is a rose a monocot or dicot?
Hi, welcome to solsarin site, today we want to talk about“is a rose a monocot or dicot”,
thank you for choosing us.
is a rose a monocot or dicot?
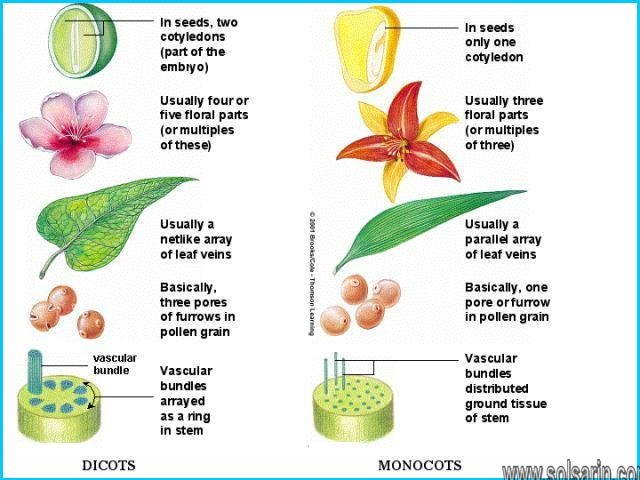
Roses are dicotyledon or dicots as they have two cotyledons, the first seed leaf, which is present in the embryo. Other characteristics are reticulate venation in leaves, monocots generally have parallel venation. Rose is a shrub. Generally, dicot flowers are tetramerous or pentamerous, i.e. 4 or 5 floral appendages such as petals, sepals, etc. Monocots are trimerous. Hence roses are dicots.
Are roses monocots or dicots?
Roses are the perfect dicots with all the features present in them. It belongs to the family called Rosaceae. Other members of this family are plums, cherries, and apples.
These all fall under the dicot section. Although roses include all the characteristics a dicot should have, it holds some other distinctive features that make the plant a special dicot.
If you want to tell whether the plant is dicot or monocot at just one glance, look at the leaves. Foliage with netted veins is the simplest way to identify a dicot.
Rose leaves hold this characteristic. Besides this, rose seedlings have two cotyledons present in them like all the dicots. You can easily distinguish a dicot by counting the number of petals the flower has, usually multiples of 4 or 5.
We know it is impossible to count rose petals because it seems infinite. But with patience, you will find it can have 32 or 250 petals. A rose will never grow flowers with 18 petals.
Next time whenever you see a rose plant, notice attentively to the stem part. Dicot plant stems differ from a monocot, and if you cut them, you will see the vein structure in them. There is also a ring-like pattern inwards and outside of it.
The roots of any dicot are taproots. You will find no difference with the roses, which have a taproot system that grows thicker and strong with time.
Unlike fibrous roots, it goes deeper into the soil instead of spreading around the upper part. The dicot root system has one thick, sturdy root called the taproot, which helps to grow smaller branches from it.


What Makes Roses Dicots?
Roses come from the Rosaceae family, which has several notable dicots like apples, plums, and cherries. All plants in the Rosaceae family are dicots. There are also a variety of characteristics that make roses distinctively dicots.
Roses have netted veins in their leaves, which is probably the most easily identifiable characteristic. Like beans and all other dicots, roses also have two cotyledons. While it may be hard to count on some rose varieties, dicots also all have flower petals in twos or multiples of four or five. So your roses may have ten or 16 or even 256 flower petals, but it won’t grow to have nine petals.
Another less than obvious dicot characteristic that roses have is in their stems. Next time you cut a rose, take a look at the vein structure in the stem. The vein structure on dicots is always in an organized ring towards the outside of the stem. Some dicots may even have hollow stems.
Roses share all the major defining characteristics of dicots.
Why are Roses Considered a Dicot?
Roses fit many of the criteria that distinguish dicots. Chiefly among them, they have two embryonic leafs house within their seeds. Other characteristics that define roses as dicots are woody stems, their number of flower petals being divisible by five, and a tap root system.
How do you know if a flower is monocot or dicot?
If your plant is flowering, you can tell if it is a monocot or dicot by the number of petals and other flower parts. Monocots have flower parts in threes or multiples of threes as shown in the flowers to the left.

What flowers are Dicots?
Dicots – has an embryo with two cotyledons, pollen with three pores, flower parts in multiples of four or five, leaf veins are netted between major veins. Examples of dicots include soybeans, roses, pansies, sunflowers, dandelions, and strawberries. Monocots and dicots have different seed characteristics.
How do you tell if a seed is monocot or dicot?
Monocots have only one seed leaf inside the seed coat. It is often only a thin leaf, because the endosperm to feed the new plant is not inside the seed leaf. Dicots have two seed leaves inside the seed coat. They are usually rounded and fat, because they contain the endosperm to feed the embryo plant.
How do you identify a Dicot?
Dicots get their names from having two cotyledons instead of one. Dicot flower parts come in multiples of 4 or 5. Count the petals and identify whether they are multiples of 4 or 5! Dicot leafs have veins that are scatter or “netted.” This means they do not follow a pattern.
The Difference Between Monocots and Dicots.
Monocots
|
Dicots
|
Definition of Monocot Flower
Monocot flowers are condensed shoot regions that are specialized for the function of sexual reproduction.
- The most definitive characteristic of monocot flowers is that these flowers usually have flower parts that occur in threes or multiples of threes.
- The observation of flowers and their parts; thus, can be used as a method to differentiate between monocot and dicot plants.
- Even though the general pattern of floral parts is similar in all monocot plants, the color, size, form, and anatomical arrangement of the flowers vary greatly among different species.
- Monocot flowers have a similar structure to dicot flowers consisting of vegetative parts and reproductive parts.
- The vegetative parts consist of calyx and corolla which are involved in providing protection to the reproductive parts and attracting different pollinators. Most of the monocot flowers pollinate via wind and water as the flowers are smaller in size and thus, light.
- In some monocot flowers, the calyx and corolla are undifferentiated, and a structure perianth is present.
- Most of the monocot flowers are complete flowers with all four floral members. The number and arrangement of the parts, however, might vary.
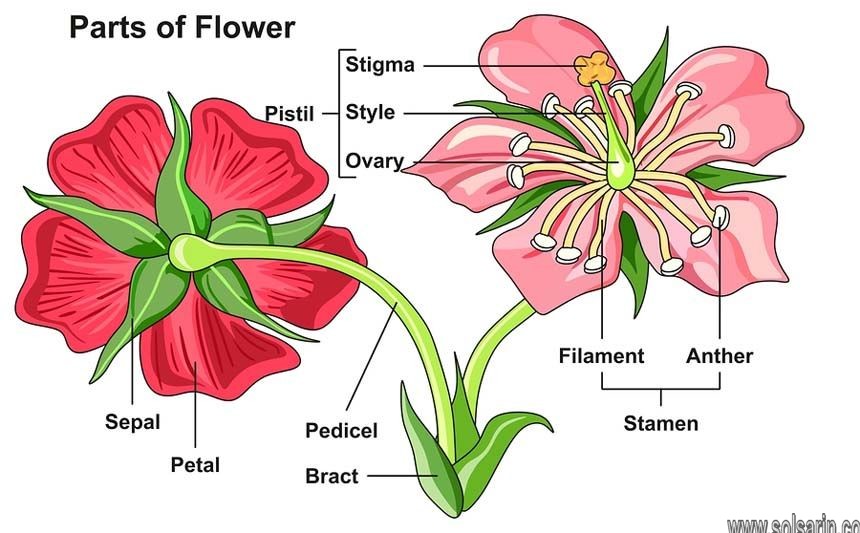
- The part in the stem from where the flowers arise is called a bract. The size of the flower depends on the length of the flower stalk called a pedicel.
- The thick upper part of the pedicel where the floral parts exist is called the thalamus. The size of the thalamus also varies among species and even within the same plant depending on the stage of the flower.

Definition of dicot Flower
Dicotyledons or dicots, on the other hand, refer to seeds that have two embryonic leaves. One of their characteristics is that they have a tap root system or a large central root with smaller roots branching out. Unlike the monocots, dicots have a ring of vascular bundles and leaves with net-like or reticulate veins. The flowers also have four or five parts.
Examples of dicot plants include peas, almonds, pecans, and walnuts, among others. The cotyledons in these plants store abundant energy that supports the new sprout before the leaves support the whole plant through photosynthesis. Roses, sunflowers, chrysanthemums, and sunflowers are also dicot plants.
What are Monocots vs. Dicots?
Monocots, short for monocotyledon, means that a plant has a single cotyledon. While dicot, short for dicotyledon, means a plant that has multiple cotyledons. Dicots may also be called eudicots, especially in scientific articles. Cotyledons are, simply put, a plant’s embryonic leaves.
When starting plants from seed, the cotyledons may be the first thing you see emerge from the soil. This is especially prominent in beans, which are dicots.
Here you can see this bean plant’s two yellow cotyledons. The cotyledons are a part of the embryo that develops into the plant’s first leaves. Hence why they can be called the plant’s embryonic leaves. The cotyledons often stick with the plant for the entirety of its life, but they may also fall off as the plant matures.
This plant is also developing its next leaf, usually called a true leaf. True leaves are generally more developed and look different from the cotyledons. You can see that this bean’s true leaves have netted veins, which are also a distinctive characteristic of dicots.


Functions of Monocot and Dicot Flower
The following are the common functions of monocot and dicot flowers;
- Different colors and shapes of flowers attract different pollinators like insects and animals for pollination.
- Flowers consist of the reproductive units of the flower that are essential for sexual reproduction in plants.
- Flowers are often used as ornaments or decorative items during functions and rituals in different cultures.
- Flowers of some plants might contain nectar which provides food to different insects which then help in the transfer of pollen grains.
- The flowers eventually lead to the formation of fruits which are used as a source of food and nutrients.
MORE POSTS:




