homozygous vs heterozygous genotypes
Hi, welcome to solsarin site, in this post we want to talk about“homozygous vs heterozygous. genotypes”,
stay with us.
homozygous vs heterozygous genotypes
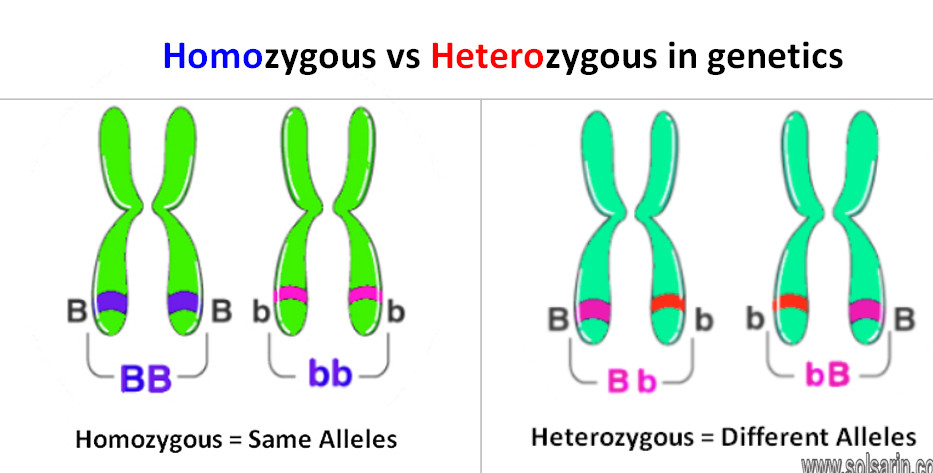
An organism that is homozygous has two copies of the same allele. An allele is one version, like a “flavor”, of a gene. Humans and other diploid organisms have two copies of every gene.
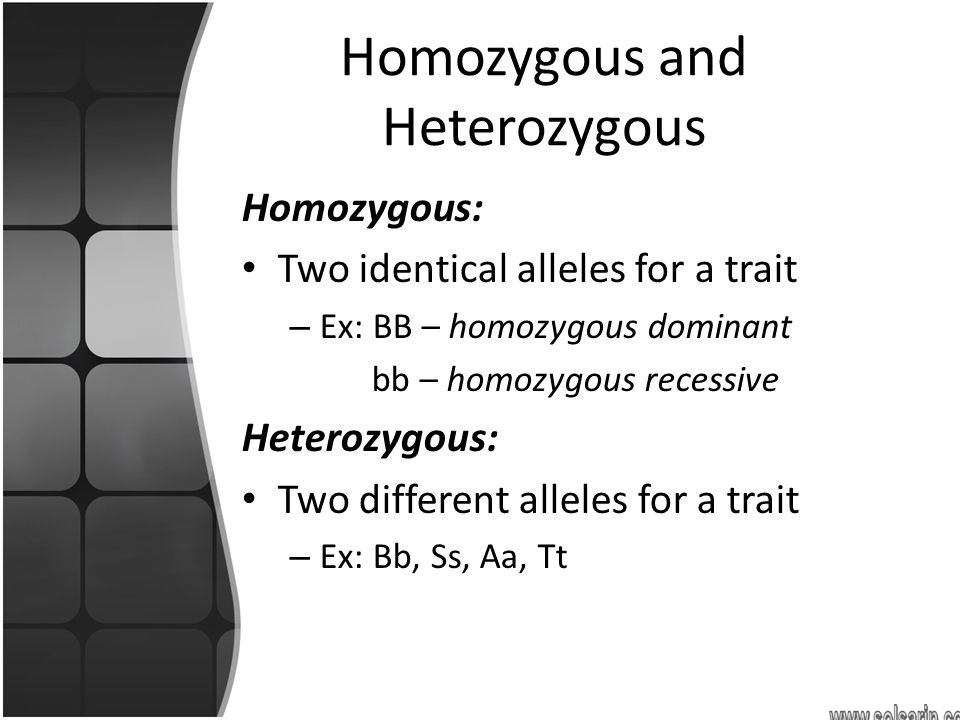
Homozygous means having two of the same allele.
heterozygous means having two different alleles.
| Homozygous | Heterozygous |
| It has two same copies of the same allele coding for a particular trait. | It contains two different copies of alleles coding for a particular trait. |
| Contains only one type of allele, either dominant or recessive | Contains different alleles for a trait. Both dominant and recessive |
| Self-fertilization results in the repetition of the same traits over generations | Self-fertilization results in different combination of traits over the next generations |
| Only one type of gamete is produced | Two types of gametes are produced |
| It can be either homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive | Heterozygous alleles can show complete dominance, codominance or incomplete dominance |

Homozygous Definition
It is a genetic condition where an individual inherits the same alleles of a gene from both the parents.
- In homozygous chromosomes, both alleles are either dominant or recessive. The dominant trait is represented by two capital letters (XX) and the recessive trait is represented by two lowercase letters (xx).
- Homozygous-dominant chromosomes carry two copies of the allele that codes for the dominant trait whereas the homozygous-recessive chromosomes carry two copies of the allele that codes for the recessive trait.
- In homozygous organisms, the dominant trait is only expressed when both the chromosomes have a dominant gene at a similar locus.
- Organisms reproducing by true breeding mechanisms are always homozygous for all traits that are held constant.
- Methods of asexual reproduction, like parthenogenesis, result in homozygous chromosome formation. This ensures that the phenotypic characteristic in the offsprings is identical to that in the parents.
- Mostly, homozygosity is defined at the specific locus where copies of the gene affecting a trait present on the two reciprocal homologous chromosomes are identical.
- Homozygous cells or organisms are also called homozygotes.
- Genes in homozygous chromosomes share readily detectable sequence similarities in their nucleotide and the proteins they code for.
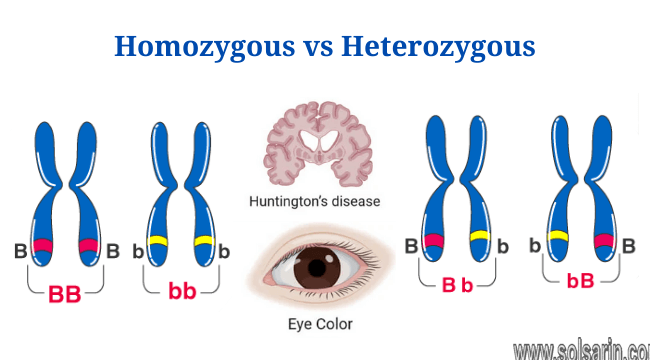
- Homozygous chromosomes are seen in various genes like the genes for eye color where the dominant trait is brown and is seen as BB in homozygous organisms.
- Homozygosity might result in various diseases in a homozygous-recessive genotype where the recessive genotype is a mutant gene.
- Diseases like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, phenylketonuria are associated with homozygous genotypes.
Homozygous examples
A homozygous genotype can appear in various ways, such as:
Eye color
The brown eye color allele is dominant over the blue eye allele. You can have brown eyes whether you’re homozygous (two alleles for brown eyes) or heterozygous (one for brown and one for blue).
This is unlike the allele for blue eyes, which is recessive. You need two identical blue eye alleles in order to have blue eyes.
Freckles
Freckles are tiny brown spots on the skin. They’re made of melanin, the pigment that gives color to your skin and hair.
The MC1R gene controls freckles. The trait is also dominant. If you don’t have freckles, it means you’re homozygous for a recessive version that doesn’t cause them.
Hair color
Red hair is a recessive trait. A person who is heterozygous for red hair has one allele for a dominant trait, like brown hair, and one allele for red hair.
They can pass the red hair allele to their future children. If the child inherits the same allele from the other parent, they’ll be homozygous and have red hair.

Heterozygous Definition
Heterozygous (and its less common form heterozygotic) means “relating to a cell that has two different alleles for a particular gene at corresponding positions on homologous chromosomes.”
Remember, a chromosome carries genes in linear order; a gene is a segment of code that dictates what trait will develop; and alleles are forms of a gene. For an organism to be heterozygous, it has to have a different allele for the same gene at the same point in the chromosome.
Let’s go back to flowers. The offspring of a flower with one allele for yellow and one allele for red could inherit one of each of these—one for yellow and one for red. Depending on how the gene works, it might result in an orange flower or in a flower that’s just yellow or in one that’s just red—but with the potential to have offspring of a different color. Such a flower would be said to be heterozygous for
flower color, because it’s got a copy of one yellow allele and one red allele.
Humans can be heterozygous for traits as well. To oversimplify it, you might inherit one copy of the “get freckles” allele and one copy of the “don’t get freckles” allele, meaning you may or may not get freckles as a result.
When an organism is heterozygous for a particular trait, how that trait develops or is expressed
depends on things like whether a gene is dominant or recessive, as well as simple mathematical odds.
Heterozygotes And Genetic Diseases
Heterozygotes can get genetic disease, but it depends on the type of disease. In some types of genetic diseases, a heterozygous individual is almost certain to get the disease.
In diseases caused by what are called dominant genes, a person needs only one bad copy of a gene to
have problems. One example is the neurological disorder Huntington’s disease.
A person with only one affected gene (inherited from either parent) will still almost certainly get Huntington’s disease as a heterozygote.2 (A homozygote who receives two abnormal copies of the disease from both parents would also be affected, but this is less common for dominant disease genes.)
