what is the capital of manitoba?
Hello. Welcome to solsarin. This post is about “what is the capital of manitoba?“.
Manitoba
Manitoba (/ˌmænɪˈtoʊbə/ (![]()
![]()
![]()
Indigenous peoples have inhabited what is now Manitoba for thousands of years. In the early 17th century, British and French fur traders began arriving in the area and establishing settlements. The Kingdom of England secured control of the region in 1673 and created a territory named Rupert’s Land, which was placed under the administration of the Hudson’s Bay Company.
1869
Rupert’s Land, which included all of present-day Manitoba, grew and evolved from 1673 until 1869 with significant settlements of Indigenous and Métis people in the Red River Colony. In 1869, negotiations with the Government of Canada for the creation of the province of Manitoba commenced. During the negotiations, several factors led to an armed uprising of the Métis people against the Government of Canada, a conflict known as the Red River Rebellion. The resolution of the conflict and further negotiations led to Manitoba becoming the fifth province to join Canadian Confederation, when the Parliament of Canada passed the Manitoba Act on July 15, 1870.
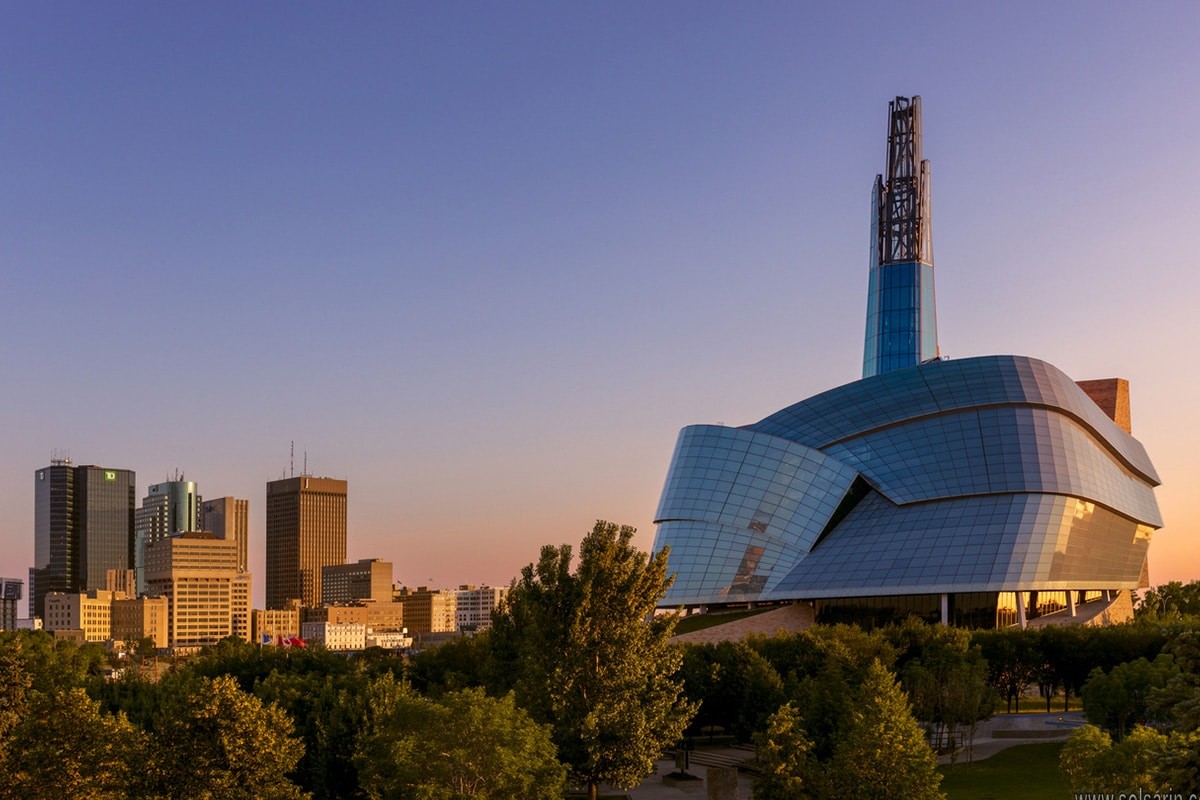


Manitoba’s capital and largest city is Winnipeg, the seventh most populous municipality in Canada. Winnipeg is the seat of government, home to the Legislative Assembly of Manitoba and the Provincial Court. Four of the province’s five universities, all four of its professional sports teams, and most of its cultural activities (including Festival du Voyageur and Folklorama) are located in Winnipeg. The city has train and bus stations and an international airport; a Canadian Forces base, CFB Winnipeg, operates from the airport and is the regional headquarters of the North American Aerospace Defense Command.
