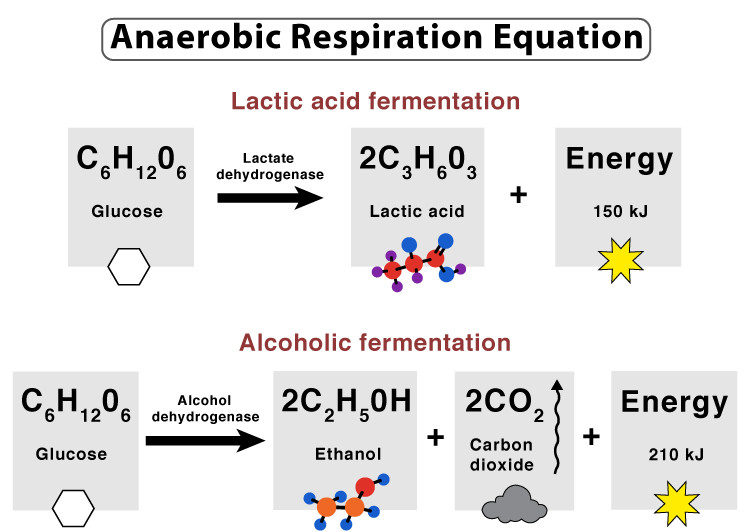
anaerobic respiration equation
Hi, welcome to solsarin site, in this post we want to talk about“anaerobic respiration equation”,
thank you for choosing us.
anaerobic respiration equation
Some examples of anaerobic respiration include alcohol fermentation, lactic acid fermentation and in decomposition of organic matter. The equation is: glucose + enzymes = carbon dioxide + ethanol / lactic acid. Though it does not produce as much energy as aerobic respiration, it gets the job done.
The equation for anaerobic respiration is:
C6H12O6 (glucose) → 2C3H6O3 (Lactic Acid) + Energy


Definition of Anaerobic Respiration
The main difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration pertains to the involvement of oxygen when the given resources like glucose are converted into energy. Moreover, this system has been evolved by some bacteria in which it makes use of oxygen-containing salts instead of free oxygen as the electron acceptor.
In addition, anaerobic respiration produces energy which is beneficial at the time of high energy demand in tissues. Thus, the oxygen which aerobic respiration produces is not able to meet the demand. However, it is not much when we compare it to aerobic respiration.
What are the 2 equations for anaerobic respiration?
What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration in yeast?
Less energy is released during anaerobic respiration in the muscles, and so they begin to feel tired. Anaerobic respiration also occurs in yeast. The yeast acts on the glucose and without oxygen it will break down the sugar into alcohol. glucose alcohol + carbon dioxide + energy This is also known as fermentation.
Process of Anaerobic Respiration
Glycolysis is the first stage of respiration, in which a glucose molecule is broken down into two pyruvate molecules, releasing electrons in the process and generating two molecules of ATP, the energy ‘currency’ of the cell, and the desired outcome of respiration. During aerobic respiration, when oxygen is present, those pyruvate molecules go through two other stages that serve to release more electrons, later used to power the generation of a very high amount of ATP.
But when oxygen is absent, as in the case with anaerobic respiration, those last two stages are bypassed. Instead, pyruvate is converted into a different byproduct through a fermentation process, and carbon dioxide is released as well. Two ATP molecules are generated in the process. While this is not as many ATP molecules generated during aerobic respiration, it is enough to get by. Enzymes are often used by the cell to help the process along, such as the zymases used in ethanol fermentation. The process is essentially: glucose + enzymes = carbon dioxide + ethanol / lactic acid.
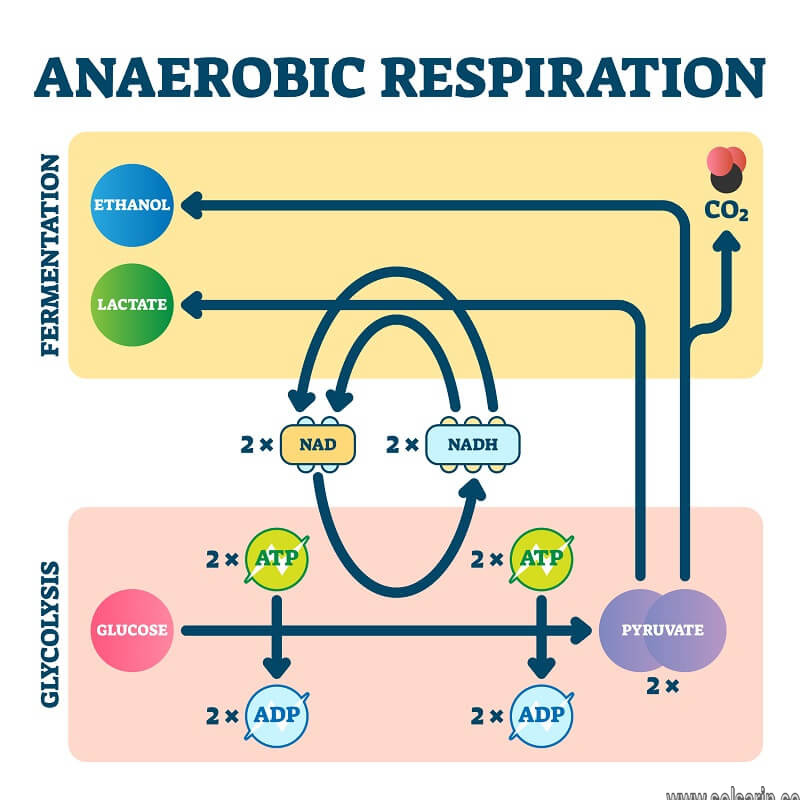

Anaerobic cellular respiration
Types of Anaerobic Respiration
In animals, anaerobic respiration primarily occurs in muscle cells in order to provide the individual with quick energy needed to sustain intense levels of activity. This form of anaerobic respiration involves the use of lactic acid fermentation. Lactic acid fermentation is also found in a few species of bacteria. Plants, by contrast undergo the process of alcohol fermentation, a method also favored by yeasts, obligate anaerobic organisms (organisms unable to survive in the presence of oxygen), and some species of bacteria. These forms of anaerobic respiration and fermentation will be further discussed below.
Glycolysis
The process of glycolysis is the same whether respiration is aerobic or anaerobic. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and involves splitting a single, 6-carbon glucose molecule into two 3-carbon pyruvate molecules. During glycolysis, several smaller, enzyme-controlled reactions occur in four stages:
- Phosphorylation – Before breaking down into two 3-carbon pyruvate molecules, the glucose must be made more reactive by adding two phosphate molecules. Therefore, we refer to this step as phosphorylation. We obtain the two phosphate molecules by splitting two ATP molecules into two ADP molecules and two inorganic phosphate molecules (Pi). We get this via hydrolysis, which uses water to split ATP. This process provides the energy needed to activate the glucose and lowers the activation energy for the following enzyme-controlled reaction.
- Creation of triose phosphate – In this stage, each glucose molecule (with the two Pi groups added) splits in two to form two triose phosphate molecules, a 3-carbon molecule.
- Oxidation – Once these two triose phosphate molecules form, we need to remove hydrogen from them. These hydrogen groups then transfer to NAD+, a hydrogen-carrier molecule, producing reduced NAD (NADH).
- ATP production – The two newly oxidised triose phosphate molecules convert into another 3-carbon molecule known as pyruvate. This process also regenerates two ATP molecules from two molecules of ADP.
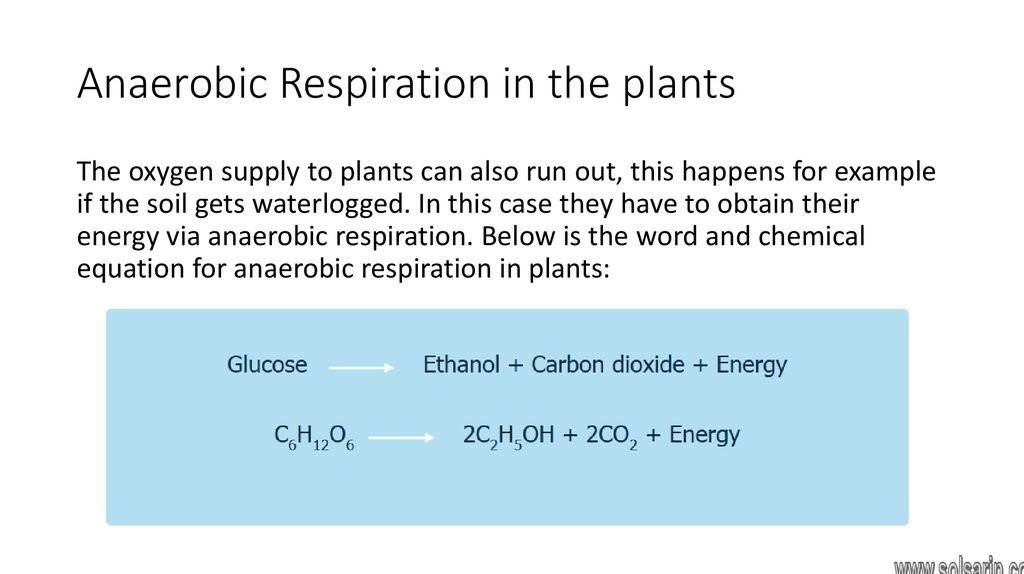

Fermentation
Some references consider fermentation as an example or part of anaerobic respiration as both of them do not use oxygen, and therefore, are anaerobic. However, other references regard them as two different processes. In this regard, we are going to deal with the two processes here.
Anaerobic stands for “without oxygen.” This method of cellular respiration does not require oxygen to generate energy. For smaller animals to breathe, there is not enough oxygen available so they need the energy to survive in the absence of oxygen. That is in contrast to aerobic respiration that requires oxygen, which serves as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain system.
After glycolysis, pyruvate (in lactic acid fermentation) or acetaldehyde (in alcohol fermentation) serves as the final electron acceptor. In this process, the energy from glucose is converted into another form that can be used by the cell or stored for later use. It produces lactic acid instead of carbon dioxide and water.
Glucose → Alcohol + Carbon dioxide + Energy
In the absence of oxygen, the process does not result in the development of any more ATP molecules.
This process mainly occurs in microorganisms, but it is also used by multi-cellular organisms, such as humans, albeit not as common. It is a temporary reaction to oxygen-less conditions.
During hard or vigorous exercise, such as biking, sprinting, cycling or weightlifting, our body needs high energy. As the availability of oxygen is reduced, the muscle cells within our body use lactic acid fermentation to satisfy the energy demand.
Anaerobic Respiration in Animals
- Anaerobic respiration mainly takes place in muscle cells during vigorous exercise
- When we exercise vigorously, our muscles have a higher demand for energy than when we are resting or exercising normally. Our bodies can only deliver so much oxygen to our muscle cells for aerobic respiration
- In this instance, as much glucose as possible is broken down with oxygen, and some glucose is broken down without it, producing lactic acid instead
- There is still energy stored within the bonds of lactic acid molecules that the cell could use; for this reason, less energy is released when glucose is broken down anaerobically
What is the equation for anaerobic respiration in animals?
Respiration: Glucose + Oxygen –> Water + Carbon Dioxide + EnergyIf there is a lack of oxygen then anaerobic respiration will take place instead of aerobic respiration, which in animals has the following word equation:Glucose –> Lactic Acid + Some energy This releases less energy than aerobic respiration and produces …
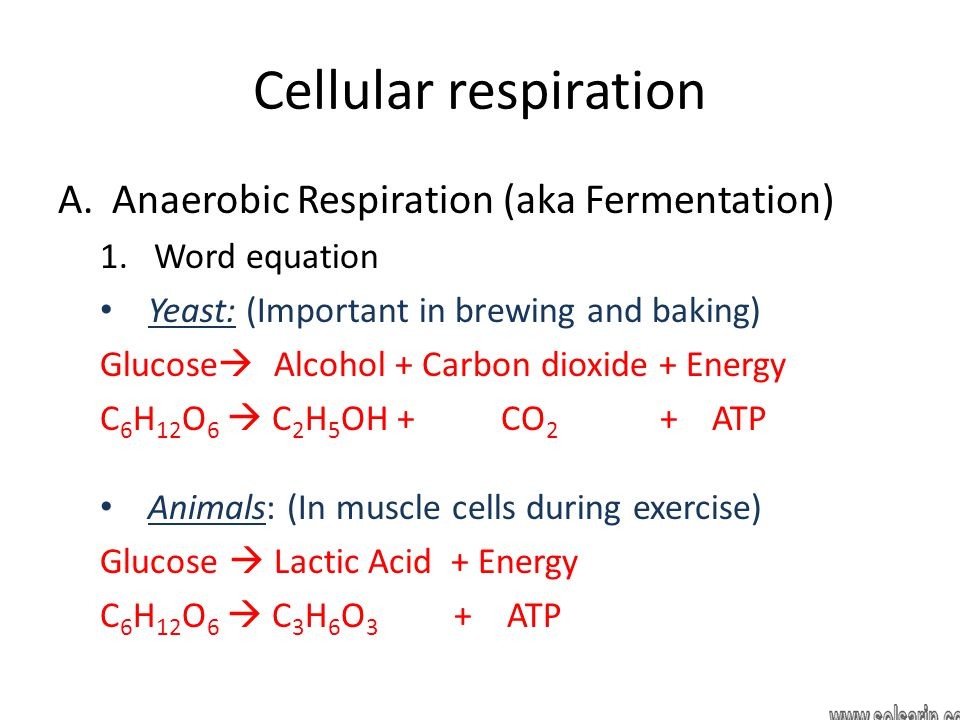

anaerobic respiration equation
Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
The primary difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration is the presence or absence of oxygen during the processes. More detailed differences are between the two are as follows:
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| Oxygen is present when this form of respiration takes place. | Oxygen is absent when this form of respiration takes place. |
| Gases are exchanged in this form of respiration. | Gases are not exchanged in this form of respiration. |
| It can be found in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria. | It can be found only in the cytoplasm. |
| Glucose breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. | Glucose breaks down into ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide and energy. |
| All higher organisms such as mammals have this type of respiration. | Lower organisms such as bacteria and yeast use this type. In other organisms, it occurs during heavy activities. |
However, it is a misconception that humans and other multicellular organisms use only aerobic respiration. This is disproven by the fact that our muscles, during vigorous exercises, undergo
anaerobic respiration, where lactic acid is produced as the waste-byproduct instead of carbon dioxide.
What is the equation for aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
| Basis of Comparison | Aerobic Respiration |
|---|---|
| Chemical Equation | C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (as ATP) |
| Final Product | Carbon dioxide and water |
| Requires | Oxygen and glucose to produce energy |
| Speed | Long Process |
MORE POSTS: