar sitting in ice cold water but you can do without.
Uses & Benefits
Ammonia in Fertilizer
Ammonia is a basic building block for ammonium nitrate fertilizer, which releases nitrogen, an essential nutrient for growing plants, including farm crops and lawns. About 90 percent of ammonia produced worldwide used in fertilizer, to help sustain food production for billions of people around the world. The production of food crops naturally depletes soil nutrient supplies. In order to maintain healthy crops, farmers rely on fertilizer to keep their soils productive. Fertilizers also can also help increase levels of essential nutrients like zinc, selenium and boron in food crops.
What ammonia used for?
About 90 percent of ammonia produced used in fertilizer, to help sustain food production for billions of people around the world. Ammonia has other important uses; for example in household cleaning products and in manufacturing other products.
What is ammonia?
Ammonia, also known as NH3, a colorless gas with a distinct odor composed of nitrogen and hydrogen atoms. It produced naturally in the human body and in nature—in water, soil and air, even in tiny bacteria molecules. In human health, ammonia and the ammonium ion are vital components of metabolic processes.
What happens to ammonia in the environment?
Ammonia occurs naturally and found throughout the environment in soil, air, and water. Ammonia also renewed naturally as part of the nitrogen cycle that already occurs as plants fertilize. As a result of this natural process, ammonia does not last long in the environment, and it also does not bioaccumulate.
What does ammonia smell like?
Ammonia has a very distinct, pungent odor, described as similar to sweat or cat urine. Strong, briny cheeses like brie can also smell like ammonia. Cheeses even have small amounts of ammonia in them, as a natural by-product of the cheese aging process.
How might I exposed to ammonia?
Ammonia occurs naturally in the environment, so everyone exposed to low levels at one point or another. It is possible for a person to exposed to higher levels of ammonia when using cleaning products containing ammonia, or if they live on or near farms where fertilizers used. It’s also possible to exposed to higher levels of ammonia if a person spends time in an enclosed building that contains lots of animals.


How ammonia exposure treated?
There is no antidote for ammonia poisoning, but ammonia’s effects can treated, and most people recover. Immediate decontamination of skin and eyes with copious amounts of water is very important. Treatment consists of supportive measures and can include administration of humidified oxygen, bronchodilators and airway management. Ingested ammonia diluted with milk or water.
Thank you for staying with this post “cloudy ammonia chemistry” until the end.