The capital of Manitoba is Winnipeg.
Winnipeg
Winnipeg (/ˈwɪnɪpɛɡ/ (![]()
![]()
![]()
The city is named after the nearby Lake Winnipeg; the name comes from the Western Cree words for muddy water. The region was a trading centre for Indigenous peoples long before the arrival of Europeans; it is the traditional territory of the Anishinabe (Ojibway), Ininew (Cree), Oji-Cree, Dene, and Dakota, and is the birthplace of the Métis Nation.[8] French traders built the first fort on the site in 1738.
A settlement was later founded by the Selkirk settlers of the Red River Colony in 1812, the nucleus of which was incorporated as the City of Winnipeg in 1873. Being far inland, the local climate is extremely seasonal even by Canadian standards with average January highs of around −11 °C (12 °F) and average July highs of 26 °C (79 °F).
1967
Known as the “Gateway to the West”, Winnipeg is a railway and transportation hub with a diversified economy. This multicultural city hosts numerous annual festivals, including the Festival du Voyageur, the Winnipeg Folk Festival, the Jazz Winnipeg Festival, the Winnipeg Fringe Theatre Festival, and Folklorama. In 1967, Winnipeg was the first Canadian host of the Pan American Games. It is home to several professional sports franchises, including the Winnipeg Blue Bombers (Canadian football), the Winnipeg Jets (ice hockey), Manitoba Moose (ice hockey), Valour FC (soccer), and the Winnipeg Goldeyes (baseball).
Fort-Rouge was established on the site in 1738 by the French voyageur La Vérendrye. It was followed later by Fort Gibraltar (built by the North West Company in 1810) and Fort Garry (Hudson’s Bay Company, 1821). These, together with the Red River Settlement (founded 1811–12) of Scottish colonists, formed the nucleus of the new city, the name of which was taken from that of Lake Winnipeg and derived from the Cree Indian words win nipee (“muddy water”).
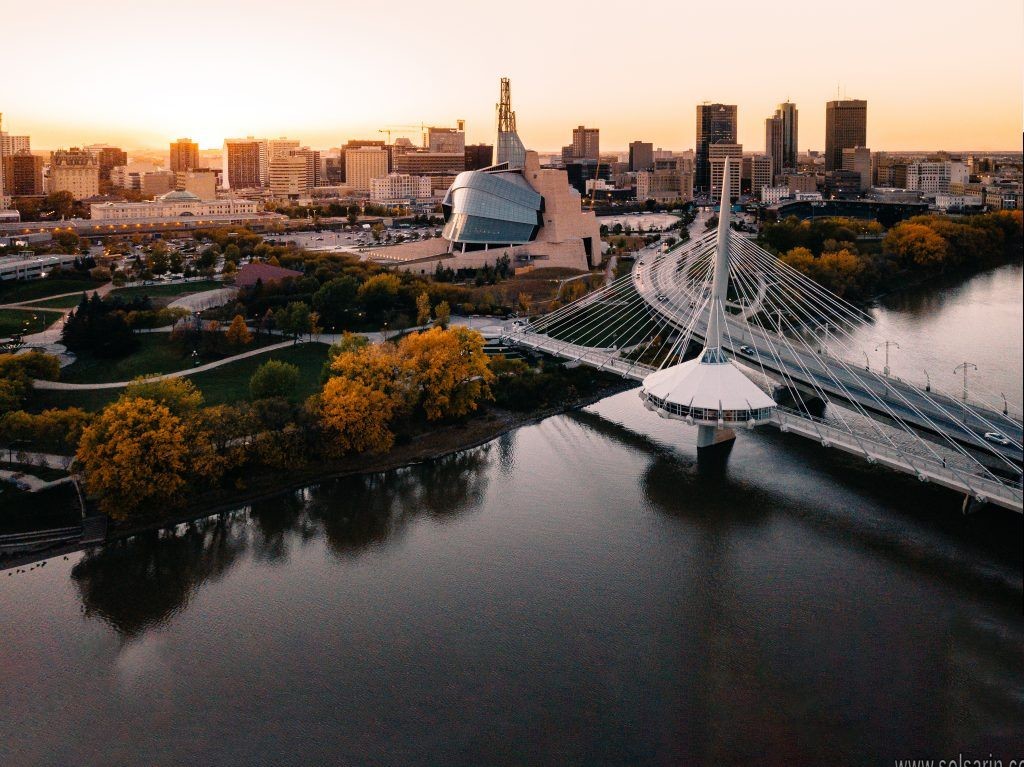


The arrival in 1885 of the Canadian Pacific, the first Canadian transcontinental railroad, led to Winnipeg’s becoming the major grain market and warehousing and distributing point for the Prairie Provinces. It has remained the headquarters of the Canadian grain industry. The city also serves the mining districts of the north and is now one of Canada’s largest industrial, communications, commercial, and financial centres.
Royal Canadian Mint
The economy is highly diversified; major activities include food processing, finance, telecommunications, printing, and the manufacture of apparel, transportation equipment, and aerospace products and technology. Winnipeg is also home to the Royal Canadian Mint, which produces all of the country’s coinage. The city’s industrial growth has stimulated by the availability of cheap hydroelectric power (from plants on the Winnipeg River) and excellent transportation facilities. A major junction on two transcontinental rail lines and the Trans-Canada Highway, Winnipeg also has a busy international airport.
Following disastrous floods in 1950, the 30-mile (48-km) Red River Floodway was built (completed 1968), allowing that river’s floodwaters to bypass the city. In 1972 the municipalities that composed the Metropolitan Corporation of Greater Winnipeg (including Saint Boniface, Saint James, East and West Kildonan, Transcona and Saint Vital) were absorbed into the city.
1938
A cosmopolitan city of many ethnic groups (including sizable populations of French-speaking and native peoples), Winnipeg dominates Manitoba’s cultural life. It is the home of a symphony orchestra, the Manitoba Opera, the Royal Winnipeg Ballet, and the Manitoba Theatre Centre. It is the seat of the University of Manitoba (1877), the University of Winnipeg (1871), and Red River College (1938).
The provincial Legislative Building (1920) is a Neoclassical structure with the well-known Golden Boy (a bronze statue of a youth carrying a torch in his right hand and a sheaf of wheat over his left arm) on top of its dome. The city’s Centennial Centre includes the Museum of Man and Nature and a planetarium. And the Winnipeg Art Gallery has an extensive collection of Inuit art.
Geographic And Economic Importance
Winnipeg is the capital of Manitoba which is the fifth most populous province of Canada. Winnipeg situated near the longitudinal center of North America. Since it is in the middle of Canada’s land mass, all rail and road traffic between Canada’s East. And West passes through or near the city. Therefore, the city also called the “Gateway to the West”. Winnipeg is a rail and road transportation hub and has a diversified economy. Winnipeg’s largest employer is the government and related organizations.
The city has notable trading and manufacturing activities as well as a Royal Canadian Mint coin producing plant. The city is located around the meeting point of two rivers, Assiniboine and Red River. Winnipeg named after the nearby Lake Winnipeg, which is Canada’s fifth largest lake. The city incorporated in 1873, however, it saw its population boom only after completion of railway through the city. There are many lakes near Winnipeg including Lake Manitoba and the Lake of the Woods.
Cultural Cradle Of Canada
Winnipeg is also termed as the “cultural cradle of Canada”. The city is home to the Royal Winnipeg Ballet and the Winnipeg Symphony Orchestra. The city hosts one of the world’s best fringe theater festivals. Every year since 1970, Winnipeg has been holding annual Festival du Voyageur to highlight stories of travelers, Métis and First Nations. The city is home to about half of province’s population.
Where In The World Is Winnipeg?
Winnipeg was named as one of the 2016 “Best Places To Visit On Earth” by National Geographic, calling it the “Little Spark On The Prairie”“.
The Rotary Club of Winnipeg, chartered in April 1912, was the first club outside the United States. And made Rotary “International”.
more than 100 languages
Winnipeg is the capital city of the Province of Manitoba, Canada and has extensive rail and air links, as well as having the head offices of several major Canadian trucking firms. Winnipeg has a diverse economy and is also a multicultural city where more than 100 languages spoken. It is the home of the NHL’s Winnipeg Jets hockey team.
Winnie The Pooh’s name comes from the city of Winnipeg. A Canadian soldier, Lt. Harry Coulebourn, rescued a black bear and named her after his home city, Winnipeg. Winnie, housed at the London Zoo, was the inspiration for the name of A. A. Milne’s famous character after his son, Christopher Robin, became infatuated with the bear.


What was the original capital of Manitoba?
As of the 2016 census, Manitoba had 1,278,365 residents, making it the fifth most populous province or territory in Canada. Manitoba joined Confederation in 1870, and its capital city, Winnipeg, incorporated shortly thereafter, in 1873.