However, for recessive diseases, like sickle cell anemia, heterozygotes do not get the disease. (However, sometimes they may have other subtle changes, depending on the disease.)

How to use homozygous vs. heterozygous?
Both words are commonly followed by the word for and the specific trait. To be homozygous for a trait is to have identical pairs of the genes (called alleles) that determine how it develops. To be heterozygous for a trait is to have different alleles for it.
Being homozygous for a trait means that it will always turn out the same. But being heterozygous means that the trait can develop in different ways.
Remember, an organism isn’t said to be homozygous or heterozygous overall—just for a single trait.
Examples of Heterozygous Traits
Genetics get a bit more complicated when it comes to heterozygous, or “different genetic” traits. Offspring who receive a dominant allele from one parent and a recessive allele from the other parent will exhibit heterozygous traits. That’s why siblings with the same parents sometimes look very different from each other: they received different combinations of genes.
Here are some examples of how offspring can exhibit heterozygous traits:
- A parent provides the dominant allele for black hair (B), and the other parent provides the recessive allele for blonde hair (b). The offspring has black hair (Bb) because they exhibit the dominant gene only.
- One parent has two dominant alleles for type A (AA) blood, and the other parent has one dominant allele (B) and one recessive allele (o) for type B (Bo) blood. One child has type AB (AB) blood but their sibling has type A blood (Ao) because they received one dominant A allele and one recessive O allele.
- A litter of puppies with a Golden Retriever mother and a Great Dane father exhibit a variety of traits. Some puppies have shorter legs from their mother’s recessive alleles, while others are very tall because of their father’s dominant alleles.
- One parent is a carrier for a genetic mutation on a dominant allele (Dd), but the other parent only has recessive alleles for that chromosome (dd). The child receives one recessive allele from each parent (dd) and neither carries nor exhibits the genetic disorder.
- Two flowers with ten petals but different genotypes (PP and Pp) produce seeds for flowers with the dominant allele for ten petals and flowers with the recessive allele for nine petals.
- One parent has poor eyesight (ee), but the other has a dominant allele for strong eyesight (Ee). Their offspring range in eyesight ability (ee and Ee).
As you can see, heterozygous traits allow for greater genetic variation. They can also protect offspring from gene mutation and possibly harmful genetic disorders. The alleles that offspring receives from its parents can determine what happens to its genetic line for generations to come.

Examples of homozygous and heterozygous used in a sentence
Here are some examples that illustrate the difference between homozygous and heterozygous.
- If you have two copies of the allele for blonde hair, you are homozygous for that trait.
- Having one copy of the allele for blonde hair and one copy of the allele for brown hair makes you heterozygous for hair color.
- Being heterozygous for a recessive trait like blue eyes means you have a pretty low chance of developing that trait, but being homozygous for it means that you’re certain to develop it.
Key Differences (Homozygous vs Heterozygous)
Basis for Comparison |
Homozygous |
Heterozygous |
| Definition | It is a genetic condition where an individual inherits the same alleles of a gene from both the parents. | Heterozygous is a genetic condition where an individual inherits different alleles of a gene from the two parents. |
| Genotype representation | Homozygous genotypes are represented as AA or aa for homozygous-dominant or homozygous-recessive conditions, respectively. | Heterozygous genotypes are represented by Aa genotypes. |
| Phenotypes | Two different phenotypes are possible with dominant or recessive homozygous conditions. | The phenotype is mostly due to the dominant allele in the heterozygous condition. |
| Gametes | Homozygous genotypes result in a single type of gamete. | Heterozygous genotypes result in two different types of gametes. |
| Traits | Homozygous genotypes produce the same traits over different generations. | Heterozygous genotypes produce different traits over different generations. |
| Hybrid vigour | The homozygous condition doesn’t show hybrid vigour. | Heterozygous condition shows hybrid vigour. |
| Types | Homozygous-dominant and homozygous-recessive are two types of homozygous conditions. | The heterozygous condition can be expressed in three different ways; co-dominance, incomplete dominance, and complete dominance. |
| Also called | Organisms or cells with the homozygous condition are termed as homozygotes. | Organisms or cells with the heterozygous condition are termed as heterozygotes. |
| Observed in | Homozygous genotypes are observed in animals reproducing by asexual means. | Heterozygous genotypes are mostly seen in animals reproducing by sexual means. |
| Diseases | Common diseases associated with the homozygous condition include fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and phenylketonuria. | Common diseases associated with the heterozygous condition include Huntington’s disease, Marfan’s syndrome, and familial hypercholesterolemia. |
What are the Similarities Between Homozygous and Heterozygous?
- Homozygous and heterozygous are two states of genotypes.
- Both states consist of two alleles.
- Also, they are present at the same locus of homologous chromosomes.
MORE POSTS: