difference between ping and telnet
Welcome to Solsarin. How much do you know about ping and telnet? Today we want to talk about difference between ping and telnet.
thanks for choosing us.
ping vc telnet
Connectivity to the target machine can be tested with Ping. In addition to its domain names, IP addresses can be resolved using them. Quality assessment of the network. A remote connection and management tool is used to manage the host from afar. The test is also intended to determine whether the target machine’s TCP port is open. Telnet IP address 3389, for instance, can be used to test if the target machine’s port 3389 is open. Firewalls may block the connection, Windows may not have the relevant remote desktop service (windows) enabled, or the port 3389 occupied by default may be modified if the connection fails. Monitoring the status of a monitoring server can be accomplished using telnet and ping. This basic command is used by a large number of monitoring tools.
ping
When you use PING, you can find out if a machine is accessible over the internet. The IP address obtained by using this tool can also be used to check that you are addressing the correct machine, such as during a DNS change. In addition to pinging a domain name or hostname, you can also ping an IP address.


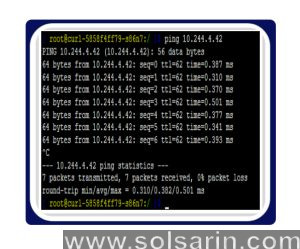
Test your ping
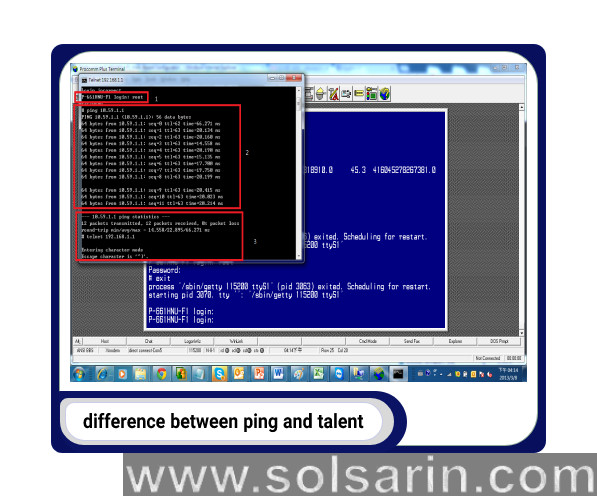
The first network test for troubleshooting client/server connections is the Ping test. In this case, we need to make sure we get a prompt reply, as well as an IP address that matches what we expect. Press Enter after pinging [server name/IP address].
what is difference between ping and telnet?
ICMP is the protocol used by Ping. ICMP calls can be answered by any system with TCP/IP if they are not filtered by a firewall.
Remote terminal servers can be accessed by Telnet. In order for it to respond, it must be enabled through system configuration and the server must be up.
An ICMP request is sent to a computer and the computer returns the request (ping reply) that is displayed along with some statistical information, such as how long it took for packets to respond. In spite of its usefulness for diagnosing problems in intranets, it is blocked by most firewalls as a security measure.
In contrast, telnet acts as a remote access server, asking for authentication data and granting shell access if the connecting user holds a valid account. Most smart network devices and UNIX systems support telnet. Telnet is an old protocol and sends usernames and passwords over networks in clear text format, so it can be eavesdropped on, and is considered very unsecure.
Many Unix systems come with it disabled by default. SSH (Secure Shell) is more commonly used by system administrators than Telnet. SSH has the advantage of encrypting all communication and sensitive user data is encrypted over the internet so credentials cannot be easily extracted.
It is possible to diagnose network problems using both ping and telnet. It is simply possible to ping and get a response. The output can be monitored using telnet.orm for a given port.
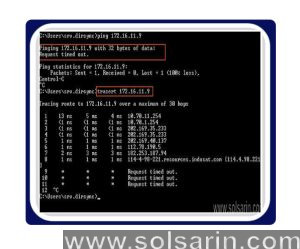

Do you have the ability to ping a specific port?
A network device uses ICMP to transmit error messages and to determine whether it has successfully communicated with an IP address. The difference between ICMP and transport protocols is that ICMP does not exchange data between systems.
It is impossible to pinge a port because ping uses ICMP packets, which do not use port numbers. In addition, ping can also be used for a similar purpose, such as checking if a port is open.
It is possible to simulate an attempt to connect to a specific port and wait to see if the target host responds to the attempt. An open port is one that receives a response. If not, the target port is closed, or the host is unable to accept a connection since it does not have a service listening on that port.
What is the purpose of pinging a specific port?
It is common for users and administrators to ping a particular port to check the status of remote services. Pinging specific ports is generally done by Linux Administrators, Windows Administrators, Network Administrators, Application Developers, and Database Administrators to identify and resolve problems. Pinging a specific port has a number of reasons, which we will discuss below.
- Database service cannot be connected by the application.
- Allowing or denying specific ports depends on how the firewall is configured.
- A proper SNMP service should be running at the remote location.
- Verify that the remote port is responding properly before attacking it.
telnet
A teletype network (telnet) is a network protocol used to provide bidirectional interactive communications over the Internet or a local area network. By using a virtual terminal connection, it connects to a command-line interface on a remote host.
There is one major disadvantage of Telnet: data is sent over the network in clear text. Network analyzers can reveal your username and password by peeking at your data packets. Remote logins could be more secure if they were done via Secure Shell (SSH), which encrypts the data sent over the Internet.
Using Telnet, you can scan remote hosts for open TCP ports.

Telnet in Windows 9x or NT
- To use Telnet with this example, open a command prompt and type the following: telnet 192.168.192.191
- When the HP Jetdirect responds, press Enter twice to make sure that the Telnet connection is initialized.
- Type a forward slash (/), and press Enter to see HP Jetdirect information.
- Type a question mark (?), and press Enter. A help screen will appear with examples of IP parameters that can be changed. With some HP Jetdirects in some Windows Telnet screens, local echo must be enabled to be able to see what is typed. To enable local echo in Telnet, select Terminal, and Preferences at the top of the Telnet window. Put a check in Local Echo and select OK.

Windows 2000
- Click Start, and then Run.
- Type telnet, and press Enter.
- To set local echo, type the following: set local_echo (Some devices, such as an HP Jetdirect 610N card, do not need local echo set. If local echo is set and double sets of characters appear, type the following: unset local_echo)
- Type the following: open ipaddress(for example, open 192.168.192.191).
Microsoft Windows XP
- Open the Command Prompt and type the following: telnet IPaddress (for example, telnet198.162.20.10).
- Type Ctrl + ] (press and hold the Ctrl key and type a right bracket), then press Enter.
- Type the following: set localecho and press Enter. Local echo will be on.
- Press Enter again and the HP Jetdirect telnet interface should be seen.
- Once a telnet connection has been established, type a forward slash (/), and press Enter to see HP Jetdirect information.
- Type a question mark (?) and press Enter. A Help screen will appear with examples of IP parameters that can be changed
note:
As long as a Telnet connection can be made, it is not necessary to make any changes in the Telnet session. The connection alone is enough to verify communication at the application layer.
Telnet to the port of the HP Jetdirect to test the printing

Once in Telnet, type some text or characters, and then close the Telnet connection:
- To close the Telnet session in Windows 2000, XP, and most variations of UNIX, press and hold down the Ctrl key, then press the right square bracket key ( ] ).
- In Windows 9x and NT, click Connect, then Disconnect in the Telnet window.
- For an internal HP Jetdirect or a single parallel port external HP Jetdirect, open a command prompt and type the following: telnet 192.168.192.191 9100 (For a three-port, external HP Jetdirect, use port numbers 9100, 9101, or 9102 for parallel ports 1, 2, or 3, respectively.)
- While in Telnet, type the following: This is a test and then press Enter.
- Type Ctrl + ] (press and hold the Ctrl key and type a right bracket), then press Enter.
- At the Telnet prompt, type the following: quit
It seems that now we have good information about ping and talent.
Thank you for being with Solsarin.